Pedigrees - Ms Kim's Biology Class

Pedigrees and Sex-Linked
Traits
H. Biology
Ms. Kim
Many human traits follow Mendelian patterns of inheritance
• Humans are not convenient subjects for genetic research
– However,
– We use pedigrees
!
The Study of Human Genetics Continues to
Advance…
• Can’t use humans
• We use pedigrees
– A family tree that describes the interrelationships of parents and children across generations
– Can also be used to make genetic predictions about future offspring
Pedigrees
• A pedigree is a family tree that traces specific traits across many generations
• Pedigrees help us determine whether alleles are recessive or dominant
How do you create a pedigree?
Collect information about a family’s history
Organize the information in a family tree
Apply Mendel’s concepts and principles
3
Inheritance patterns of particular traits can be traced and described using pedigrees
First generation
(grandparents)
Ww ww ww Ww Ff Ff ff Ff
Ww ww ww Ww Ww ww
Second generation
(parents plus aunts and uncles)
FF or Ff Ff ff Ff Ff ff
WW or
Ww ww
Third generation
(two sisters) ff
FF or
Ff
Widow’s peak
Figure 14.14 A, B
(a) Dominant trait (widow’s peak)
No Widow’s peak Attached earlobe Free earlobe
(b) Recessive trait (attached earlobe)
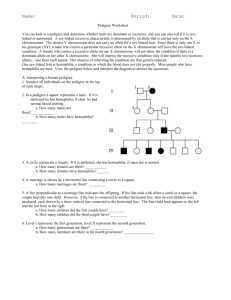
Pedigree Basics
• BASIC SYMBOLS:
Males = Square
Females = Circle
Horizontal Line =
Mating
Pedigree Basics
• BASIC SYMBOLS:
Offspring are drawn below the parents
What gender are the offspring pictured here?
Note: Adopted children have a dotted line…
+
OTHER SYMBOLS
ADOPTION DIVORCE
DEATH TWINS
Pedigree Basics
• By coloring in the shapes you are…
– …indicating an expressed trait/phenotype
Pedigree Basics
• By using Mendel’s concepts and principles:
– Can determine if a trait is:
• Dominant or Recessive
• Sex-linked or Autosomal
– Can determine genotypes
USUALLY IN IN SEX-LINKED
Homozygous Homozygous Heterozygous
What would a dominant trait look like in a pedigree?
• It will usually show up in every generation:
What would a recessive trait look like in a pedigree?
WHY?
• It will usually not be in every generation:
Practice
?
?
?
?
?
What genotype MUST II-4 and II-5 have?
What about III-4 and III-10 ???
BOTH must be Ff
III-4 MUST be Ff
III-10 could be FF or Ff
12
How is Sex Determined?
• Male can give either an
X or a Y
MALE
X Y
XX
X Y
• Females can only give an X
WHAT IS THE
PROBABILITY OF
HAVING A MALE OR
A FEMALE
OFFSPRING?
XX X Y
Sex Determination
What is a sex-linked gene?
• Sex- Linked Gene:
– Any gene that resides on a sex chromosome
– X-linked - gene resides on X chromosome
– Y- linked – gene resides on Y chromosome
In humans:
- Most sex-linked genes are on the X chromosome
- Since, typically the X chromosome is longer, it bears a lot of genes not found on the Y chromosome
(Usually on X chromosome called x-linked)
What is a sex-linked gene?
•
• The "a" recessive allele will be The "a" recessive allele will not expressed in his phenotype be expressed in her phenotype
What is a sex-linked gene? (Y-LINKED)
• Genes on the Y chromosome can only be passed to sons. NOT to daughters.
FEMALE
X X
XX XX
X Y a XY a
What is a sex-linked gene? (X-LINKED)
Genes on the X chromosome can be passed to either sons or daughters.
• Females can be homozygous or heterozygous.
• Males are hemizygous.
What is the probability of having a son with recessive phenotype? Daughter?
X A
FEMALE
X a
X A Y
X A X A
X a Y
X A X a
• What will the phenotypes be for the following fruit flies?
– X R X R
– X r X r
– X R X r
– X R Y
– X r Y
R=Red eyes r=white eyes
• White eyes (recessive) are very rare compared to red (dominant) eyes in fruit flies
• Eye color is located on the X chromosome
• Cross a red eyed female (X R X R ) with a white eyed male (X r Y)
• Now, cross a female and male from the possible offspring produced in earlier cross.
• If certain recessive disorders, such as color blindness and hemophilia, are sex-linked on the X chromosome, are they more common in males or females? Explain
SEX-LINKED TRAITS
Why are males more often affected by hemophilia?
• Men only have one copy of the X chromosome.
• If a male inherits a mutated gene on the X chromosome, the trait is expressed.
• Females have two copies of the X chromosomes, so the mutated gene may be masked by a normal gene copy.
• Red-green colorblindness is caused by lightsensitive cells (cones) in the eyes that aren’t working properly
– Individuals who are affected can’t distinguish reds from greens
• The two genes that produce red and green light-sensitive proteins are located on the X chromosome. Mutations in these genes can cause color blindness.
• Color blindness is a common inherited sex-linked disorder that affects a person's ability to see or recognize certain colors.
• Eight to ten percent of all males and one half of a percent of all females are color-blind.
What are Sex-linked Disorders?
• Usually inherited as sex-linked recessive traits.
– Males need only to inherit one recessive allele to have disorder ( X a Y )
– Females must inherit two recessive alleles to have disorder ( 1 from mother, 1 from father) (X a X a )
Pedigree for Colorblindness in a family
X
What genotype is our 2 nd generation female “?”
B
X B
X B X B
X
X B
?
X ?
Y X B Y X ?
Y
She MUST be X B X B
Otherwise, her son would be colorblind!
29
How will I know if a trait is sex-linked?
• Y- linked:
– Only males will express trait
• X-linked:
– Females and males will express trait
– There will be a bias for males to express trait
– WHY?
Males are more likely to have sex-linked disorders, b/c they only need one affected X chromosome (XY)!
What would an X-linked trait look like in a pedigree?
Example of Pedigree Charts
• Is it Autosomal or X-linked?
Recessively Inherited Disorders
• Many genetic disorders are inherited in a recessive manner
– Need 2 recessive alleles (ex: ff)
• Some people can be carriers
– heterozygous individuals, who carry recessive allele but are show “normal” phenotype
– Ff carry the cf gene (“f”) but don’t have the disorder b/c you have to be ff (recessive)
Mating of Close Relatives
• Matings between relatives
– Can increase the probability of the appearance of a genetic disease
– Are called consanguineous matings
– Increases changes of inheriting mutated alleles (ex: lethal mutations)
What is a genetics counselor?
• Creates pedigrees
• Analyzes information for parents
– Can tell parents the risk of passing disorders/diseases to offspring