CONJUNCTIONS
advertisement

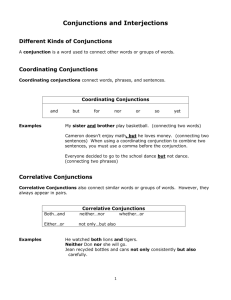
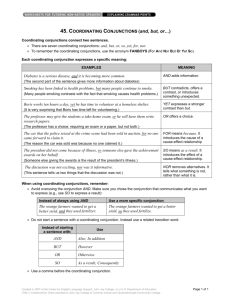
CONJUNCTIONS ---- a word that joins single words or groups of words COORDINATING CONJUNCTIONS -- JOINS WORDS OR GROUPS OF WORDS THAT HAVE EQUAL GRAMMATICAL WEIGHT IN A SENTENCE AND BUT OR SO NOR YET FOR EXAMPLE: -- ONE AND SIX ARE SEVEN. (2 NOUNS) -- MERLIN WAS SMART BUT IRRESPONSIBLE. (2 ADJECTIVES) -- LET’S PUT THE NOTE ON THE TV OR ON THE REFRIGERATOR. (2 PREPOSITIONAL PHRASES) -- I WANTED A NEW SUN HAT, SO I BOUGHT ONE. (2 COMPLETE THOUGHTS) -- WE DIDN’T EXPLORE THE SUMMIT THAT NIGHT, FOR THE CLIMB HAD EXHAUSTED US. ▪ FOR MEANS “FOR THE REASON THAT” OR “BECAUSE.” Correlative Conjunctions -- works in pairs to join words and groups of words of equal grammatical weight in a sentence -- make the relationship between words or groups of words a little clearer than do coordinating conjunctions both…and either…or just as…so not only…but(also) neither…nor whether…or EXAMPLES Coordinating He and I were there. She will sew new curtains, or I’ll put up the old blinds. I scrubbed and waxed the floor. Correlative Both he and I were there. Either she will sew new curtains, or I’ll put up the old blinds. I not only scrubbed but also waxed the floor. PRACTICE: WRITE THE SENTENCE. UNDERLINE ALL CONJUNCTIONS. IDENTIFY THEM AS EITHER COORDINATING OR CORRELATIVE. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. At the shore, you’ll see seagulls both on the sand and in the water. Neither Louis nor I voted for the amendment. In 1500 the cities now known as Cahokia, Illinois, and Albuquerque, New Mexico, were already large. Either come to the party or stay away. Apparently Ron found nothing on the counter or under the table. Mr. Palumbo ordered the pasta primavera, and he ate it with gusto. The weather has grown very cold today, yet it has not snowed. Just as the days grow longer in springtime, so the nights grow longer in fall. Ebenezer Scrooge was rich but not happy. ANSWERS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. both, and -- correlative neither, nor -- correlative and -- coordinating either, or – correlative or – coordinating and – coordinating yet – coordinating just as, so – correlative but – coordinating SUBORDINATING CONJUNCTIONS -- joins two clauses, or thoughts, in such a way as to make one grammatically dependent on the other -- the thought, or clause, that a subordinating conjunction introduces is said to be “subordinate,” or dependent, because it cannot stand by itself as a complete sentence Examples: 1. We can skate on the pond when the ice is thicker. 2. We can’t skate until the ice is thicker. 3. Because the ice is still too thin, we must wait for a hard freeze. COMMON SUBORDINATING CONJUNCTIONS after although as as far as as if as long as as soon as as though because before considering (that) if inasmuch as in order that since so long as so (that) than though till unless until when whenever where whereas whenever while PRACTICE: WRITE THE SENTENCE. UNDERLINE THE SUBORDINATING CONJUNCTION. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. I’ll go with you wherever you go. You may as well eat dinner as long as you’re here. Since Peppermint may be upset by our move, I’ll keep her inside for now. No one may leave until the exam is over. Although it was cold that morning, Keith wore only a light jacket over his school clothes. New England’s climate is cool and humid, whereas the Southwest’s is hot and dry. After his stay on the Mir space station, the astronaut headed back to Earth. Please come to visit us if you’re ever in Topeka. While you finish your homework, I’ll scrub the floor. Don’t expect lunch unless you’re home by noon. ANSWERS wherever 2. as long as 3. since 4. until 5. although 6. whereas 7. after 8. if 9. while 10. unless 1. CONJUNCTIVE ADVERBS is used the clarify the relationship between clauses of equal weight in a sentence are usually stronger, more precise, and more formal instead of using just a comma, a semicolon precedes the conjunctive adverb and a comma follows it Examples: Coordinating Conj. Conjunctive Adverb The civilization of the Incas was advanced, but they never invented the wheel. The civilization of the Incas was advanced; however, they never invented the wheel. CONJUNCTIVE ADVERBS To replace AND To replace BUT To state a result To state equality also, besides, furthermore, moreover however, nevertheless, nonetheless, still accordingly, consequently, then, therefore, thus equally, indeed, likewise, similarly PRACTICE: WRITE THE SENTENCE AS IS. LABEL THE UNDERLINED WORD CC FOR COORDINATING CONJUNCTION OR CA FOR CONJUNCTIVE ADVERB. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. It’s my turn to fix dinner; therefore, I can’t go to the mall with you after school. Celia didn’t buy any peaches, but she got a melon. Luke’s new tennis racket lies forgotten in his closet, and his new skates are in a dark corner; similarly, these new skis will probably be abandoned soon. Of course you may come along on our trip to the park; indeed, I’ll be glad of your help with the dogs. Bella didn’t want a new coat, nor did she think new boots were necessary. CONTINUED… 6. Robin’s recipe for hot cider is my favorite, for she stirs it with a cinnamon stick. 7. Leeza has become better organized lately; consequently, she found her summer school application form after only a short search. 8. The vandals were evidently wearing gloves; we did find one long blonde hair stuck to a chair, however. 9. Going to that movie would keep you out too late on a school night; also, the subject matter isn’t suitable for a person your age. 10. This applicant lacks experience; she has, nonetheless, demonstrated the ability to manage a big project. ANSWERS therefore CA 2. but CC 3. and CC, similarly CA 4. indeed CA 5. nor CC 6. for CC 7. consequently CA 8. however CA 9. also CA 10. nonetheless CA 1.