QUIZ
• 1. This was connected (completed)
with the golden spike.
• A. George Pullman
• 2. Is responsible for creating his
own railroad town south of
Chicago.
• B. Credit Mobilier
• 3. Scandal in which the Federal
government was ripped off for $25
million
• C. Interstate Commerce Act
• 4. Through this, states won the right
to regulate railroad rates
• D. Munn v. Illinois
• 5. Set up a commission to regulate
railroad rates from one state to
another.
• E. Transcontinental railroad
14.2 The age of railroads
OBJECTIVES:
• Identify the role of the railroads in unifying the
country
• List positive and negative effects of railroads on the
nation’s economy
• Summarize reasons for, and outcomes of, the demand
for railroad reform
Promontory Point: Golden Spike!!
• Union Pacific (East to West)
construction begins during
Civil War
• Central Pacific (West to East)
begins after
• Golden Spike driven in Ogden,
Utah 1869
• Promontory Point
•
Effect: Unites East and West;
Opens trade with Asia
3
RAILROADS OPEN THE
WEST
• US govt. gives huge land grants to railroad companies
to encourage construction
• Union Pacific and Central Pacific meet at Promontory
Rock, Utah on May 10, 1869.
• Railroads built with Irish, Chinese, Mexican and
African American labor.
• Homesteaders and immigrants flood west on new
railways.
Introduction of time zones
• How did people keep track of the time before
times zones?
• Why did they feel the need to adapt time zones
for the railroads?
Map: Transcontinental Railroads and Federal Land
Grants, 1850-1900
Transcontinental Railroads and Federal Land Grants, 1850-1900
Despite the laissez-faire ideology that argued against government interference in business, Congress heavily subsidized
American railroads and gave them millions of acres of land. As illustrated in the box, belts of land were reserved on either
side of a railroad's right of way. Until the railroad claimed the exact one-mile-square sections it chose to possess, all such
sections within the belt remained closed to settlement.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
New Towns and
Markets
Examine the map on the next slide
to understand how the
transcontinental railroad changed
the economy.
Map: Mining and Cattle
Frontiers, 1860-1890
Mining and Cattle Frontiers, 1860-1890
The western mining and ranching bonanzas lured thousands of Americans hoping to get rich quick.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Pullman, Illinois
• George Pullman created a town
for his workers
• Created this town to ensure a
steady workforce
• Medical offices
• Legal offices
• Church
• Library
• Theater
• Athletic field
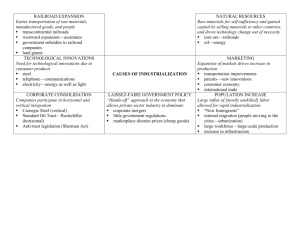
Crédit Mobilier Scandal
• Example of profiteering and greed of industrialists
• Union Pacific stole over $25 million from the government
• Basically a “front company” formed by the financiers/builders of
the Transcontinental Railroad
• Insiders of the Union Pacific Railroad hired and paid themselves
as much as $50,000 a mile for construction that cost $30,000.
• Stock was sold to influential Congressmen to keep them quiet.
• New York Sun unearthed the scandal and kept attention on the
“Trial of Innocents” = public figures in the Grant Administration
and Congress that were involved. Only 2 Congressmen formally
censured. Even Vice President Colfax escaped serious charges.
Granger laws
• Businesses were given the land grants instead of farmers
• Railroads entered into formal agreements to fix prices to keep
the farmers in debt
• Railroads would charge different rates at different times to make
a bigger profit (ex: RRs would charge a higher rate for a shorter trip,
knowing there was no competition)
• Munn v. Illinois allowed the states to control the railroad rates
• IMPORTANT because now the Federal government can intervene with
11
private businesses for the public good
Interstate commerce act
• Grangers success was short lived
• Wabash decision in 1886 overturned Munn v. Illinois because
it dealt with interstate commerce
• Why does this matter?
• BUT, they instead passed the Interstate Commerce Act to
regulate rates
• Didn’t really gain the power it needed for about 20 years
STRIKES
PULLMAN STRIKE
1894
GREAT STRIKE
OF 1877
Pullman Comp.
cuts wages
during Panic
of 1893
Does not raise
after ends
Workers strike
Railroad strike
Paralyzed rail
& commerce
Pres. Hayes
Sent US troops
to end it
US troops end it
CHINESE
EXCLUSION ACT
15
Debs arrested
Workers
Blacklisted
LABOR WEAK
Railroads and
Corruption
SCANDALS
REFORM EFFORTS
Credit Mobilier
Granger Laws (reversed by
Wabash case)
Stock watering
Interstate Commerce Act of
1887
Bribery of officeholders
Creation of “pools”
Secret “rebates”
Were these effective? Why or
Why Not?
16
What are the effects of the
finalization of the
transcontinental railroad?
• Closing of the “Wild West”-ecological disaster
• Spurs industrialization
• Tie the country together/decline in sectionalism
• Decline in Native American societies
• Corruption/Speculation
• Population shift
• Time zones created
• Millionaire class created (i.e Vanderbilt)
• 1886 – Supreme Court’s Wabash decision!!!
• Interstate Commerce Act-1887!!! the formation of the
Interstate Commerce Commission
18
• TERMS:
OBJECTIVES:
• Transcontinental Railroad
• Identify the role of the
railroads in unifying the
country
• George M. Pullman
• Credit Mobilier
• Munn v. Illinois
• Interstate Commerce Act
• List positive and negative
effects of railroads on the
nation’s economy
• Summarize reasons for, and
outcomes of, the demand for
railroad reform