The Theory of production
advertisement

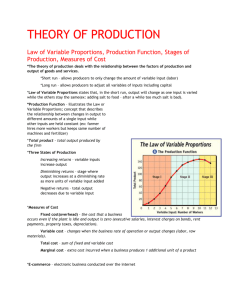
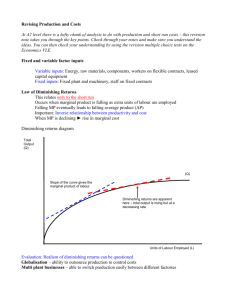
THE THEORY OF PRODUCTION Chapter 5 Section 2 The Theory of Production • What are the four Factors of Production? 1. Land 2. Labor 3. Capital 4. Entrepreneurship • The Theory of Production = the relationship between the factors of production (inputs) and the output of goods and services. It examines how output changes when inputs change. The Theory of Production Con’t • The short run = short period of time during which producers can change variable (change-able) inputs. Most often, LABOR is the input producers change in the short run. • The long run = longer period of time, where producers can adjust all inputs, like land, capital and labor. Law of Variable Proportions • The law of variable proportions states that in the short run, output (what you make) will change as one input (like labor) is varied while the others are held constant. • In our lemonade example water stayed the same and we change the input of lemonade powder. The book discusses the addition of chili powder to chili. • How can the input of one resource change the final product? The Production Function • Production Schedule / Function = Graphs or charts which illustrates INPUT and OUTPUT, see p112, Figures 5.4 • Total Product = The total amount of goods or services produced by the business (Examples: Number of donuts made by Donut Connection) • Marginal Product = The extra output generated by adding one more unit of variable input. • Example: the number of additional haircuts performed by adding one more stylist Three Stages of Production • Stage I – Increasing Returns = Adding one more input increases production and increases the total output. In this stage, marginal product is increasing. • Stage II – Diminishing Returns = Adding one more input still continues to make output greater, but the increase becomes smaller and smaller, so the benefit is not as much as in Stage 1. • Stage III – Negative returns = Adding one more input makes marginal product decrease; there is no added benefit . Workers (Input) Total Product (Output) Marginal Product (what you get for each additional worker) Stage of Production 3 75 4 112 112 – 75 = 37 5 150 150 – 112 = 38 6 180 180 – 150 = 30 Stage II 7 203 203 – 180 = 23 Diminishing Returns 8 216 216 – 203 = 13 9 207 207 – 217 = -9 Stage III 10 190 190 – 207 = -17 Negative Returns Stage 1 Increasing Returns