A New Model for Pre-Service Elementary Mathematics Teacher
advertisement

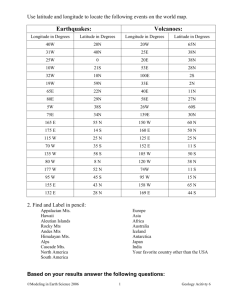
Experiences and Third Spaces: A Model for Pre-Service Elementary Mathematics Teacher Education Marcy Wood, Erin Turner, Courtney Koestler University of Arizona Marta Civil University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill The Beyond Bridging Project is supported by the National Science Foundation (Grant No. DRL-1019860.) Any opinions, findings, and conclusions are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation. Introduction • Theory-Practice divide between university methods courses and elementary classrooms (Anderson, 1997; Bencze, Hewitt, & Pedretti, 2001; Zeichner, 2010). • Field has explored various ways to bridge this gap, such as cases and a focus on high leverage practices (Campbell, 2008; Feiman-Nemser & Beasley, 2007) • Our project, Beyond Bridging, seeks to build connections through co-educational learning spaces, involving mentor teachers (MTs), preservice teachers (PSTs), teacher educators (TEs) and mathematicians Co-Educational Learning Spaces as Third Spaces • Building co-educational, “third space” learning environments (Moje et al., 2004) where the perspectives and expertise of each group (MTs, PSTs, TEs, mathematicians) are leveraged to enhance the understanding of all • Third spaces have the potential to bridge different discourses and to work towards shared and potentially more robust understandings of teaching and learning mathematics Elementary Education Program Context • Cohort, Field-Based Model • Groups of 20-30 PSTs are placed at cluster of 2-3 elementary schools for a three semester sequence • Two semesters of methods and foundations coursework • Courses 2.5 days per week at one elementary school in the cluster • Field applications 1.5 days per week at the same school or other cluster school • One semester of full time student teaching at one of the cluster schools with one of the cohort mentor teachers Co-Educational Learning Spaces in Elementary Math Teacher Preparation Joint Mathematics Methods Sessions PSTs and their MTs attend selected sessions of a methods course together Example: Prepare to conduct task-based interviews with students in MTs classroom. Parallel Professional Development and Mathematics Methods Sessions Mentor Teachers Co-Teaching in Mathematics Methods PSTs attend methods course and MTs attend a professional development sessions focused on similar topics MTs and teacher educator (TE) co-plan and co-teach a specific math methods class. MTs contribute to class sessions in various ways, e.g., bring student work, modeling activities, and discussing curriculum. Example Parallel Sessions: -Cognitively Guided Instruction -Status and Complex Instruction Joint Math Methods Sessions Goals of working jointly with PSTs and MTs: 1) Familiarize MTs with key theories of methods course so that they might continue conversations in their classrooms with PSTs 2) Leverage MTs unique knowledge and experiences with students, classrooms, and curriculum to enhance PST learning Structure of Joint Methods Sessions • Two sessions • Focused on interviewing students • Sequence of events: • AM in methods class: introduction to interviewing and CGI problem structures/children’s strategies • PM in MTs’ classrooms: MT/PST pairs interview several MT students • Afterschool debrief session with MT/PST/TE Methods • Transcription of 7 hours of audio and video involving whole group and small group talk • Coding for MT contributions Research Focus • In the context of a common mathematics methods activity, conducting and discussing problem solvingbased interviews for the purpose of learning about children’s mathematical thinking: • How do MTs draw on experiences to think about children’s activity and their teaching? • In what ways might MTs contributions create opportunities to expand the learning of PSTs? • What challenges and tensions arise? Findings Overview 1. Classroom CONTEXT 2. Some ideas that were DISSONANT with methods 3. Some ideas that RESONATED with methods 4. LINKING interviews to teaching 1. Bringing in CONTEXT Problem: There are 20 marbles that 4 friends want to share evenly. Each friend wants to have the same number. How many marbles can each friend have? Ria (PST): One of the girls…wrote 4, 8, 16, 20, and she said, 'oh, each is going to have 4.' She didn't like click in her head that each person is going to get 5 marbles… Zelda (MT): because we have really been doing …floors and rooms, so what my kids have been doing is doing patterning, they're saying 'for one, 4 marbles; for two, 8 marbles', so what she was just doing is doing what she is remembering which was number patterns. So she's not thinking about dividing them out… I understand her thinking because I know what we just did. We were just doing number patterns and so she was doing a number pattern thing, 4, 8, 12, 16, 20. See? That’s why. 2. Some DISSONANCE with Methods (but not as much as one might think….) TE: There's some blue blocks and some red blocks, you know the total and the number of blue, so how many are red? So you know the parts, you know one part and you know the whole and you're trying to find the other part. Ron (MT): That is a really, I'm finding for the ELL students, that is a really hard concept for them to understand because they see the first part of the number and then they see the end number, and they want to combine them even though they know it's not addition, but they still end up doing addition, when you look at their answers. TE: And I would add that it's not ELL kids who struggle with that; that all kids struggle with that 3. RESONANCE with methods Example Problem: Ana has 8 flowers. How many more flowers does Ana have to pick to have 12 flowers? Celine (MT): When I was in first grade, my kids, I remember that my kids had a lot of trouble with starting with a number and trying to get to a stopping number. Because they would start to add them and then they would be counting the ones that they were putting on and not realize that when they get to twelve. Or, they would get to twelve and not realize how many they added on, so then they have to stop, and then separate out again. And so that made it another step in the problem that they would get confused on. 4. Linking to Teaching Evan (MT): I know, like I saw my influence, my imprint, or whatever you were saying, especially on the second kid… because he was having a little more trouble actually doing the problems, and he got stuck at one point, and I asked him to do an easier way of doing more methods, and then he showed me a grid multiplication method that I had thought I had taught them, but he was unclear on that, and it was kind of uncomfortable because, you know, that was totally me, my responsibility, I showed him that, because he kept on looking at me Benefits for PSTs and TEs • Provide contextualization otherwise not available • Get deficit thinking in the open • Demonstration of linking interviews to teaching • Present the complexity of teaching and reflection on learning • Explore use of institutional labels Tensions for PSTs and TEs • Contextualization adds complexity • supplant methods goal • lots for PSTs to manage • Much less control, can’t select MT talk or prepare specific responses • Additional teachers = shift in addressing PST ideas • Different interactions • Less time for PST talk • MTs as co-teachers AND co-learners Implications These findings mean that we can • Specifically address/invite certain MT input • Craft TE responses to best leverage MT input • For when MT talk might not parallel TE message • For when MT talk adds complexity • That recognize and utilize potential of MT talk • Like asking MTs to elaborate/explain their talk But we need to know more about • How PSTs think about the complexity • Multiple teachers • Multiple messages • How CONTEXT (methods vs. field) might matter Questions? • • • • Marcy Wood, mbwood@email.arizona.edu Erin Turner, eturner@email.arizona.edu Courtney Koestler, ckoestler@email.arizona.edu Marta Civil, civil@email.unc.edu • For more information about the Beyond Bridging Project see, http://www.coe.arizona.edu/bb