Chapter 11
advertisement

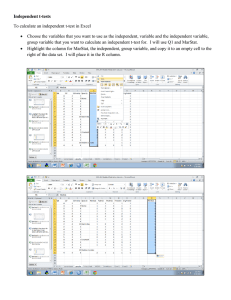
Click OK Alternative = Click Samples nature of H1 IfInput we in different assume that Confidence Input (in ourFirst case, =C1, columns population Level =(1α) × 100 greater Second than) = C2 variances are (95.0 in our case) equal, then select Input Click Click Click the Stat Basic 2first sample Assume Sample data Statistics in column t... C1equal and thevariance. second in(In our example, column C2 we do not select this.) Chart 11-1: Minitab Difference Between 2 Population Means Click t-Test: Two-Sample Click OK Input Variable(If1 Range = Assuming Unequal Variances Click OK of sample data 1 in we know that therange two population column A, Variable 2 variances are equal, choose Range =Equal range of sample Two-SampleClick Assuming Input Tools Input Hypothesized Alpha = Input Click the sample Data data 2 in column B Variances.) Mean value Difference of level of = data 1Analysis in column A test significance value of (μ(In 1μ2) and the Sample our (In our case, case, 0.05) 60) data 2 in column B Chart 11-2: Excel Difference Between 2 Population Means Click Click OK Options Click OK Click Input Click Click Stat the Basic two sample data Paired Statistics Input Input in two Test tConfidence columns mean = of Level the testworksheet =(1)×100 value of (µ (95.0 in ) ( our =of0 case) in our Input = 1µ2Alternative Input names case) of H1 (in our columnsnature containing case,and less than) first sample, second sample in appropriate place Chart 11-3: Minitab Paired T-Test Input Input Input data Hypothesized Alpha range = for Variables Mean value Difference of level 1 andof2= Click t-Test: test significance value Pairedof (µ(1µ = 2) ( Two Sample = 0.05 0 in forour in our case) Click Input Tools, the case) Means Data sample Analysis data Click OK Chart 11-4: Excel Paired T-Test