Poetry Unit
advertisement

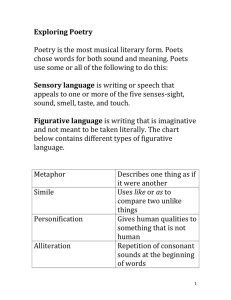
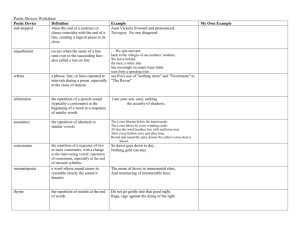
Poetry Unit Terms, Definitions and Examples Dialect- a version of a language spoken by the people of a particular place, time, or social group Ex: ya’ll, yun’z Onomatopoeia- the use of words or phrases that sound like the things to which they refer Ex: bang, pop, buzz Alliteration- the repetition of initial consonant sounds Ex: sally sells sea shells, tip of the tongue Atmosphere- that emotion created in the reader by all or part of a literary work, also known as “mood” or “tone” Ex: Dark and eeriness of “Emmett Till” by James A. Emanuel: “I hear a whistling / Through the water / Little Emmett / Won’t be still. / He keeps floating / Round the darkness, / Edging through / The silent chill.” Rhyme- the repetition of sounds at the ends of words Ex: mine and pine Rhyme Scheme- a regular pattern of end rhymes Ex: ABAB, ABBA, ABBB, AABB, AABA, ABCA…etc. Assonance – repetition of the same vowel sounds Ex: “The crumbling thunder of the seas” Concrete - printed or written in a shape that suggests its subject matter Ex: Action- the sequence of events that occur in a literary work, as opposed to those that occur off-scene or precede or follow the events in the work itself. Ex: “My love is like a red, red rose” Takes place RIGHT NOW Analyze - To discover something through detailed examination of a text; an analysis is that examination Ex: Through usage, tone, and symbolism, Margaret Atwood discusses the position of women in society in her poem “Siren Song.” Quatrain- four-line stanzas Ex: “’Hope’ is the thing with feathers – That perches in the soul And sings the tune without the words – And never stops – at all” Tercet- three-line stanzas Ex: Do not go gentle into that good night, Old age should burn and rave at close of day Rage, rage against the dying of the light Hyperbole – an extreme exaggeration Ex: “I’m so hungry I could eat a horse!” Symbol- a thing that stands for or represents both itself and something else Ex: Dove = peace, rose = love Theme – a central idea in a work Ex: Good is better than evil Personification – giving inanimate objects human-like qualities Ex: “The fog comes / on little cat feet. / It sits looking / over harbor and city / on silent haunches / and then moves on.” Ambiguity– word or phrase that can be read one in more than one way Ex: “The whiskey on your breath / could make a small boy dizzy; But I hung on like death: / Such waltzing was not easy.” Figurative language– tool that an author uses to help the reader visualize what is happening Ex: Simile, metaphor, etc. Appositive-a grammatical form in which a thing is renamed, in different words, in a word or phrase Sandra, my best friend, writes nature poetry. Lovely, dark and deep Simile- a comparison using like or as Example: “O my love is like a red, red rose / That’s newly sprung in June.” Metaphor- a comparison that is directly stated Example: “Shall I compare thee to a summer’s day? / Thou art more lovely and more temperate.”