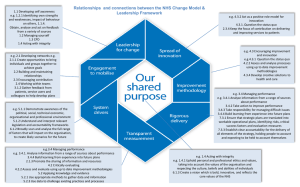
PPT_Develop implement a business plan_220115
advertisement

DEVELOP AND IMPLEMENT A BUSINESS PLAN D1.HCS.CL6.05 D1.HSM.CL5.06 D2.TRM.CL9.02 Slide 1 Subject elements This unit comprises four Elements: 1. Analyse the internal and external business environment 2. Formulate business plans and strategies 3. Implement the business plan 4. Monitor the business plan Slide 2 Assessment Assessment for this unit may include: Oral questions Written questions Work projects Workplace observation of practical skills Practical exercises Formal report from supervisor Slide 3 Element 1: Analyse the internal and external business environment Slide 4 Analyse the internal and external business environment Performance Criteria for this Element are: Determine information requirements and undertake research to deliver relevant information Consult with all internal and external stakeholders in the research process Use research to assist in the prediction of social, political, economic and technological trends and developments Identify and seek assistance and advice from appropriate experts when necessary Slide 5 Analyse the internal and external business environment Performance Criteria for this Element are: Review and analyse the existing internal resources and capabilities Document and analyse business opportunities and obstacles based on valid and reliable comparative market information Review and analyse current and emerging competitors for their potential impact Slide 6 Business planning A business plan A business plan is a written document that presents detailed information about: The business Its projected plans and projections for the future Slide 7 Business planning Importance of a business plan A business plan is the key formal document that sets out a total picture of how a business will operate It helps to establish standards for measuring the success of all aspects of a business Slide 8 Business planning Basis of a business plan The plan is based on: An analysis of the business’ current situation Forecasts of future trends within the relevant industry and economy Includes results from research into all aspects of the business operation Is a logical and structured document Slide 9 Business planning Purpose of a business plan Preparation of a business plan: Gives a sense of ownership and involvement in the future of the business Ensures that the commercial directions planned have been tested for their viability in the marketplace Slide 10 Business planning process Business planning process The planning consists of three activities: Core business concept Feasibility study Business plan Slide 11 Business planning process Core business concept Defines the essence of a new business idea: What are the products and/or services your business will market? What markets will you target with your products and/or services? Slide 12 Business planning process Feasibility study In three steps, the feasibility study determines the initial viability of the core business concept: Technical feasibility Market feasibility Commercial feasibility Slide 13 Business planning process Business plan If the feasibility study indicates that the business concept is a viable proposition, a detailed business plan must be prepared Slide 14 Research process The Research Process You need to undertake initial research to determine your idea is viable before progressing on to a detailed business plan Slide 15 Research process Five steps in the research process Define the problem Analyse the situation Collect information and data Interpret the information Decide on a plan of action Slide 16 Research process Types of research Research may include: Interviewing colleagues and clients Focus groups Data analysis Product sampling Documentation reviews Slide 17 Research process Types of relevant information Common types of relevant information may include: Current performance data Sales and contracts Forecasted trends and opportunities Available resource commitments and capacity Slide 18 Research process Sources of research information Trade associations Unions Trade journals Daily newspapers Internet Government departments Local council Friends, colleagues, business associates Other associated businesses in the field Slide 19 Consult with stakeholders Importance of consulting with stakeholders Who are possible stakeholders? Why is it important to consult with them? What do you require from them? Slide 20 Key stakeholders Types of stakeholders Stakeholders may include: Customers Employees Government agencies Owners Suppliers Strategic alliance partners Slide 21 Involving stakeholders Importance of involving stakeholders Communication throughout the planning, preparation and delivery of new concepts is vital to ensure that all stakeholders: Are involved Had the chance to contribute ideas Provide feedback on initial concepts Understand how concepts will affect them How concepts interrelate or impacts other stakeholders Slide 22 Conducting research When researching information to help facilitate the business planning process, it is essential to collecting and analysing information in a wide variety of 'environmental areas' that may impact on an organisation in the future. Information must ensure it not only explores: External environment - what is provided or needed by competitors and the industry as a whole Internal environment - what the organisation provides Slide 23 Analysing the environment Importance of analysing the environment What do you want to analyse? What information do you seek? Where do you get this information? Slide 24 Understand external environment What is market analysis? Market analysis provides us with the information necessary to understand what can cause changes in our operational environment A prime intent of this activity is to gain a more insightful and detailed view of the organisation and where it sits in the overall business and other settings Slide 25 Analysis of external environment Analysis of external environment Competitors Economic climate Customer preferences E-business Markets Slide 26 Analysis of external environment Analysis of external environment Environment Technology Political issues Legal issues Social issues and trends What other external influences exist? Slide 27 Evaluating market trends Types of information sources Why is it important to understand trends? Which trends and statistics are important? How can you collect this information? Slide 28 Evaluating market trends Types of information sources Colleagues, supervisors and managers Representatives Developing your own industry network Conferences and seminars Product launches Trade magazines Slide 29 Evaluating market trends Types of information sources Industry Publications Newsletters Brochures Advertisements Government bodies Slide 30 Evaluating market trends Types of industry statistics and trends Types of tourism and tourism businesses Types and demographics of customers Top destinations Hotel occupancy percentages Reasons for stays Current industry information Destination countries Departure months Slide 31 Evaluating market trends Types of industry statistics and trends Length of stay Type of organisation for the trip Transport mode Accommodation type Expenditure Popular tourist attractions Tourism patterns Technology Slide 32 Customer demands Impact of customer demands What are common customer demands? What influences customer demand? Slide 33 Seeking advise from experts Before you start your business it is advisable to consult as many organisations and persons that you believe can inform and assist you in your planning. Why is this important? What types of assistance and advice can be sought? What are sources of assistance and advice? Slide 34 Seeking advise from experts Types of assistance and advice Assistance and advice from appropriate experts may be sought for: Collection and collation of facts and information Review or verification of facts Legal or financial advice Ensure compliance of regulations and laws Issuing of permits and licences Strategic planning Specialist skill sets Slide 35 Seeking advise from experts Sources of assistance and advice Local government agencies Tourism associations Non-government organisations Media personnel including journalists Copy writer Professional research organisations Solicitors Slide 36 Seeking advise from experts Sources of assistance and advice Family Existing employees Your existing bank Your accountant Financial adviser Your planning consultant Your architect Your local council Slide 37 Seeking advise from experts Sources of assistance and advice Your potential financier (if not your current bank) Tourism agencies (local/regional/state) Tourism operators Shareholders/business partners Customers Suppliers Neighbours and the local community Slide 38 Analysis of internal environment Once management have had a thorough look at the external environment, the focus must be internally focused The internal environment is the environment within the business Slide 39 Analysis of internal environment Review internal resources and capabilities Location including premises Market share Turnover Profitability Staff Resources Future potential Slide 40 Analysis of internal environment Internal considerations Products and or services Skill level of staff and management Commitment to growth Current market share Level of debt Slide 41 Analysis of internal environment Internal considerations Profit margins Capacity to produce goods and/or services Competition Skills of the owners Location of the business Equipment Slide 42 Analysis of internal environment Organisational requirements Access and equity principles and practices Maintaining ethical standards Meeting goals, objectives, plans, systems and processes Legislated obligations Slide 43 Analysis of internal environment Organisational requirements Management and accountability channels Manufacturer’s and operational specifications OHS policies, procedures and programs Quality assurance and continuous improvement processes and standards Slide 44 Analysis of internal environment Types of resources Resources can encompass: Physical resources Human resources Financial resources Intellectual property Slide 45 Analysis of internal environment Common resources Location/premises Occupational safety and health (OSH) resources Plant/machinery Raw materials – used to produce the products or service Refurbishment requirements Staff amenities Slide 46 Analysis of internal environment Common resources Stock and supplies Storage space Technical equipment and software Staffing Training Training materials Slide 47 Analyse the environments Analyse business opportunities and obstacles How can you do this? Slide 48 Analyse the environments SWOT Analysis Strengths – what the business does well Weaknesses – what the business can improve upon Opportunities – where the business can improve or take advantage Threats – where the business may become disadvantaged, weakened or susceptible Slide 49 SWOT Analysis Strengths and Weaknesses Finance Production Resources Offerings Marketing Product life cycle Business relationships Relationships with customers Personnel Slide 50 SWOT Analysis Opportunities and threats Political considerations Economic considerations Social considerations Technological considerations Legal considerations Environmental considerations Slide 51 SWOT Analysis Opportunities New markets New, up-dated or modified products or services Occasions where new/higher prices may be charged Problems being experienced by other providers which result in an opening for you Closure of an opposition business Fresh markets now available Slide 52 SWOT Analysis Threats Introduction of new or more severe legislation Opening of a new competitor Worsening economic conditions Staff shortages Difficulty in obtaining physical resources An unsettled domestic situation which scares off tourists Negative comparative monetary exchange rates with countries who are major clients Slide 53 Review current and emerging competitors Importance of understanding competitive advantage Why is this important? How can you see what competitors are doing? How can you create a competitive advantage? Slide 54 Review current and emerging competitors Review and analyse current and emerging competitors Areas of review may relate to: Volume Price Territory Customer accounts Trading terms Market share Customer satisfaction Slide 55 Current market situation Market situation Total market characteristics - size, growth, trends Customer needs, perceptions and buying behaviour Products - service characteristics Prices Customer service and distribution Channels Communication Slide 56 Current market situation Competitive situation Industry structure The geographic market in which they compete Their current marketing performance Their competitive position Strengths and weaknesses, and vulnerabilities of each significant competitor Their objectives and competitive strategies Industry profitability Slide 57 Current market situation Product situation For each product/service that the organisation offers, sales, profits, contribution margins and growth should be displayed Product lifecycle and expected demand over the product’s life should be considered Growth of the product/service should be contrasted to total market growth Slide 58 Joint ventures and strategic alliances Explore the potential for joint ventures and strategic alliances. It may be that there is an opportunity for your business to form a joint venture or strategic alliance with another organisation Slide 59 Element 2: Formulate business plans and strategies Slide 60 Formulate business plans and strategies Performance Criteria for this Element are: Create or confirm enterprise mission, vision and purpose as the starting point for the business plan in consultation with stakeholders Establish realistic, clearly stated and measurable objectives for the business Develop appropriate strategies and tactics to address objectives across all areas of business operation Identify and include opportunities for strategic business alliances Slide 61 Formulate business plans and strategies Performance Criteria for this Element are: Develop all aspects of the business plan to ensure the business meets relevant legal, social, environmental and ethical obligations Include appropriate action plans and evaluation processes, including key performance indicators Consult with appropriate staff, management and other stakeholders to encourage support for the planning process so that all perspectives are taken into account in the development of the plan Slide 62 Formulate business plan Focus of business plans The business plan may be for: A new or existing small business venture A division or department of a large organisation A new product development initiative Slide 63 Formulate business plan Contents of a business plan What needs to be included in a Business Plan? Slide 64 Executive Summary Business Profile Your Products and/or Services The Market The Business Potential Mission, Goals and Objectives Strategies Business Structure Finance Conclusion Slide 65 Business Profile Business Name Business Location/s Business Activity/Activities Business Objectives Business History/Entry Strategy Ownership Structure Legal Requirements Slide 66 Market Report Industry Profile Review of Existing Operation (if appropriate) Your Product and/Service Competition Environmental Information and Trends Slide 67 Marketing Plan Market Segmentation Your Customers Target Markets Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats Analysis Key Issues Slide 68 The Marketing Plan Sales and Marketing Goals and Objectives Value Proposition (Competitive Advantages) Marketing Strategies Pricing Promotion Sales and Distribution Slide 69 Operational Plan Premises, Plant and Equipment Floor plan Production Purchasing List of Suppliers Stock levels Purchasing Policies and Controls Purchasing Controls Break-even Analysis Slide 70 Finance Plan Current Financial Position Capital Requirements and Funding Proposal Financial Budgets Cash-flow Projection Projected Statement of Financial Performance (Profit and Loss) Slide 71 Finance Plan Projected Statement of Financial Position (Balance Sheet) Financial Ratios Financial Controls Business Insurances Slide 72 Risk Plan Risk Identification and Mitigation What are different types of risks? What needs to be considered? What are the steps to reduce risks? Slide 73 Structure and Management Plan Organisational Chart and Structure Key Personnel Labour Requirements and Skills Staffing Strategies Professional Advisers Staffing Controls Slide 74 Strategic alliances Identifying possible strategic alliances Your industry association can provide substantial information, and through trade shows and networking you will meet other similar or allied businesses that lead to new and expanded operations. How are suitable alliances in the tourism industry? What makes successful alliances? Slide 75 Meet legal requirements Requirements and Obligations Registration of Business Name Business Licenses Taxation Registration Industrial Awards Medical Insurance Intellectual Property Registration Other insurances Pollution/environmental controls Slide 76 Action Plans One of the key requirements of any business plan is to outline how the goals, objectives and strategies will be accomplished. What actions need to be done To what standard must it be done What policies or procedures must be adhered to Who is responsible for action What tasks are associated with actions Timelines for actions Support mechanisms Slide 77 Action Plans Areas requiring action plans Areas of business operation in the business plan should have action plans include: Business establishment Operations Marketing Technology Human resources/labour requirements Management and organisational structure Financial plan and projections Quality management Slide 78 Monitoring and evaluation Monitoring and evaluation mechanisms Evaluation processes may include: Key performance indicators Gap analysis Customer feedback Compliance reports Employee feedback Slide 79 Monitoring and evaluation Key Performance Indicators (KPI’s) Total number of customers Total number of customers per department or market segment Average dollar spent Total revenue per capita Sales per product group Average sales per day’s trading Slide 80 Monitoring and evaluation Key Performance Indicators (KPI’s) Average total revenue per client Marketing expense per customer Marketing expense and sales revenue per customer from a specific campaign Total revenue / full time employee Gross profit margin Slide 81 Appendices What documents go into the appendices? Slide 82 Consult with stakeholders Importance of stakeholders What are examples of stakeholders? Why involve them? Slide 83 Element 3: Implement the business plan Slide 84 Implement the business plan Performance Criteria for this Element are: Communicate the business objectives and content of plans in a timely manner to facilitate a clear understanding of the plan and associated activities and individual responsibilities Use appropriate leadership techniques to encourage team commitment to the business plan Encourage staff to provide ongoing input into the business plan Implement and organise actions detailed in the plan in a cost-efficient manner and in accordance with schedule and contingencies Slide 85 Communicate business plan Present final business plan to relevant stakeholders accurately Once business plans, including objectives have been finalised, it is now time to present the final version to relevant stakeholders Slide 86 Communicate business plan Stakeholder considerations Get a clear understanding of the business plan Ensure that all key concerns have been considered Understand the benefits of the business plan Understand how the business plan will benefit them Understand how the business plan will impact on them Slide 87 Communicate business plan Stakeholder considerations Understand their role in implementing the business plan Any potential problems identified Have their concerns addressed Be excited and reassured about the business plan Slide 88 Communicate business plan Types of stakeholders Clients Business partners Colleagues Staff Event organisers Sponsors from other companies Superiors Suppliers / vendors Team leaders Team members Venue operator / leaser Slide 89 Communicate business plan Communicate business plan information Key vision of the plan Reasoning or purpose behind the business plan Background information Business objectives How the plan will be implemented Roles and responsibilities of key stakeholders Timelines Support mechanisms Slide 90 Communicate business plan Communicate information How can you communicate information to: Staff Managers Clients Suppliers Slide 91 Use leadership techniques Leadership styles The role of leadership is vital in ensuring that new business plans and the implementation actions associated with them are: Understood by staff Staff are motivated and committed to its success What types of leadership styles are there? Slide 92 Leadership styles Autocratic and democratic leaders An autocratic leader is one who centralises authority and relies only on legitimate reward and coercive power A democratic leader delegates authority to others, encourages participation and relies on expert and referent power to influence others Slide 93 Leadership styles Charismatic leadership theory The key characteristics of charismatic leaders are: Self confidence Vision Ability to articulate that vision Strong convictions about the vision Behaviour that is out of the ordinary Appearance as a change agent Environment sensitivity Slide 94 Leadership styles Transactional versus transformational leadership Transactional leaders are leaders who guide or motivate their followers in the direction of already set goals by making them clear and explaining task requirements Transformational leaders are leaders who inspire people beyond their own goals through individual consideration and charisma. They are capable of having a profound and extraordinary effect on their followers Slide 95 Leadership styles Additional leadership techniques Have clear goals Develop mutual trust Encourage good communication Provide internal and external support Slide 96 Encourage staff to input into plans Encourage staff to provide ongoing input into the business plan How can a manager do this? Slide 97 Encourage staff to input into plans Methods to encourage staff input Asking for ideas Having an ‘open door’ policy regarding suggestions Sharing ideas Being prepared to test new ideas Seeking information and ideas from non-traditional places Slide 98 Encourage staff to input into plans Methods to encourage staff input Thanking people for their contributions Taking the time and effort to explain to someone who contributed an idea why their idea was not implemented Ensuring the person responsible for suggesting an effective new approach receives the credit for doing so Slide 99 Implement action Implement business plan actions Now that business plans have been communicated with stakeholders responsible for its delivery, it is now time to implement any actions Slide 100 Implement action Implementation considerations Compliance requirements Occupational safety and health (OSH) Legal liability exposure Integration with other aspects of the business Timing issues Slide 101 Implement action Implementation considerations Resources Changes to policies and procedures Documentation and record keeping Service delivery Impact on organisational culture Slide 102 Implement action Implementation planning inclusions Details of intended actions to be taken Allocation of responsibilities for action to nominated persons Determination of accountability for actions taken Timelines for completion of nominated actions Details of the budget and resources allocated Description of monitoring progress Details and timelines for reviewing progress Slide 103 Implement action Defining and assigning roles It is important that everyone knows what is expected of them. What do staff need to know? How can they understand their roles and responsibilities? Slide 104 Implement action Identify predictable consequences of change Disruptions to routine Problems with timelines Issues with reporting structure Extra support required by employees Slide 105 Implement action Provide support and resources to support implementation actions The aim is to enable staff to be able to learn and implement new changes into the workplace. During this period, you must manage the twin functions of: Task functions Maintenance functions Slide 106 Element 4: Monitor the business plan Slide 107 Monitor the business plan Performance Criteria for this Element are: Review the business plan regularly and adjust in the light of changing circumstances Monitor activities detailed in the plan on an ongoing basis Identify and analyse successes and performance gaps on an ongoing basis Implement agreed changes to plans promptly Report performance in a transparent manner to all stakeholders Slide 108 Reviewing business plans Timing of business plan reviews They may be based on: Quarterly reviews Business plan cycle Performance reports Major events triggering a review Slide 109 Monitor activities In order for an organisation to be successful in being able to provide the highest quality of service whilst still making an adequate financial return for investors, it is vital that every aspect of the operation is operating to the best of its ability Therefore management must constantly assess and evaluate the performance of all areas that contribute to the functioning of the business Slide 110 Monitor activities In order to do this, activities must be assessed and evaluated to find out: What is being done correctly What needs improvement by: Identifying problems Understanding causes Providing and implementing a suitable remedy Slide 111 Monitoring and evaluation methods Reports Obtaining customer feedback Using a pretend customer Walking around and observing Use of checklists Brainstorming sessions Staff input and review Slide 112 Monitoring and evaluation methods Observation Statistical and written reports Surveys Checklists Flowcharts Benchmarking Slide 113 Identify performance gaps Compare what is happening against benchmarks Comparing actual performance against key performance indicators and/or service standards set Comparing actual performance against benchmark indicators, which can include industry indicators or performance levels of other branches Slide 114 Comparison against KPI’s Organisation’s key performance indicators Organisation’s key performance indicators are a set of metrics which organisations can use to measure the success of business plan actions. What are examples of KPI’s? Slide 115 Comparison against KPI’s Types of key performance indicators Market share Sales figures Customer satisfaction Growth Profitability Turnaround times Output rates Slide 116 Comparison against KPI’s Types of key performance indicators Quality rates Customer feedback Equipment usage rates Lead times and down times Compliments-complaints ratio Customer Satisfaction Index (CSI) Slide 117 Identify performance gaps Types of performance gaps Product or service failures Long wait times for service High volume of customer traffic Inaccurate or conflicting information provided to customers Lack of follow-up action by customer care representatives Slide 118 Identify performance gaps Types of performance gaps Aggressive cross-selling or up-selling by customer service representatives or sales persons Lack of resources required to implement service operations Conflicts in priorities Resource constraints Lack of information Supplier delays Differences in opinion Slide 119 Identify performance gaps Types of performance gaps Interpersonal conflict Hazardous events Time constraints Electricity shortages Bad weather Shortfalls in expected outcomes Poor staff performance Slide 120 Implement agreed changes Managers need to identify gaps and issues quickly and take appropriate action swiftly. Failure to identify these can lead to: Lack of repeat business Damage to the reputation of the venue General decline in sales and profit Slide 121 Corrective action Types of corrective actions Quite simply, types of corrective actions taken to improve service operations may include: Improvements in the design of products or services Reviewing the allocation of resources for service operations Tweaking standard operating procedures to improve efficiency Slide 122 Initiate corrective action Take appropriate corrective action This involves making the necessary adjustments to improve the level of service, productivity or customer satisfaction Depending on what is being monitored, involving staff in all or some stages of the monitoring process is likely to achieve better results Slide 123 Initiate corrective action Short and long term corrective action Corrective actions taken within an operation workplace context can be seen as either: Short term corrective action Long term corrective action Slide 124 Taking corrective action Short term corrective action It is sometimes necessary to take short term action to solve a problem until it can be looked at more closely and the problem dealt with more thoroughly. Slide 125 Short term corrective action Reasons for short-term action Isn’t time to stop and analyse the problem more carefully and in more detail To provide the necessary or expected services to the customer To meet OHS requirements To deal with a complaint To get staff working together again To give you time to analyse and work through the problem at a later date Slide 126 Short term corrective action Considerations for short-term action Make a definite time to look at it more thoroughly later on Decide who to involve in further problem solving Inform staff and management it is a short term solution Cost the implications of tackling the problem this way Slide 127 Long term corrective action Management changes New management Change in orientation to service Setting of some new directions in relation to several other factors New management focus Slide 128 Long term corrective action Organisational re-structures Change of personnel structure Elimination of positions New job roles Changes in job roles New knowledge or skills Slide 129 Long term corrective action Introduction of new equipment New equipment means: Possible interruptions to operations for installation Training for staff Requires that staff can explain the new equipment to customers Changes in job roles Changes in procedures Changes to workflow Slide 130 Long term corrective action Recruitment practices Need to establish comprehensive job descriptions and job specifications Seeking of new knowledge and skills Change advertising strategy Revised interviewing and selection process Revised selection criteria Slide 131 Report performance Report performance in a transparent manner Periodically, there will be a need for you to provide your team and management with feedback in regard to achievement or non-achievement of business plan initiatives Slide 132 Report performance Methods to sharing performance related information Holding team meetings Providing hard copy information Sharing information via the intranet Disseminating information at staff briefings Slide 133 Report performance Explaining performance related information Explaining if your business plan strategy and effort work Identifying the reasons why they work or not work. Significant variations and the factors associated with the changes. Unusual results and determine their causes Slide 134 Report performance Explaining performance related information Patterns and trends in consumer behaviours, and the factors that resulted in those behaviours Strengths and marketing opportunities Weaknesses and potential areas of improvement Impact / implications of the results and conclusions on performance Slide 135 Report performance Present recommendations for variation to business or operational plans What are possible reasons for recommendations? What information needs to be included in a recommendation What are types of recommendations? Slide 136