Social Emotional Learning - National Clearinghouse on Supportive
advertisement

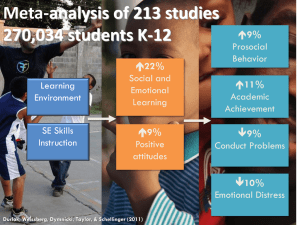
Social Emotional Learning: What do we know, what do we need to know and how do we contextualize it? David Osher, Ph.D. October 18, 2012 Overview What is (and is not) Social Emotional Learning and What Are Social Emotional competencies? Why is it important? What is the relationship between SEL, School Climate, School Culture, and the Conditions for Learning. WHAT IS (AND IS NOT) SOCIAL EMOTIONAL LEARNING AND WHAT ARE SOCIAL EMOTIONAL COMPETENCIES? What Is Social and Emotional Learning (SEL)? SEL is a process for helping children and adults develop the basic skills necessary for a safe and happy life. SEL teaches the skills we all need to handle ourselves, our relationships, and our work effectively and ethically. 4 Emotional Intelligence Framework Self Awareness Social Awareness Self Management Relationship Management Based on Daniel Goleman and Linda Lantieri What Is, Is Not, and Can Be SEL? Executive Function- yes Grit-yes Mindfulness-yes Emotional Intelligence-yes Character Education-sometimes Effective character education incorporates SEL, e.g., Caring School Communities PATHS Positive Action Lion's Quest What Is, Is Not, and Can It Be SEL? Providing Children and Youth With Social and Emotional Support-no Can support SEL and be supported by SEL Educational Mindsets-no SEL can be foundational to developing mindsets E.g., self-regulation, attentional control Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports-no PBIS and SEL can be aligned Restorative Practices-yes/no SEL can be foundational for restorative practices Restorative Practices can teach and reinforce SEL Where Can and Does SEL Take Place? All Settings Intentional Modeling and Reinforcement How Do We Conceptualize SEL and Social Emotional : CASEL’s Approach Resource: http://casel.org Individuals Who Are SelfAware Have the ability to: Accurately assess their feelings, interests, values, and strengths; and Maintain a wellgrounded sense of self-confidence. Demonstrate it by: Recognizing and accurately labeling simple emotions such as sadness, anger, and happiness. Analyzing factors that trigger their stress reactions. Analyzing how various expressions of emotion affect other people. Individuals Who SelfManage Have the ability to: Demonstrate it by: Regulate their emotions Describing the steps of setting to handle stress, control and working toward goals. impulses, and persevere Making a plan to achieve a in overcoming obstacles; short-term personal or Set and monitor progress professional goal. toward personal and Identifying strategies to make professional goals; and use of available resources and Express emotions overcome obstacles in appropriately. achieving a long-term goal. Individuals Who Are Socially Aware Have the ability to: Take the perspective of others and empathize with others; Recognize and appreciate individual and group similarities and differences; and Recognize and use family, school, and community resources. Demonstrate it by: Identifying verbal, physical, and situational cues indicating how others feel. Predicting others’ feelings and perspectives in various situations. Evaluating their ability to empathize with others. Individuals Who Have Good Relationship Skills Have the ability to: Establish and maintain healthy and rewarding relationships based on cooperation; Resist inappropriate social pressure; Prevent, manage, and resolve interpersonal conflict; and Seek help when needed. Demonstrate it by: Describing approaches to making and keeping friends. Being cooperative and working on a team to promote group goals. Evaluating the uses of communication skills with peers, teachers, and family members. Individuals Who Make Responsible Decisions Have the ability to: Make decisions based on consideration of ethical standards, safety concerns, appropriate social norms, respect for others, and likely consequences of various actions; Apply decision-making skills to academic and social situations; and Contribute to the well-being of their school and community. Demonstrate it by: Identifying a range of decisions they make at school. Evaluating strategies for resisting peer pressure to engage in unsafe or unethical activities. Analyzing how their current decision making affects their college and career prospects. What is Emotional Literacy? (Brackett & Rivers, 2011) Recognizing Understanding Labeling Expressing Regulating Spectrum of Program Theory Direct Instruction Coconstruction Different Approaches to Social and Emotional Learning Programs Direct Instruction Emphasizes highly scripted teacher led lessons. Requires the teacher to become fluent with a specific lesson protocol and packaged teaching materials. Constructivism Focuses on taking advantage of the spontaneous interactions that take place the school. Requires teachers to create ways for the learning to take place. Different Approaches to Social and Emotional Learning Programing Levels of Intervention Universal Early Intervention Intensive Intervention Setting Level Programs Infusion Kernels (Biglan & Embry) District, State, Ministry Social Emotional Learning Standards Common Programs WHY IS SEL IMPORTANT? What Affects Learning Outcomes Teaching Learning Better Competencies Outcomes Conditions What Affects Performance Such As Staff in an Organization Supervisors Staff Competencies Higher Job Satisfaction & Productivity Conditions Why SEL: Some Reasons Addressing Trauma & the Adversities of Poverty Compromised attachment Compromised ability to self-regulate Can buffer the response to stress, toxic stress, and adversity Developing Portable Assets in an evolving world Empowering learners A prerequisite to academic mindsets Tools for cooperative learning Self-regulated learning Why SEL: Some Reasons Helping students stay our of harm’s way Avoid school-reloaded unsafe & antisocial behavior Avoid community-related unsafe antisocial behavior Making values real Moral education is not enough Building as well as building upon compassion Support active citizenship and drive for social change How To Use Social Emotional Learning In Building Human Capacity • Facilitation • Coaching • Mentoring – mentor has to be SEL sensitized; be aware of the mentee’s point of view & feelings • Being learner centered • Believing in human potential and capacity SEL Program Impacts: Evidence from One Program—Seattle Social Development Program Lowered teacher-rated aggressive behavior in boys and self destructive behavior in girls Improved bonding to family and school Students less likely to use alcohol and engage in delinquent behavior Reduced involvement in sexual activity, violent delinquency, drunkenness, and drinking Improved Long Term Academic Results Social Emotional Competencies Can Be Learned They can be modeled nurtured taught practiced and reinforced Implications of Various IOM and NRC Studies Nurturing Environments Minimize Toxic Conditions Richly Reinforce Prosocial Behaviors Limit Opportunities for Problem Behavior Promote Psychological Flexibility Social & Emotional Competencies Can Be Developed: Evidence of Success with SEL 23% increase in skills 9% improvement in attitudes about self, others, and school 9% improvement in prosocial behavior 9% reduction in problem behaviors 10% reduction in emotional distress 11% increase in standardized achievement test scores (math and reading) Source: Durlak, J.A., Weissberg, R.P., Taylor, R.D., & Dymnicki, A.B. (in press, Child Development). The effects of school-based social and emotional learning: A meta-analytic review. Meta-analysis: SEL Promotes Success in School Durlak, Weissberg, Dymnicki, Taylor, & Schellinger (2009) Coordinated School, Family, and Community Programming Positive Social Behavior SEL Learning Environment SE Skills Instruction SE Skill Acquisition Improved Attitudes Fewer Conduct Problems Less Emotional Distress Academic Success SEL Can Be Adapted and Adopted. Cambodian SEL VISION Teachers and students who care, respect each other and who are able to make responsible decisions. 31 SEL Around the World: Some Examples Canada--BC United States- Collaborating Districts Initiative Singapore-social emotional learning standards Cambodia-teacher “stop and think” Thailand-SEL in Basic Education China-Child Friendly Schools for Vulnerable Children UK-SEAL; Meta Analysis Bangladesh-BRAC schools for first generation students WHAT IS THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SEL, SCHOOL CLIMATE, SCHOOL CULTURE, AND THE CONDITIONS FOR LEARNING? School-Based Prevention Focuses on Nurturing Resilience Self-Control/Emotion Regulation Cognitive Abilities – Problem Solving Skills Building Attention and Learning Capacity Healthy relations with peers and adults Safe, Welcoming, Caring Classrooms (Mark Greenberg, 2012) Supporting Effective Social and Emotional Development Teacher WellBeing and Awareness Effective Conditions for Learning Social and Emotional Skill Development Conditions for Learning: Key Aspects of School Climate Students are safe Students are supported Physically safe Meaningful connection to adults Emotionally and socially safe Treated fairly and equitably Avoid risky behaviors Positive peer relationships School is safe and orderly Effective and available support Students are challenged Students are socially capable High expectations Emotionally intelligent and culturally competent Strong personal motivation School is connected to life goals Rigorous academic opportunities Page 36 Strong bonds to school Responsible and persistent Cooperative team players Contribute to school community Address Variation of Impact Why Are Social Emotional Competencies & the Conditions For Learning Important - The Neurochemistry and Neurobiology of Learning Attending Concentrating Using working memory Memorizing Handling Emotions Why SEL? Life success Individually Relationallly School success Individually Collectively Doing more good and healthy things Avoiding bad and unhealthy things E.g., Drugs Implicit bias Why SEL? A Vision Portable assets in an evolving world Making values real Moral education is not enough Building as well as building upon compassion Resilience and recovery Emotionally literate and competent adults raising the next generation of children Emotionally competent adults collaborating to create a just world Thriving, Flourishing, Well-being