Jeopardy--Campaigns & Elections
advertisement
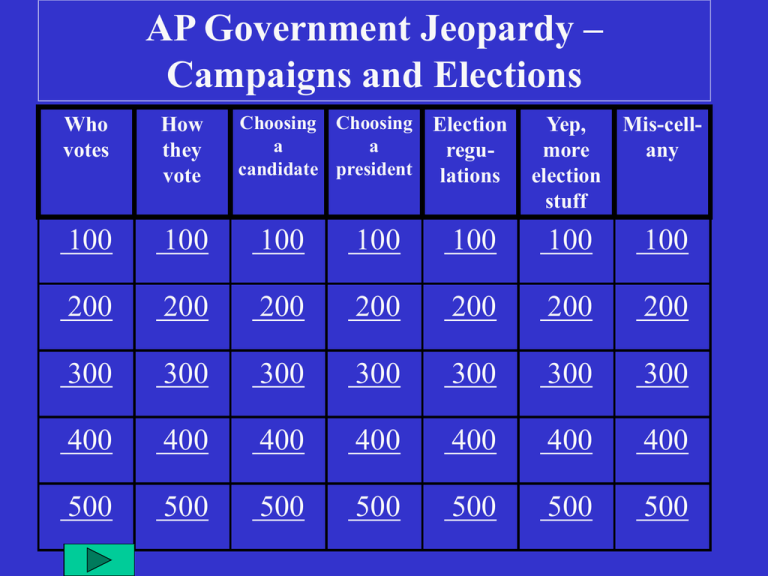
AP Government Jeopardy – Campaigns and Elections Choosing Choosing a a candidate president Who votes How they vote Election regulations Yep, Mis-cellmore any election stuff 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 Final Jeopardy! Question Campaigns and Elections Suffrage Suffrage The right to vote, a fundamental principle of democratic government Who votes 100 Fifteenth Amendment (1870) Guarantees right to vote to all races Who votes 200 Nineteenth Amendment (1920) Extended the right to vote to women Who votes 300 Twenty-Sixth Amendment (1971) Lowered age requirement to vote to 18 in all states Who votes 400 Electorate Term used to describe the voters of a nation, state, city, or county collectively Who votes 500 Split-ticket voting Voting for candidates of different parties for different offices How they vote 100 Issue voters Voting based on positions on specific policies How they vote 200 Referendum Proposed law or state amendment referred by the state legislature to the people for a vote; only at the state level, and only in some states How they vote 300 Initiative Proposed state law or amendment brought by the citizens through a petition process; only at the state level, and only in some states How they vote 400 Recall election Special election initiated by a petition that allows citizens to remove an official before his/her term has expired; only in some states How they vote 500 Caucuses Local party meetings to select delegates to state convention, which then selects delegates to party’s national convention Choosing a candidate 100 Open primary Election in which voters choose which party’s primary ballot they wish to vote on Choosing a candidate 200 Closed primary Election in which only voters registered in the party may vote in the party’s primary Choosing a candidate 300 Blanket primary Election in which only one primary ballot is used and voters may choose from candidates of either party and split votes between them; ONLY used in Louisiana, Washington, and California Choosing a candidate 400 Superdelegates Democratic Party leaders who are able to cast votes at the national convention for the party’s presidential candidate Choosing a candidate 500 General election Election in which officeholders (not nominees) are selected; for federal offices, these are held the first Tuesday after the first Monday of November in evennumbered years Choosing a president 100 Swing states States without strong party alignment, that could vote either Democratic or Republican in the general election; candidates devote much of their time campaigning in these states Choosing a president 200 Electoral College 538 member body that elects the president and vice president; in most states, these individuals pledge to vote according to the results of the popular vote Choosing a president 300 Winner-take-all system All of a state’s electors voting as a block for the winner of the state’s popular vote; many believe this makes the electoral college nonreflective of the will of the electorate Choosing a president 400 Coattail effect When the popularity of the victorious presidential candidate helps his party’s candidates for Congress win as well Choosing a president 500 Motor Voter Law National Voter Registration Act of 1993 requires that states pass these laws allowing voters to register when they renew their driver’s licenses or apply for social services Election regulation 100 Federal Election Commission Independent regulatory agency founded in 1975 to enforce federal campaign finance laws and administer public financing of presidential campaigns Election regulation 200 Buckley v. Valeo (1976) Supreme Court ruled that Federal Election Campaign act campaign spending limits violated First Amendment guarantees of freedom of expression Election regulation 300 Soft money Money donated to a political party rather than a candidate to avoid limits imposed by campaign finance reform laws, a loophole closed by the Bipartisan Campaign Finance Reform Act (2002) Election regulation 400 527 Political Organizations Nonprofit organizations that engage in issue advocacy, not candidate advocacy – a fine line often blurred; not subject to campaign finance limitations Election regulation 500 Literacy test A reading test citizens were required to pass in order to vote; widely used in the South to discourage blacks and poor whites from voting Banned by the Voting Rights Act of 1965 Yep, more election stuff 100 Poll tax A tax levied on voters; widely used in the South to discourage blacks and poor whites from voting Banned by the 24th Amendment (1964) Yep, more election stuff 200 Plurality election When the leading candidate receives the greatest number of votes, but not more than 50% (a true majority) Yep, more election stuff 300 Midterm election Federal election held in the middle of a president’s term of office; all House seats and 1/3 of Senate seats are elected; the President’s party generally loses seats in Congress Yep, more election stuff 400 House of Representatives Governmental body responsible for choosing the President when no candidate wins a majority of votes in the Electoral College Yep, more election stuff 500 Voter apathy A reason for low turnout in U.S. elections; generally defined as a lack of interest in politics, but may also result from a mistrust in government or lack of political efficacy; generally, younger people, racial and ethnic minorities, males, and lower income individuals have the greatest Mis-cell-any issues with this 100 Political Efficacy The belief that a person can influence politics and public policymaking Mis-cell-any 200 National convention Before the primary system, this meeting served the purpose of choosing the party’s nominee for president; in recent years, its fundamental purpose is the adoption of the party platform Mis-cell-any 300 Front-loading Choosing an early date to hold the primary election in a state Mis-cell-any 400 Party identification The most important single factor in determining how someone will vote in an election Mis-cell-any 500 • Compare the extension of suffrage in the pre-Civil War period to the postCivil War period FINAL JEOPARDY • Pre-Civil War extensions were aimed at eliminating barriers to universal white male suffrage, including property ownership and payment of taxes • Post-Civil War extensions eliminated restrictions based on race (15th Amendment), gender (19th Amendment), and age (26th Amendment) FINAL JEOPARDY