113883_Circulatory_System
advertisement

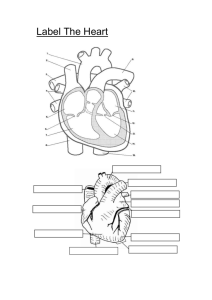
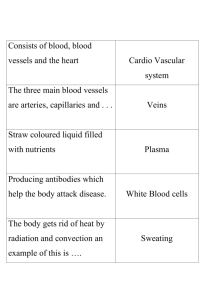
Science Module th 7 Grade Circulatory System Structures • Heart • Blood Vessels – Arteries – Veins – Capillaries • Blood Circulatory System Function • The overall function of the circulatory system is to transport materials throughout the body toward and away from particular target organs and tissues. Two Pathways • Pulmonary Circulation – Carries blood to lungs and back to the heart • Systemic Circulation – Carries blood to body and back to the heart Capillaries of head and arms Superior vena cava Aorta Pulmonary artery Pulmonary vein Capillaries of right lung Capillaries of left lung Inferior vena cava Capillaries of abdominal organs and legs Your Blood Vessels: Pathway of Circulation 3 types of vessels – Arteries – Capillaries – Veins Arteries: carries blood Away from heart – – – – Large Thick-walled, Muscular Elastic Oxygenated blood Exception Pulmonary Artery – Carried under great pressure – Steady pulsating Arterioles: smaller vessels, enter tissue Capillaries – – – – Smallest vessel Microscopic Walls one cell thick Nutrients and gases diffuse here Veins: Carries blood to heart – Carries blood that contains waste and CO2 – – Exception pulmonary vein Blood not under much pressure Valves to prevent much gravity pull Venules: larger than capillaries Varicose Veins Damaged Valves in Veins Artery vs. Vein Your Heart: The Vital Pump At REST, the heart pumps about 5 QUARTS of blood a minute. During EXTREME EXERTION (exercise) it can pump 40 quarts a minute. Structure of Heart Four chambers – Two upper (Atria) Right Atria Left Atria – Two lower (Ventricles) Right Ventricle Left Ventricle Heart Pumping http://library.med.utah.edu/kw/pharm/hyper _heart1.html Lyrics Pump, pump, pumps your Blood. The right atrium’s where the process begins, where the CO2 Blood enters the heart. Through the tricuspid valve, to the right ventricle, the pulmonary artery, and lungs. Once inside the lungs, it dumps its carbon dioxide and picks up its oxygen supply. Then it’s back to the heart through the pulmonary vein, through the atrium and left ventricle. Pump, pump, pumps your Blood. Blood Flow Through Heart Label the Following Structures Right ventricle Left ventricle Right atrium Left atrium Pulmonary arteries Pulmonary veins Aorta Superior vena cava Inferior vena cava Semi-lunar valves Bicuspid valve Tricuspid valve Cardiac muscle Pericardium Septum Color in oxygenated blood red & de-oxygenated blood blue Draw arrows showing blood flow Through the heart & adjacent Blood vessels Indicate the location of the lungs Heart Sounds First heart sound or “lubb” – Atrioventricular valves and surrounding fluid vibrations as valves close at beginning of ventricular systole Second heart sound or “dupp” – Results from closure of aortic and pulmonary semilunar valves at beginning of ventricular diastole, lasts longer Third heart sound (occasional) – Caused by turbulent blood flow into ventricles and detected near end of first one-third of diastole The Blood Body contains 4-6 L Consists of – – – – Water Red Blood Cells Plasma White blood cells and platelets Erythrocytes (RBC) Transporters of – Oxygen – Carbon Dioxide RBC are produced in red bone marrow of – – – – ribs, humerus, femur, sternum, and other long bones Leukocytes (WBC) WBC fight infection – Attack foreign substances Less abundant Large cells Platelets PLATELETS are for CLOTTING blood Cell fragments Produced in bone marrow Fibrin (sticky network of protein fibers) – Form a web trapping blood cells Blood Clotting Section 37-2 Break in Capillary Wall Clumping of Platelets Clot Forms Blood vessels injured. Platelets clump at the site and release thromboplastin. Thromboplastin converts prothrombin into thrombin.. Thrombin converts fibrinogen into fibrin, which causes a clot. The clot prevents further loss of blood.. Blood Types Massive loss of blood requires a transfusion Four Types –A –B – AB –O Inherited from your parents Blood Types What happens when you mix blood types? Plasma contains proteins that correspond to the shape of the different antigens If you mix one type with the wrong one, you get CLUMPING Type O is the universal donor Type AB is the universal acceptor What Makes Our Blood Type? Blood Transfusions Blood Type of Donor Blood Type of Recipient A B AB O A B AB O Unsuccessful transfusion Successful transfusion Rh Factor Rhesus factor (Rh), also inherited – Rh+ (have antigen) – Rh- (NO antigen) Can cause complications in pregnancies – mother Rh- 1st baby Rh+ : blood mixes with mother; mother’s body makes anti-Rh+ antibodies – 2nd Rh + body attacks baby – Now have medicine to prevent antibody formation