Chapter 14 Objectives final

AP Biology 14-15
Chapter 14 Objectives
1.
Describe how to interpret a pedigree.
2.
Describe sex determination in humans.
3.
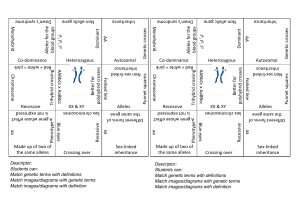
Describe the characteristics of autosomal-dominant and autosomal-recessive inheritance patterns and give examples of disorders for each.
4.
Describe characteristics of X-linked dominant and X-linked recessive inheritance patterns and give examples of disorders for each.
5.
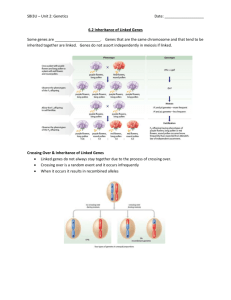
Describe the inheritance of a sex-linked gene such as color blindness
6.
Explain why a recessive sex-linked gene is always expressed in human males
7.
Explain how an organism compensates for the fact that some individuals have a double dosage of sex-linked genes while others have only one (X-inactivation –chapter 10)
8.
Distinguish among nondisjunction, aneuploiody, and polypolidy; explain how these major chromosomal changes occur; and describe the consequences of their occurrence
9.
Distinguish between trisomy and triploidy
10.
Name and explain some ordinary and extraordinary chromosomal events that can create new phenotypes (outward appearances).
11.
Explain how changes in chromosome structure and number can affect the outward appearance of organisms.
12.
Compare and contrast duplication, deletion, inversion, and translocation.
13.
Outline the variety of genetic screening options that are available.