Polypetides and proteins
advertisement
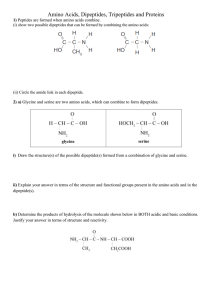
Polypetides and proteins L.O.: • Explain the formation of a peptide (amide) linkage between α-amino acids to form polypeptides and proteins. • Describe the acid and alkaline hydrolysis of proteins and peptides to form α-amino acids or carboxylates. Formation of a dipeptide between glycine and alanine Peptide: compound containing amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Peptide bond: amide bond in proteins and peptides. Formation of a dipeptide between glycine and alanine Draw an alternative dipeptide made from the condensation of glycine and Alanine. Alternative reaction of alanine and glycine Section of a polypeptide showing four different amino acids Acid hydrolysis of a dipeptide Reaction conditions: reflux with HCl for 24 hours. Alkaline hydrolysis of a polypeptide chain Reaction condition: NaOH, heat Note: sodium salts are formed. Peptide hydrolysis (powerPoint) Draw the organic products formed when the following protein is heated with concentrated hydrochloric acid: CH3 OH O HO C H O N C C H H CH2 N H C H O C O CH3 C H N H C CH2 C N H H H