Presidential Rolescandacemedellin
advertisement
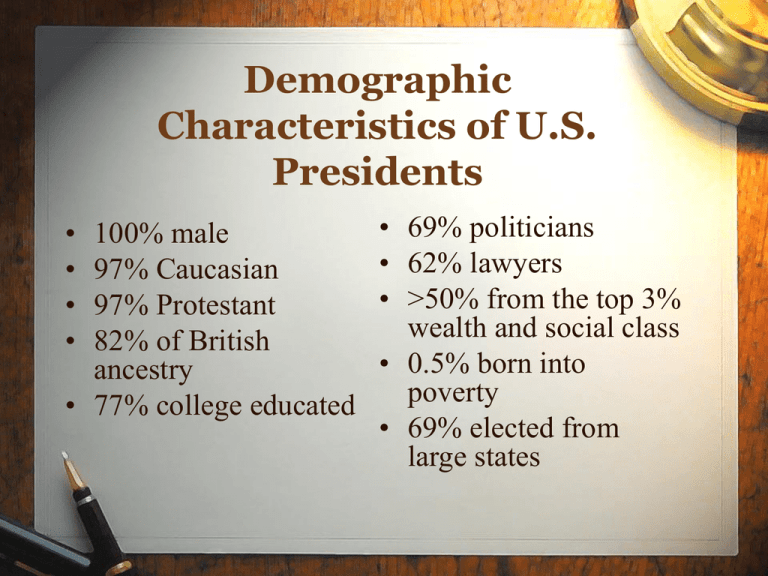
Demographic Characteristics of U.S. Presidents • • • • 100% male 97% Caucasian 97% Protestant 82% of British ancestry • 77% college educated • 69% politicians • 62% lawyers • >50% from the top 3% wealth and social class • 0.5% born into poverty • 69% elected from large states Constitutional Qualifications Must be at least 35 years old Must have lived in the United States for 14 years Must be a natural born citizen Presidential Benefits $400,000 tax-free salary $50,000/year expense account $100,000/year travel expenses The White House Secret Service protection Camp David country estate Air Force One personal airplane Staff of 400-500 Christmas at the White House, 2004 Presidential Roles Constitutional Roles There are 5 expressed roles of the president found in the constitution Head of State Queen Elizabeth and President Reagan, 1983 President Kennedy speaks at Berlin Wall, 1963 Head of State • Performs ceremonial roles • Some examples include: – Hosting foreign leaders – Throwing the first baseball at a game – Meeting public figures, kings, and queens. Bush throws first pitch last Sunday at the opening game between the washington nationals and the atlanta braves Chief Executive President Clinton with Janet Reno, the first female Attorney General, February, 1993 President Bush holds cabinet meeting in October, 2005 Chief Executive • Makes sure the laws of congress are carried out Examples: – Executive Orders- rules that have the force of the law – Presidential Appointments/Removalsappoint or remove people from cabinet, government agencies, etc. Chief Executive • Reprieve- postponement of legal punishment • Pardon- release from legal punishment • Amnesty- a group pardon to people for offenses against the government ex: Carter’s amnesty for draft dodgers Commander-in-Chief President Johnson decorates a soldier in Vietnam, October, 1966 President Bush aboard U.S.S. Lincoln, May, 2003 Commander in Chief • Power to make “war” or send troops to fight in a certain area • Power to support war effort by raising gas, ration food, and use industries to make war goods Chief Diplomat President Bush and President Putin of Russia Ronald Reagan 1987 “Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall” Chief Diplomat • Makes foreign policy decisions – Constant struggle between president and congress over foreign policy • Signs Treaties – checks and balances- Congress must approve Chief Legislator President Clinton delivers the State of the Union Address, 1997 President Roosevelt signs into law the Social Security Act, 1935 Chief Legislator • President describes laws and policy he would like to create • See political cartoon on page 255. Unwritten Roles • Many roles of the President have developed over the course of history. Political Party Leader President Reagan & Vice-President Bush accepting their party’s nomination in 1980 Party Leader • Supports his own party • Patronage: Appoint loyal party members to important positions Party Leader • President should represent all people so what about his party? • Presidents are sometimes criticized for crossing party lines by the party, the media, and the public. • When President Clinton compromised with the Republican Congress to enact legislation in 1996, more liberal members of his own party criticized him. Crisis Manager President Bush at Ground Zero after 9-11 Vice-President Johnson sworn in aboard Air Force One after President Kennedy’s assassination, 1963 Moral Persuader President Lincoln during the Civil War, 1862 President Roosevelt and the “Bully Pulpit,” 1910 Economic Planner FDR New Deal Economic Planner • This role greatly increased after the “New Deal” of FDR. • Makes decisions about the budget, government spending, tax policy, etc. Chief Administrator • Directs government agencies • Employs 3 million people to conduct government businesses Chief Citizen • Representative of all people • Works for and represents the public interest