CB098-011.28_Eukaryote Organelles
advertisement

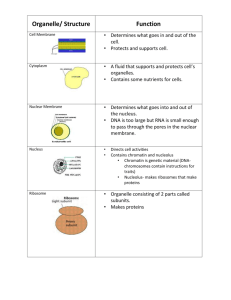
Eukaryote Organelles BIO 224 Intro to Molecular and Cell Biology Endoplasmic Reticulum • A network of cisternae (enclosed tubular sacs) extending from the nuclear membrane throughout the cytoplasm • The largest organelle of most eukaryotic cells • Two general types – Rough ER has ribosomes on its surface • Transitional ER buds off vesicles that exit to the Golgi apparatus – Smooth is involved in lipid metabolism Rough ER • Surface covered in ribosomes • Site of synthesis of proteins • Proteins travel to Golgi in vesicles for modification and secretion • Proteins to be secreted or incorporated into ER, Golgi, lysosomes, or plasma membrane targeted to ER for synthesis • Proteins to remain in cytosol or be incorporated into nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, or peroxisomes made on free ribosomes Smooth ER • Major site of membrane lipid production – Synthesized in association with existing membranes – Most made in ER, some in other membranes • Transported to destination by vesicles or carrier proteins • Most phospholipids made on cytosol side of ER – Enzymes called flippases allow half of the phospholipids to pass through to even out the bilayer • Ceramide products go to Golgi for conversion to glycolipids or sphingomyelin • Cholesterol and steroid hormones made in ER • Smooth ER of the liver detoxifies drugs Golgi Apparatus • Factory that receives protein products from the ER to process and sort for transport to their destination • Site of glycolipid and sphingomyelin synthesis • Site of cell wall polysaccharide synthesis in plants • Made of flattened membrane enclosed sacs (cisternae) and associated vesicles • Contains 4 discrete compartments – cis Golgi network, medial and trans Golgi stacks, trans Golgi network • Proteins enter cis face and exit trans face of Golgi Golgi Organization • Proteins enter at cis Golgi network • Move to medial and trans compartments for most metabolic processes like modification • trans Golgi network receives modified products to be sorted and distributed to final destinations • Mechanism of protein movement through Golgi not entirely understood Golgi Processes • Site of glycosylation of glycoproteins – Glycosyltransferases add sugar groups and glycosidases remove them • Site of glycolipid and sphingomyelin production using ceramide from ER as precursor • Plant cells use Golgi to produce polysaccharide hemicelluloses and pectins of cell wall Transport in the Golgi • Proteins, polysaccharides and lipid transported from Golgi to final destination by the secretory pathway – Proteins sorted into different types of transport vesicles that bud from trans Golgi network • Some proteins carried by constitutive pathway to be incorporated into plasma membrane or continuously secreted from cell • Others transported to cell surface through regulated secretion or specifically targeted to other intracellular destinations like lysosomes or vacuoles • Proteins with functions internal to Golgi remain there – Golgi proteins associated with the membrane – Constitutive pathway allows for their continued unregulated secretion • Some cells use regulated secretion pathway with proteins secreted in response to environmental signals – Proteins made and packaged into vesicles to be stored until needed Lysosomes • Membrane enclosed organelles containing enzymes for degradation of polymers • Act as cellular digestion system • Breaks down internalized materials and recycles old cell components • Contain 50 different enzymes to break down molecules – Most enzymes are acid hydrolases • Activity at pH near 5, nonfunctional in cytoplasm • Use a proton pump to increase H+ ion concentration for maintaining pH • Mutation in genes for those enzymes cause lysosomal storage disease in humans Lysosome Functions • Destroy material taken in by endocytosis – Extracellular material is “eaten” by cell – Transport vesicles fuse with endosomes for digestion • Phagocytosis: type of endocytosis by macrophages and other cells to ingest large particles (bacteria) for digestion • Autophagy: process used to recycle cell components – Occurs in all cells, important in embryonic development Mitochondria • Major site of energy production in eukaryotic cells • Provide most of the usable energy from carbohydrate and FA breakdown via oxidative phosphorylation • Most of their associated proteins translated on free cytosolic ribosomes and imported into the organelle • Have their own DNA coding for tRNAs, rRNAs, and some mitochondrial proteins • Assembled from proteins internally coded for and translated along with proteins encoded for by nuclear genome and imported after translation Mitochondrial Organization • Surrounded by double membrane • Inner and outer membranes separated by mitochondrial space • Inner membrane has cristae (folds) extending into matrix – Internal fluid material • Matrix and inner membrane are major working compartments Mitochondrial Organization • Matrix contains genetic system and enzymes used for oxidative phosphorylation – Citric Acid Cycle takes place here • Inner Membrane has electron transport chain embedded into it – Primary site of ATP production using chemiosmosis – Surface area increased for reaction by folding into cristae – High protein concentration for oxidative phosphorylation and metabolite transport between cytosol and mitochondria – Impermeable to most ions and small molecules • Outer membrane permeable to small molecules because of porins – Proteins that form channels allowing diffusion of small molecules Mitochondrial Genetic System • • • • • Separate and distinct from nuclear genome Similar to free-living bacteria Circular DNA molecules in multiple copies per organelle Size of genome varies by species Most code for small proteins used in oxidative phosphorylation – Code for all rRNAs and most tRNAs needed for internal translation of protein coding sequences • Other mitochondrial proteins coded for by nuclear genes – Human mitochondrial DNA codes for 13 proteins, 2 rRNAs and 22tRNAs • Uses slightly different genetic code due to latitude in recognition of codons • Can be altered by mutation – Germline mutation can be passed to next generation mainly via mother – Mutation associated with disease and aging in humans • Proteins not well understood, only half mammalian mitochondrial proteins identified – Mitochondria in different tissues produce different proteins based on function of specialized cells Protein Import in Mitochondria • Proteins needed for DNA replication, transcription, and translation of mitochondrial genome coded for by nuclear genome • Nuclear genome codes for most proteins needed for oxidative phosphorylation and all enzymes of mitochondrial membrane • >95% mitochondrial proteins made on cytosolic ribosomes and imported as complete chains Chloroplasts • Share similarities to mitochondria • Generate metabolic energy, evolved through endosymbiosis, separate genetic system, replicate by division • Convert CO2 to carbohydrates, synthesize amino acids, fatty acids and membrane lipids, reduce nitrate to ammonia Chloroplast Structure • Large organelle (5-10um) • Double membrane chloroplast envelope (outer and inner) and internal thylakoid membrane system – Network of flattened thylakoids arranged in stacks called grana • Chloroplasts divided into compartments by the three membranes – Intermembrane space between the envelope membranes • Outer membrane contains porins permeable to small molecules • Inner membrane impermeable to ions and metabolites • Stroma inside chloroplast envelope, outside thylakoid membrane – Stroma contains genetic system and metabolic enzymes • Thylakoid lumen inside the thylakoid – Thylakoid membrane contains electron transport system and site of chemiosomtic production of ATP Chloroplast Genome • Circular DNA molecules in multiple copies per organelle • Larger and more complex than mitochondrial genome • Genes code for RNAs (rRNAs, tRNAs) and proteins involved in gene expression and proteins for photosynthesis • Uses standard genetic code • Codes for 1/3 of ribosome proteins for chloroplast Chloroplast Import and Sorting • 95% of chloroplast proteins coded for by nuclear genes • Made on cytosolic ribosomes and imported as complete chains into chloroplast Peroxisomes • Small membrane enclosed organelles • Contain 50 different enzymes involved in various biochemical pathways in different cell types • Human cells have about 500 • Do not have their own genome • All proteins (peroxins) made from nuclear genome – Most peroxins made on free ribosomes and imported as complete chains • Replicate by division • Can be rapidly regenerated if lost Peroxisome Function • Oxidative reactions lead to production of H2O2 – Catalase degrades H2O2 for protection of cellular components • Various substrates metabolized down by peroxisomes – Involved in production of lipids and amino acids – Some animal cells make cholesterol and dolichol in peroxisomes in addition to ER • Contain enzymes for production of plasmalogens – Found in membranes of brain and heart tissue • Important in fatty acid breakdown in plants and yeasts – Convert stored FAs in plants to carbohydrates for energy for growth of germinating plants – Peroxisomes in leaves metabolize side products of photosynthesis Disclaimer • This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community-Based Job Training Grants as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. The Department of Labor makes no guarantees, warranties, or assurances of any kind, express or implied, with respect to such information, including any information on linked sites and including, but not limited to, accuracy of the information or its completeness, timeliness, usefulness, adequacy, continued availability, or ownership. This solution is copyrighted by the institution that created it. Internal use by an organization and/or personal use by an individual for non-commercial purposes is permissible. All other uses require the prior authorization of the copyright owner.