lazy notes - TeacherWeb
advertisement

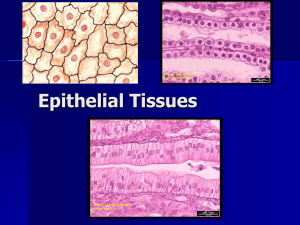
Chapter 5 - HISTOLOGY Histology - ___________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________ - layers or groups of similar cells with a common function. There are four major tissue types: 1.____________________________________________ 3.______________________________________________ 2.____________________________________________ 4.______________________________________________ Intercellular junctions - connections between cell membranes which hold the cells together to form tissue. Three types (see diagram) : 1) Tight junctions 2) Desmosomes 3) Gap junctions EPITHELIAL TISSUE - general characteristics: * Covers the body surface and organs, lines body cavities and the inside of hollow organs, ducts and vessels. * Has two sides: apical surface - exposed to open space; Other side - attached to a basement membrane: * Basement membrane - _________________________________________________________________________________ * Avascular (no blood vessels) - nutrients diffuse to epithelium from the underlying connective tissue. Cells readily divide, so that injuries heal quickly. Cells are tightly packed to form _____________________________________________________. * Functions - ___________________________________________________________________________________________ * Classification based on __________________________________________________________________________________ 1. Simple squamous epithelium - single layer of flat cells. Substances pass easily through this epithelium by diffusion. Location - ______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Simple cuboidal epithelium - single layer of cube-shaped cells Location - ______________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Simple columnar epithelium - single layer of elongated cells _________________________ - movement of material across the surface of the cell _______________________________________ - increase surface area of cell membrane for absorption _______________________________________ - secrete mucus, a protective fluid, onto the free surface of the epithelium Location - ______________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium - single layer of elongated cells that appears stratified because the nucleii are at various levels, giving a stratified appearance. Often have cilia and goblet cells. Location - _______________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Stratified squamous epithelium -many layers of cells to provide protection; top cells are flat. Forms the epidermis - outer layer of skin. Accumulates keratin in the outermost cells - tough, waterproof protein. Other locations -_________________________________________________________________________________ 6. Stratified cuboidal epithlium - 2-3 layers of cube-shaped cells. Protection. Location - ______________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Stratified columnar epithelium - top layer of cells are columnar, deeper layers are cuboidal Location - _______________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Transitional epithelium - many layers of cuboidal and columnar cells; can stretch in response to increased tension, forming an expandable barrier. Location - ______________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Glandular epithelium - composed of specialized cells that secrete substances. There are two types of glands: A) Endocrine glands - _________________________________________________________________________________ B) Exocrine glands - __________________________________________________________________________________ Exocrine glands can be unicellular (_______________________________) or multicellular - sweat glands, salivary glands, etc. Exocrine glands can be simple (duct does not branch) or compound (duct branches before reaching secretory cells) Exocrine glands are also classified according to how they secrete their products (see diagram): 1) Merocrine glands 2) Apocrine glands 3) Holocrine glands