The theory of production deals with the relationship
advertisement
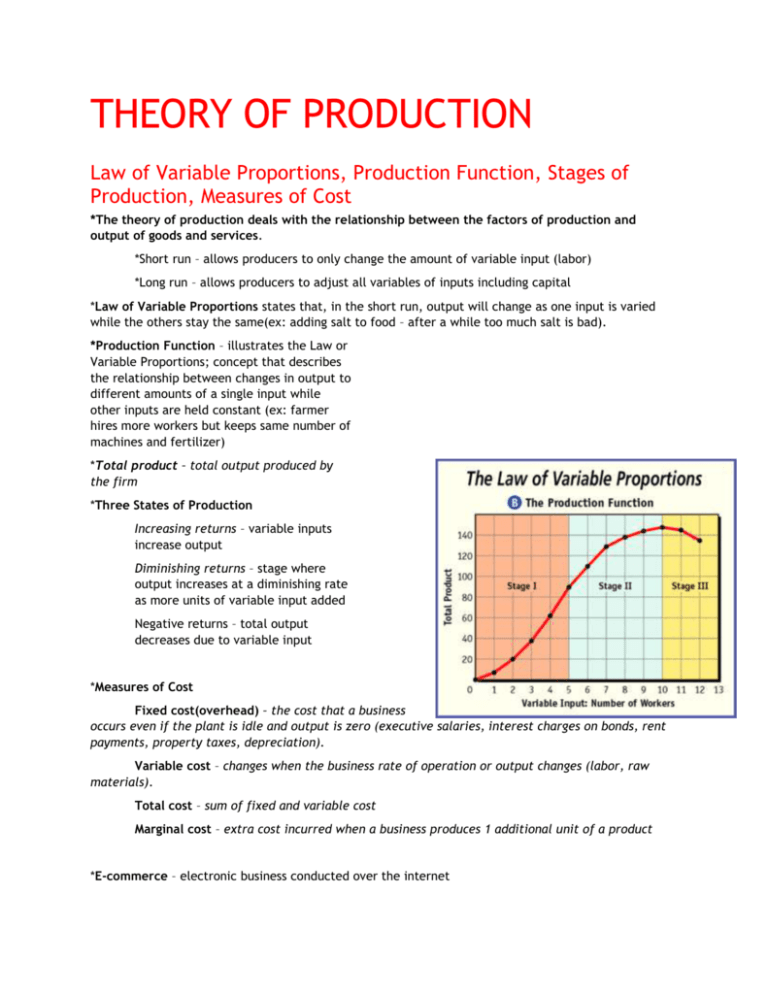
THEORY OF PRODUCTION Law of Variable Proportions, Production Function, Stages of Production, Measures of Cost *The theory of production deals with the relationship between the factors of production and output of goods and services. *Short run – allows producers to only change the amount of variable input (labor) *Long run – allows producers to adjust all variables of inputs including capital *Law of Variable Proportions states that, in the short run, output will change as one input is varied while the others stay the same(ex: adding salt to food – after a while too much salt is bad). *Production Function – illustrates the Law or Variable Proportions; concept that describes the relationship between changes in output to different amounts of a single input while other inputs are held constant (ex: farmer hires more workers but keeps same number of machines and fertilizer) *Total product – total output produced by the firm *Three States of Production Increasing returns – variable inputs increase output Diminishing returns – stage where output increases at a diminishing rate as more units of variable input added Negative returns – total output decreases due to variable input *Measures of Cost Fixed cost(overhead) – the cost that a business occurs even if the plant is idle and output is zero (executive salaries, interest charges on bonds, rent payments, property taxes, depreciation). Variable cost – changes when the business rate of operation or output changes (labor, raw materials). Total cost – sum of fixed and variable cost Marginal cost – extra cost incurred when a business produces 1 additional unit of a product *E-commerce – electronic business conducted over the internet