Chapter 17 Section 4
advertisement

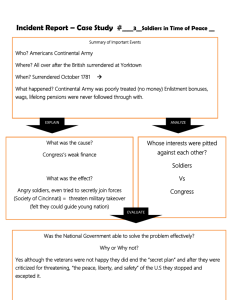
Chapter 17 Section 4 The Home Front Brainstorm: What impact would the war have on American minorities and women? Objective: Describe the economic & social changes that reshaped American life during World War II Summarize both the opportunities and discrimination African Americans and other minorities experienced during the war How did the war and its immediate aftermath affect the following? 1. Labor Defense Industries boom Unemployment at 1.2% Able to save $ because their pay went up 10% even with price fixing & inflation Some complaints about long hours, not enough pay & night shifts People buy war bonds 35% or 6M women in work force 2. Agriculture 1940s provides good growing weather Improvements in machinery & fertilizers Crop prices increase / farm income triples Crop production increases by 50% Some farmers pay off mortgage 3. Population Centers One of greatest mass migration in history, look at page 591 1941 to 1944 1M newcomers to CA Towns with defense industries triple in size African Am look for jobs in the North Soldiers training in different parts of US 4. Family Life Soldiers at war / moms home alone Children taken care of by relatives or first day care centers Teenagers run into trouble Marriage increases & Baby Boom Tension with returning soldiers 5. Returning GIs Serviceman’s Readjustment Act or GI Bill of Rights helps with education or training for veterans 50% take advantage / get education or training Lower interest rates or loans to help buy homes, farms or businesses How did these groups react to discrimination and racism during and after the war? 6. African Americans Majority of Southern Af. Am move to Midwest for better jobs 1940 to 1944, Af Am increase from 16% to 30% in work force Farmer & CORE in 1942 (Congress of Racial Equality / interracial) founded to confront urban segregation in the North / sit-ins Race riot in Chicago: all is not well 7. Mexican Americans 1943 Zoot Suit riots in LA Refer to page 593 11 sailors claimed they had been attacked by Mexicans / 1 week Mexicans believe their sacrifices would lead to a better future 8. Japanese Americans Fear of J-A sabotaging or mining coastal harbors & poisoning food supply War Dept orders General Delos Emmons, the military governor of Hawaii to evacuate J-A from Hawaii Emmons declines because 37% of population is J-A. / Economy & war effort / 1% internment camps 8. Japanese Americans 110K J-A from CA, WA, OR, & AZ sent to internment camps in CA, ID, WY, UT, CO, AZ, & AK Supreme Ct ruled this was justified Korematsu v. United States 1965 Japanese American Citizens League gets Congress to allocate survivors $38M Ronald Reagan & Congress allocate $20K to each survivor