IndustryIntro
advertisement

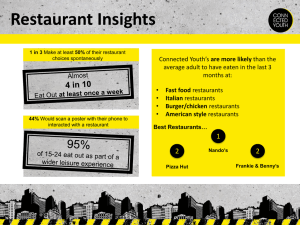
Food & Beverage Overview What does the career path look like? Maps & Guides Sporting Events Airlines Lodging Restaurants Travel Agencies Travel & Tourism Country Clubs Retirement Communities Contract Food Service Hospitality Travel and Tourism Industries Hotels/motels Natural attractions Entertainment venues Resorts Gaming entertainment Arts venues Vacation ownership Travel agencies Historical sites Hostels Convention bureaus Museums Caravans Tour companies Luggage Camping Hotel/rest. suppliers Real estate Airlines Taxi services Construction Cruise ships Cameras and film Luggage Rail Maps & travel books Beverage mfr & dist Car rental Shopping malls Auto/aircraft mfr Bus coaches Service stations Motor fuel producers Restaurants Sporting events Recreation equipment Fast food Banking services Food producers Wine merchants Reservation systems Advertising media Theme parks Auto clubs Souvenirs Hospitality Industries Hotels/motels Natural attractions Entertainment venues Resorts Gaming entertainment Arts venues Vacation ownership Travel agencies Historical sites Hostels Convention bureaus Museums Caravans Tour companies Luggage Camping Hotel/rest. suppliers Real estate Airlines Taxi services Construction Cruise ships Cameras and film Luggage Rail Maps & travel books Beverage mfr & dist Car rental Shopping malls Auto/aircraft mfr Bus coaches Service stations Motor fuel producers Restaurants Sporting events Recreation equipment Fast food Banking services Food producers Wine merchants Reservation systems Advertising media Theme parks Auto clubs Souvenirs The Hospitality Industry Lodging Food service Clubs Cruise ships Gaming Theme parks Sports and entertainment Travel The Hospitality Business Lodging – putting heads on beds Many U.S. markets are mature Expansion and growth overseas Food service – putting cheeks in seats What would you like to eat? Where would you like to meet? Expansion and growth overseas Hospitality Industry Numbers Lodging 11.4M rooms worldwide 3M rooms in U.S. Slowing in U.S. Exceptions; casinos, limited service, timeshare Continued expansion Food Service Strong growth $1 billion/day sales 10.2M employees 12M in 2006 1/2 of all adults/day eat in restaurants 44% of food $ spent in restaurants Where are the jobs? Professional Corporate Operations management, finance, accounting, human resources, customer relations, marketing, food science Marketing, business development, human resources, training, quality assurance, real estate, accounting, purchasing Entrepreneurial Owner, operator, franchisor Food Service Eating and drinking places Quick service restaurants (QSR) Full service restaurants / bars White table cloth restaurants / bars Lodging food service Education food service Employee food service Health care Recreational food service Off-premise catering Restaurant Industry Positions Banquet manager Bartender/cocktail server Broiler cook Busperson Counter person Dining room manager Dishwasher Executive chef Expediter Food & beverage director Food server Fry/Sauté cook Host/hostess Kitchen manager Pantry cook Pastry chef Restaurant manager Sous chef Storeroom person Unit manager Hospitality Careers The industry offers more career options than most The work is varied There are many opportunities to be creative This is a “people” business Hospitality Careers Hospitality jobs are not nine-to-five jobs There are opportunities for long-term career growth There are perks associated with many hospitality jobs Hospitality jobs can be intrinsically satisfying and meaningful The Down Side Long hours Nontraditional schedules Pressure Low beginning salaries Frequent relocation Lodging Careers Entry level Housekeeper Front desk clerk Reservations clerk Food service staff Mid level Reservations manager Executive housekeeper Front office manager Catering sales manager Sales manager Upper management Personnel director Senior sales manager Controller Food & beverage director Director of sales & marketing General manager Food Service Careers Entry level Crew person Crew supervisor Lead positions Mid level Manager trainee Chef Unit manager Controller Kitchen manager Catering manager Upper management Executive chef General manager District manager Regional manager Operations director Other directors CFO President/CEO Chain Operations Better training More opportunities for advancement Better benefits Frequent relocation More control by management Bonus plans impact pay Independent Operations More chances to be creative More control Better learning environments Less job security Fewer chances for advancement Harder to market and sell Foodservice Industry Commercial Foodservices Institutional Foodservices Military Foodservices Foodservice Industry Commercial Foodservices Restaurants Lunchrooms Cafeterias Fast food restaurants Hotel foodservice operations Food stands Social caterers Foodservice Industry Institutional Foodservices Hospitals Nursing homes Schools & colleges Correctional facilities Employee cafeterias Airline catering Surface transportation catering Foodservice Industry Military Foodservices Military bases Combat foodservices Officers clubs Cafeterias Restaurant Industry The National Restaurant Association [NRA] defines the restaurant industry as that which encompasses all meals and snacks prepared away from home, including all takeout meals and beverages. Restaurant Industry Restaurant industry sales were forecast to reach $ 399.0 billion in 2001, an increase of 5.2 over the year 2000. Restaurant Industry On a typical day in 2001, the restaurant industry will post average sales of $1.1 billion Restaurant Industry Sales at full service restaurants are forecast to reach $143.3 billion and sales at quick service [fast foods] restaurants are forecast to reach $ 112.0 billion. Restaurant Industry The overall impact of the restaurant industry is expected to reach $ 1 trillion in 2001. This includes sales in related industries such as agriculture, transportation, wholesale trade and food manufacturing. Restaurant Industry Sales: $ 399 billion – average $1.1 billion on a typical day Locations: 844,000 – more than 54 billion meals will be eaten in restaurants and school and work cafeterias. Restaurant Industry Employees: 11.3 million – more than 8 percent of those employed in the United States, which makes the industry the largest employer besides government. Food-and-drink sales [billions $] 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 399.2 239.3 119.6 42.8 1970 1980 1990 2001* Restaurant Industry One-third of all adults in the United States have worked in the restaurant industry at some time during their lives Per-person check averaged $4.72 in 1999 Average unit sales in 1998 were $ 601,000 at full service restaurants and $555,000 at limited-service [fast-food] restaurants. Distribution of Restaurant Customer Traffic [1998] Breakfast 11% Lunch 37% Dinner 52% Restaurant Industry Restaurant Industry remains to be very competitive Three out of four consumers report that they have more restaurants to choose from today than they did two years ago. Restaurants are paying more attention to design, décor and atmosphere Restaurant Industry: Ranking of Consumer Choices Food and Service Physical setting Moods and Impressions Restaurant Industry: Quick Service Intense competition Convenience is number one factor Carryout or delivery market Time savings meal options Ever-changing consumer needs Shortage of labor Training needs Restaurant Industry: Full Service Tied to economy Baby-boom generation Increased competition Importance of repeat customers Portion sizes Dietary needs Restaurant Industry: Growth in Other Segments Managed services [1%] Educational institutions [4.4%] Recreational services [3.3%] Transportation [3.8%] Health care [2.2%] Lodging places [2.7%] Military [2.2%] Restaurant Industry: Trends Labor shortage issues Cost of providing food and service Technology issues and benefits Consumer preferences Training Expansion