Do Now: Answer the following
Questions.
• What is the function of the cell membrane?
• Do animals, plants, or both have a cell
membrane?
• What does a plant have surrounding the cell in
addition to a cell membrane?
Announcements
• Organelle Quiz - Friday!
Cell Membrane Function
Objective: To be able to understand the
function of the cell membrane as it
relates to diffusion, osmosis, and active
transport.
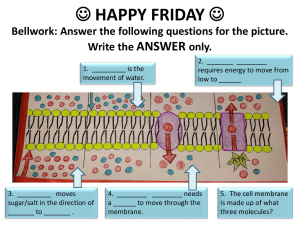
Cell Membrane
Cell Membrane
Outside of
cell
Proteins
Carbohydrate
chains
Cell
membrane
Inside of cell
(cytoplasm)
Protein
channel
Functions
• Regulates what goes in and out of a cell
• Maintains homeostasis
Characteristics
• Lipid bilayer that carries a charge
• Protein channels
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Lipid bilayer
Cell Membrane
Cell Membrane
Outside of
cell
Proteins
Carbohydrate
chains
Cell
membrane
Inside of cell
(cytoplasm)
Protein
channel
2 ways to enter or leave a cell
• Passive Transport (Diffusion)
• Through the membrane
• Through a protein channel
• Active Transport
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Lipid bilayer
Cell membranes
• Have pores (holes) in it
• Selectively permeable
(semi-permeable)
• Allowing some
molecules in and
keeps other molecules
out.
• Materials are moved
through membrane by
passive transport or
active transport
Types of Cellular Transport
Weeee!!!
•
Passive Transport
(High Concentration to Low Concentration)
cell doesn’t use energy
high
1. Diffusion
2. Facilitated Diffusion
3. Osmosis
•
Active Transport
low
This is
going to
be hard
work!!
high
(Low Concentration to High Concentration)
cell does use energy
low
Cell Model Project
• Create a model of a cell
• Can be 2-D or a 3-D model
– CANNOT be a colored diagram of a cell
• Be creative
– use food, household materials to make different
organelles!
• Choose a plant or animal cell to create (fill in
on your instruction form).
Cell Model Project
• Rubric
– Creativity
– Labelling
– Organelle
– Organelle Function
– Organelle Identification
Complete the Venn Diagram Below
Do Now!
• Record data for the Osmosis/Diffusion Lab (Cell
Membrane Model)
• Make sure you have your “Control Group” Data
(Chemical Test Results) – record the color of the
solution in your table.
Benedicts and
water or starch
Row 1
Benedicts
and glucose
Iodine and
starch
Iodine and water
or glucose
Row 2
Announcements
• Homework: Answer the questions on your
Osmosis/Diffusion Lab. Due on Monday.
• Clear your desks for the quiz.
Passive Transport
• How to cross the membrane without
using
_________________
Weeee!!!
high
low
Passive Transport: Diffusion
What Happens During Diffusion?
• Particles move from high concentration to low
concentration
• When the concentration of the particles is the same
throughout a system, the system has reached
equilibrium.
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Why do molecules diffuse?
• Because they are in constant motion
Diffusion Through Cell Boundaries
Solution
• A solution is a mixture of two or more
substances.
– Examples: Lemonade
– Solute – substance that is dissolved
(powder)
– Solvent – material that is dissolving the
substance (water)
Concentration = the mass of solute (mass
of powder) in a given volume of solution
(volume of water), or mass/volume.
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Diffusion Through Cell Boundaries
Time
A
B
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
C
Diffusion
• Some molecules are too large or charged, to
pass through the membrane using simple
diffusion.
• How will the cell reach equilibrium with the
external environment?
Facilitated Diffusion
(High Concentration to Low
Concentration)
Facilitated diffusion:
• Diffusion of specific
particles using protein
channels found in the
membrane
• Protein channels allow
only specific molecules
through
Facilitated
diffusion
(Protein
channel)
Osmosis
What is osmosis?
Osmosis the diffusion of water through a selectively
permeable membrane (semi-permeable)
Time
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Red Onion Cell Osmosis
• http://www.microbehunter.com/wp/wpcontent/uploads/2014/04/onion_plasmolysis_
animated_sm.gif
Which way will the water move?
Selectively permeable membrane
Which way will the water move?
Watch this Video!
Pay attention to when
the following terms are
mentioned
• Isotonic • Hypertonic • Hypotonic -
Egg Osmosis
Write a definition for
the following terms
related to osmosis
based on the pictures
(Describe which way the water
is moving).
• Isotonic • Hypertonic • Hypotonic -
Exit Slip: What are two differences
between diffusion and osmosis? Give an
example of each.
• 1.
• 2.
What does diffusion, facilitated diffusion,
and osmosis all have in common?