Cell Types and Organelles PPT
advertisement

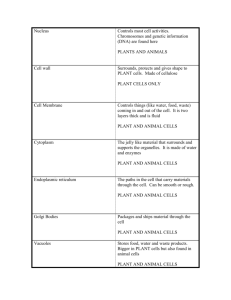
CELLS The Microscope • The light microscope – Invented by Anton van Leeuwenhock in 1600’s – Improvements brought about the compound light microscope – Enabled scientists to view and study cells The Cell Theory • • • Started with the work of Robert Hooke Took about 200 years of work to develop Three basic principles of cell theory… The Cell Theory 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3. All cells come from preexisting cells. Remember the 8 Characteristics of Living Things: ***living things are made up of units called cells Cells are Really Small! • Cell Size and Scale http://learn.genetics.utah.e du/content/cells/scale/ What’s a cell? • A cell is the basic element of life and the simplest unit of structure and function in living things. Levels of Organization Unicellular Organisms • Unicellular organisms have one single cell. How many wheels does a unicycle have? One. UNIcellular means ONE cell! Multicellular Organisms • Multicellular organisms are made up of many cells. Multicellular Organisms • Multicellular organisms depend on cell communication because they have different cells that perform different functions. Multicellular Organisms • Because of cell specialization and differentiation, cells within an organism can develop to perform different tasks. Think About It. What cells in humans help us…..move? Muscle Cells! Think About It. What cells in humans help us…..feel? Nerve Cells! Think About It. What cells in humans help us.....carry blood? Red Blood Cells! Think About It. What cells in humans help us.....think? Brain Cells! (Nerve Cells) Think About It. • These cells have different structures and different functions, but they are all cells. We need all of our cells to communicate and work together in order to survive. Basic Cell Types: Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes • Prokaryotes are very small cells without membrane-bound organelles. • These cells hold little more than ribosomes and loose DNA that is not contained in a nucleus. Examples: bacteria Basic Cell Types: Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes • Eukaryotes are organisms with many membrane-bound organelles. • They can be single-celled or multi-celled, and they have DNA contained in a separate area of the cell called the nucleus. Examples: fungi, protists, plants, animals Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes • Humans are animals – YOU are a “you”karyote! Prokaryotes Both Eukaryotes Ribosomes, DNA, DNA in a nucleus, DNA loose in cell, Cytoplasm Includes fungi, Includes animals, Includes bacteria, Includes plants Mitochondria, Cell membrane, Small and simple, More complex Basic Cell Types: Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells • Plant and animal cells contain most of the same organelles, but there are a few differences: – Plant cells have a cell wall, which is made of cellulose (starch) Basic Cell Types: Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells • Plant and animal cells contain most of the same organelles, but there are a few differences: – Plant cells have chloroplasts, which are used during photosynthesis Basic Cell Types: Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells • Plant and animal cells contain most of the same organelles, but there are a few differences: – Plant cells (usually) have one larger vacuole Basic Cell Types: Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells • Plant and animal cells contain most of the same organelles, but there are a few differences: – Animal cells have centrioles, which are used during cell division Plants Both Animals Cell Wall, Centrioles, Chloroplasts, Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, Cytoplasm, Lysosomes, Mitochondria, Nucleus, Cell Membrane, Ribosomes, Vacuole (large), Vacuole (small), Cytoskeleton Eukaryotic Cell Structure • A eukaryotic cell is like a busy factory. It has lots of little “machines” that work together and interact. Some give instructions, some produce energy, some create products, and others provide storage or get rid of waste. These little machines are called organelles. Eukaryotic Cell Structure • Organelles are literally “little organs”. They are smaller structures within a cell that act like specialized organs. Eukaryotic Cell Structure • Organelles are literally “little organs”. They are smaller structures within a cell that act like specialized organs. Organelles – Nucleus Organelle Function Nucleus - Controls all the activities of the cell (like gene expression) - Where DNA is located In A Factory… Main Office Organelles – DNA Organelle Function In A Factory… DNA - DNA/Chromosomes provide directions for the assembly line workers (the ribosomes Blueprints Organelles – Ribosomes Organelle Function Ribosomes - Ribosomes use instructions from DNA to make cellular products --PROTEINS! In A Factory… Assembly Line Workers Organelles – Mitochondria Organelle Mitochondria Function -Converts food energy (glucose) into cell energy - The cell “powerhouse” - Contains its own DNA In A Factory… Generato r Organelles – Golgi Apparatus Organelle Golgi Apparatus Function - Packages proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum and sends them to other parts of the cell In A Factory… Mailroom Organelles – Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Organelle Endoplasmic Reticulum Function - Ribosomes are attached to Rough ER - Transports materials - Prepares proteins for export In A Factory… Assembly Line or Conveyor Belt Organelles – Vacuole Organelle Vacuole Function - Stores cellular materials (like nutrients nd waste products) - Provides structure and support to plant cells In A Factory… Storage Warehouse Organelles – Centrioles Organelle Centrioles ***found only in animal cells Function -Tiny tubes that help organize cell division - Helps make new cells! In A Factory… Human resources Organelles – Cytoskeleton Organelle Cytoskeleton Function - Network of proteins - Like scaffolding and walls – provides support, shape, and structure inside of our cells - Also involved in movement - Cilia and flagella In A Factory… Walls, scaffolding within factory Organelles – Cell Membrane Organelle Function Cell Membrane (plasma membrane) - Regulates what enters and leaves the cell - Keeps unwanted things (like bacteria) out and lets wanted things (like nutrients) in In A Factory… Main Door Organelles – Chloroplasts Organelle Function In A Factory… -Where photosynthesis occurs Chloroplast ***found only in plant cells - Chloroplasts convert energy from the sun into food energy (sugars) - Enclosed by two membranes - Contains green pigment called chlorophyll Solar Panels Organelles –Cell Wall Organelle Cell Wall ***found only in plant cells Function -Provides structure and protection for the cell - Outside of the cell membrane - Made of cellulose In A Factory… Security Fence Organelles – Lysosome Organelle Lysosome Function In A Factory… - Contains enzymes that break down (digest) lipids and proteins - Removes “junk” from the cell Trash Compactor Organelles – Nuclear Membrane and Nucleolus Organelle Function Nuclear Membrane (nuclear envelope) - Two-membrane envelope - Dotted with nuclear pores that allow materials to move in and out of the nucleus Nucleolus Small, dense region of the nucleus that produces ribosomes In A Factory… Door to main office Quality Control Organelles –Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Organelle Function Smooth -Similar structure to rough Endoplasmic ER, but no ribosomes are Reticulum attached (feels ‘smooth’) -Helps make lipids for the cell In A Factory… Conveyor Belt/ Assembly Line Organelles – Cytoplasm Organelle Cytoplasm Function - Gel-like part of the cell located outside of the nucleus In A Factory… Factory Floor