Structure and Function of the Central Nervous System
advertisement

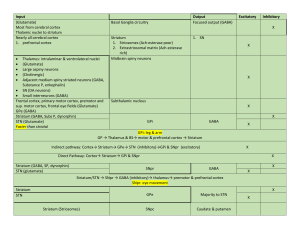
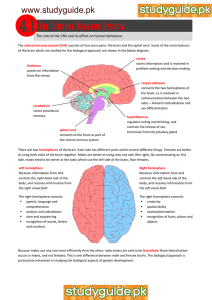
Psychopharmacology Complex 1.4 kg in weight Pre frontal cortex 2% of body weight 20% of oxygen 15% of our cardiac input 10% of all energy Brain protection system The BBB is both; A physical barrier that restricts the entrance of potentially harmful substances A system of cellular transport mechanisms that controls the entrance of essential nutrients Cerebrum and Cerebral cortex Left and Right Hemispheres Left Hemisphere- dominant hemisphere Production of language Mathematical ability Problem solving •Right Hemisphere - Creativity - Spatial ability Located at the front of both cerebral hemispheres Primary motor cortex Pre motor cortex Broca’s Area Complex Functioning – personality, judgement, insight, reasoning, problem solving, abstract thinking and working memory Located behind frontal lobe Somatosensory cortex Spatial orientation, perception and comprehension of language function recognising objects by touch Links visual and somatosensory information together Neglect Located et each side of the brain Involved in receiving and processing auditory information, higher order visual information , complex aspects of memory and language Wernicke’s area Visual processing area Corpus Callosum • Thalamus • Filter for sensory information • Control of mood states • Body movement • Hypothalamus • Central control • Regulate autonomic, emotional, endocrine and somatic function • Stress Cerebellum Equilibrium Muscle tone Postural control Coordination of muscle movement Pons Relay station • Medulla Oblongata Skeletal muscles Balance Coordination Inner ear sound impulses • Heart rate, vomiting, sneezing • • • • • Reticular formation • Arousal • Circadian rhythm • respiration Basal ganglia Muslce tone Posture Movement Substantia Nigra Amygdala Mood Hippocampus Memory The structural unit of the brain Cell body Axon Dendrites Synapse • The Information that flows in the neurone • Approximately 10 billion neurons are responsible for receiving, organising and transmitting information in the central nervous system • Ions in the intracellular fluid (inside the cell) have a negative charge • Ions in extracellular fluid (outside the cell) have a positive charge attracting positively charged cells (cations) ‘Potential difference’ between the inside and the outside of the cell • • Ions are sodium, potassium, calcium and chloride ‘voltage gated’ Resting Potential vs. Action potential The flow of neurotransmitter across the synapse Neurotransmitter; Made in the pre synaptic neurone Stored inactively in synaptic vesicles Released from the synaptic vesicles into the synapse Binds to receptors Binds to reuptake transporters to be taken back into the neurone Is degraded by specific enzymes Acetylcholine (ACh) Norepinephrine (NE)( also known as noradrenaline) Dopamine(D) Serotonin (5HT) Glutamate Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) There are two kinds of neurotransmitters – INHIBITORY and EXCITATORY. stimulate the brain calm the brain • Cholinergic pathways • thought to be involved in cognition (esp. memory) and our sleep/wake cycle • parasympathetic nervous system regulating bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, secretion of saliva and bladder function • Alzheimer’s disease and myathesia gravis (weakness of skeletal muscles) • Anti-cholinergic effects • attention, alertness and arousal • NE levels fluctuate with sleep and wakefulness and changes in attention and vigilance • mood, affective states and anxiety • antidepressant • complex movement and cognition • Emotional responses such as euphoria or pleasure (seen in amphetamine/cocaine use). •Significant role in motor control •EPSE’s • Great influences on behaviour. • Low serotonin activity is associated with aggression, suicide, impulsive eating and disinhibited sexual behaviour • modulating general activity levels of the CNS, particularly the onset of sleep • depression and anxiety disorders • delusions, hallucinations (LSD) • negative symptoms of schizophrenia Glutamate is found in all cells of the body control the opening of ion channels that allow calcium to pass into nerve cells producing impulses Blocking of glutamate receptors produces ( eg. By PCP) schizophrenic like symptoms Over exposure of neurons to glutamate cause cell death seen in stroke and Huntington’s disease (PN). Inhibitory and its pathways are only found within the CNS. control excitatory neurotransmitters in the brain and controlling spinal and cerebral reflexes. anxiety disorders decreased GABA can lead to seizure activity Benzodiazepines and barbiturates sedative medication act on GABA