outline
advertisement

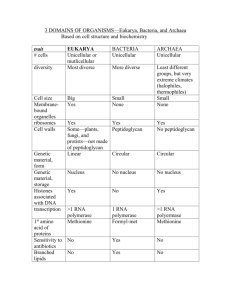
BIO 208 Unit 1 Lecture 6 1 This outline is intended to facilitate your preparation for lecture. This web outline will NOT substitute for regular lecture attendance. Your textbook does not contain much information on this topic; lecture will be your primary source of information. Lecture 6 - we will discuss the following topics: B. The Eukarya 1. Compare/contrast with Bacteria and Archaea a. Major differences b. Similarities 2. Origins of the Eukarya (p. 106 and lecture) a. History of evolution of cells and cellular based life Symbiosis = living together Endosymbiont = living inside BIO 208 Unit 1 Lecture 6 2 b. Theory of Serial Endosymbiosis - Lynn Margulis *Eukarya evolved as a result of multiple mergers of Bacteria and Archaea. How Eukarya may have evolved – in reverse chronological order (starting with most recent evidence) 1. Cholorplasts Evidence: a. same size as cyanobacteria b. surrounded by a membrane c. have their own DNA d. contain 70S ribosomes e. have same pigments as cyanobacteria All organisms with chloroplasts have mitochondria – therefore, mitochondria evolved as organelles before chloroplasts did 2. Mitochondria Evidence: a. same size as proteobacteria b. surrounded by a membrane c. have their own DNA d. contain 70S ribosomes e. grow and divide on their own schedule f. some modern Eukarya do not have mitochondria but do have bacterial endosymbionts 3. Flagella and cilia 4. Centrioles Evidence for 3 & 4: “docking” flagella and centrioles of Eukarya have DNA and RNA there are protists that have flagella but do not have mitochondria 5. Nucleus Evidence: nuclear envelope is a lipid membrane Archea have histones for organizing DNA, so do Eukarya some Archea have no cell walls, only a plasma membrane. BIO 208 Unit 1 Lecture 6 3 Putting it together in chronological order – the evolution of Eukarya from multiple mergers of Archaea and Bacteria = The Theory of Serial Endosymbiosis 1. Archaea attacked by spirochetes 2. Archaea surrounded its DNA with membrane evolved into a nucleus 3. Captive internal spirochetes evolved into centrioles ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4. Endosymbiotic proteobacteria evolved into mitochondria 5. External spirochetes evolved into flagella and cilia 6. Endosymbiotic cyanobacteria evolved into chloroplasts Assignments to complete before Test 1. CH 4: - Review: 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7a, b, c, d, e - Multiple Choice: 1, 6, 7, 8, 9 - Critical Thinking: 2, 3 - Clinical Applications: 2 This ends the lecture material for Test 1.