Honors econ chapter 5
advertisement

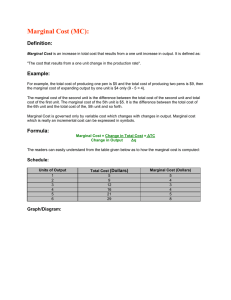
Chapter 5 Supply Chapter 5 Section 1: What is Supply Main Idea: For almost any good or service, the higher the price, the larger the quantity that will be offered for sale. Supply Law of Supply Supply schedule Supply curve Market supply curve Quantity supplied Change in quantity supplied Change in supply Subsidy Supply elasticity Vocabulary What is the difference between a supply schedule and a supply curve? How are market supply curves obtained? What factors cause change in supply? ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ A B C D E F G Notes Study the graphs in figures 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 Answer the questions (in complete sentences) that appear in yellow at the bottom of each figure box. Assignment to turn in Ch 5 section 2: The Theory of Production Main Idea: A change in the variable input called labor results in a change in production Theory of production Short run Long run Law of variable proportions production function raw materials total product marginal product stages of production diminishing returns vocabulary What relationship is the theory of production based on? How does marginal product change in each of the 3 stages of production What will happen if companies continue to hire workers? Notes Figure 5.5 Activity to turn in Ch 5 section 3: Cost, Revenue, and Profit Maximization Main Idea: Profit is maximized when the marginal costs of production equal the marginal revenue from sales. Fixed cost Overhead Variable cost Total cost Marginal cost E-commerce Total revenue Marginal revenue Marginal analysis Break even point Profit-maximizing quantity of output vocabulary What are the 4 measures of cost? What are the 2 measures of revenue? How is marginal analysis used to determine break-even and profit maximizing decisions? Notes