The Human Brain Functions (from ppt)
advertisement

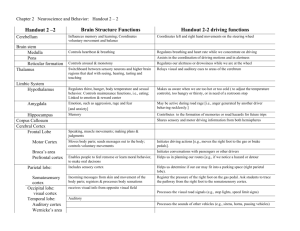
The Human Brain “I once thought about cloning a new, more efficient brain, but then I realized that I was getting a head of myself.” The Brain is a jellylike mass of fat and protein weighing about 3 pounds. It is one of the body's biggest organs, consisting of some 100 billion nerve cells that create thoughts, coordinate physical actions, and regulates our unconscious processes, such as digestion and breathing. The Spinal Cord (Brain Stem) The brain stem is located at the base of the brain It controls the body’s reflexes and involuntary actions like breathing, sleeping and blood pressure The Cerebrum It lies in front/on top of the brainstem Is the largest part of the brain, processing thought, memory, language, sensory information and movement It is divided into right and left hemispheres that are connected by the corpus callosum. Each hemisphere is in turn divided into four lobes. The Hemispheres Left-Brain Functions Controls movements on the right side of our bodies. Analytical thought Logic Language Science and Math Right-Brain Functions Controls movements on the left side of our bodies. Holistic thought Intuition Creativity Art and music The Four Lobes of the Brain The brain is divided into four lobes: The frontal lobe The parietal lobe The occipital lobe The temporal lobe The Frontal lobe processes speech, thought, learning, emotion and movement The Occipital lobe processes vision The Parietal lobe processes interprets sensations like touch, heat and pain The Temporal lobe processes sounds The Cerebellum The second largest part of the brain (aka “little brain”) Coordinates muscle movement and controls balance Receives information from the spinal cord and other parts of the brain The Medulla Oblongata Makes up the lower part of the brain stem and regulates breathing, blood pressure and heartbeat The Pons Located within the brain stem and acts as a relay station for the senses, movement and it regulates sleep The Reticular Formation or The Reticular Activating System (RAS) The RAS receives input from many parts of the brain and sends info to various parts of the Cerebral cortex. It is responsible for regulating arousal and sleep to awake transitions. The Thalamus Relays sensory and motor signals from around the body to the cerebral cortex Regulates consciousness, alertness and sleep based on the body’s needs The Hypothalamus It regulates: Food intake and hunger The body’s fluid balance (thirst) Internal body temperature (controls when the body sweats to cool off by dilating the blood vessels, or makes the body shiver to warm up by constricting the blood vessels) The hypothalamus also regulates sexual drive The hypothalamus is responsible for the monthly female hormonal cycle in humans through its control of the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus contains programming for male and female sexual behavior. The Pituitary Gland Produces and distributes hormones that control growth, sexual drive and hunger. The Hippocampus The hippocampus is located in the temporal lobe of the brain. The hippocampus is responsible for the formation of new memory. Without the hippocampus one cannot form any new permanent (long-term) memories. The Auditory Cortex The primary auditory cortex is located in the temporal lobe and it is responsible for the basic analysis of sound. Input from the ears is crossed over: The left auditory cortex receives input primarily from the right ear, and the right auditory cortex receives input primarily from the left ear. The Visual Cortex lies at the very back of the brain in the occipital lobe. The visual cortex processes visual information in the brain . Information from the left visual field, from both eyes, goes to the right visual cortex. Information from the right visual field, from both eyes, goes to the left visual cortex. The Somatosensory Cortex Is in the parietal lobe. The somatosensory cortex receives sensory information from the thalamus and sensory receptors on the body’s surface. The Motor Cortex This area is at the back of the frontal lobe, separating the frontal and parietal lobes. The primary motor cortex sends impulses to the muscles of the body. Final Question: Why didn’t the brain want to take a bath? Answer: Because it didn’t want to get brain washed! Brain Games There are a number of workstations set up around the classroom. Complete the following: 1. Complete the activity outlined at the workstation. 2. Try to guess what parts of the brain being used in the activity. 3. Describe the function of that part of the brain.