Chemical Reactions Metabolism PP Chemical Reactions
advertisement
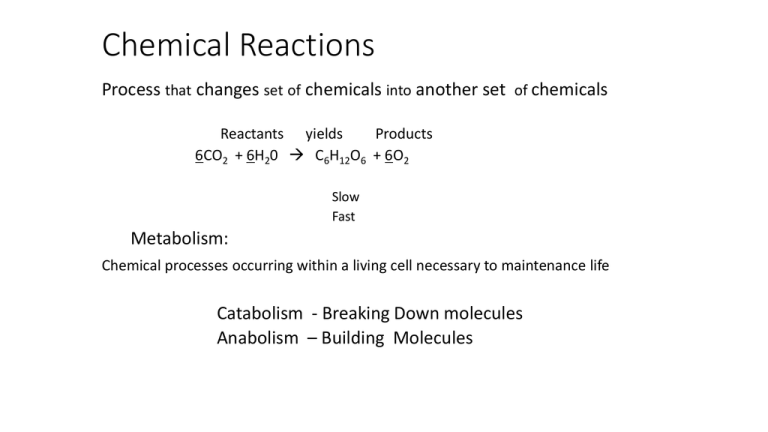
Chemical Reactions Process that changes set of chemicals into another set of chemicals Reactants yields Products 6CO2 + 6H20 C6H12O6 + 6O2 Slow Fast Metabolism: Chemical processes occurring within a living cell necessary to maintenance life Catabolism - Breaking Down molecules Anabolism – Building Molecules Reaction Energy • Energy is Released when chemical bonds Break • Energy is Absorbed when chemical bonds Form • Reactions that release energy Spontaneous • Reactions that require energy Non Spontaneous Energy requirements in chemical reactions Energy-Releasing Reaction Burning a Log C6H12O6 → CO2 + H2O Activation energy Reactants Products Enzymes • Chemical reactions in the human body require energy • Enzymes serve as a CATALYST • Speed up reactions that take place in cells a lot of Reaction using Enzyme Candy Bar Reaction pathway without enzyme Reactants Reaction pathway with enzyme Activation energy without enzyme Activation energy with enzyme Products Chapter 02D.mpg CARBOHYDRATES Characteristics of Carbohydrates • Consist of carbon, hydrogen, & oxygen • Energy containing molecules • Some provide structure: Celulose • Basic building block is a monosaccharide (CH2O)n ; n = 3,5,6 • Two monosaccharides form a disaccharide Three Monosaccharides C6H12O6 Dehydration Synthesis of a Disaccharide Formation of Disaccharides Hydrolysis of a Disaccharide Important Polysaccharides: Starch • Consists of glucose subunits • Plant energy storage molecule • Glycogen is a very similar molecule in animals. • Starch and glycogen can be digested by animals. Important Polysaccharides: Cellulose • Composed of glucose subunits • Different bond formed than starch • Structural component in plants • Cannot be digested by animals LIPIDS Characteristics of Lipids • Composed of: Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen • Includes: Fats, Oils, Phospholipids, and Cholesterol • Phospholipids part of cell membrane • Building blocks: • Fatty Acids and Glycerol. • Energy storage molecules Fatty Acid Structure •Carboxyl group (COOH) forms the acid. •“R” group is a hydrocarbon chain. A Representative Fatty Acid Unsaturated Fatty Acid Saturated Fatty Acid Glycerol Synthesis of a Fat A Phospholipid PROTEINS Characteristics of Proteins • Contain: • Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, sulfur • Function: • Structural components of animals • Control molecules (enzymes) • Transport and messenger molecules • Basic building block is the amino acid Amino Acid • Amine group acts like a base, tends to be positive. • Carboxyl group acts like an acid, tends to be negative. • “R” group is variable, from 1 atom to 20. • Two amino acids join together to form a dipeptide. • Adjacent carboxyl and amino groups bond together. Some Amino Acids Some More Amino Acids Still More Amino Acids Formation of a Dipeptide Dehydration synthesis Amino Acid + Amino Acid --> Dipeptide Amino Acid + Dipeptide --> Tripeptide A.A. + A.A. + …..+ Tripeptide --> Polypeptide A protein consists of one or more polypeptide chains.






