Bio426Lecture20Mar10 - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
advertisement

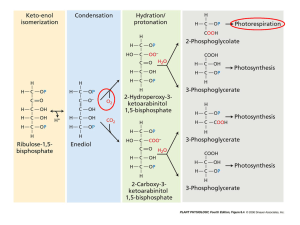
I. Photorespiration II. CO2 concentrating mechanisms - variation on the “C3” photosynthetic metabolism. Plant of the day, Zea mays (Poaceae) How does the photosynthetic response to light compare in corn and beans? Corn vs. bean Corn has: 1. Lower QY Corn Bean 2. Higher max. photosynthesis 3. Higher light saturation 4. O2 insensitive The first step in the Calvin cycle is the carboxylation of RUBP by Rubisco. Remember Rubisco’s full name? Ribulose 1,5 bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase Rubisco can catalyze the oxygenation (O2) of RuBP and the carboxylation (CO2) of RuBP. Rubisco Fig. 8.8 The set of reactions that begins with Rubisco oxygenation of RUBP is called photorespiration. When Rubisco oxygenates RUBP, a CO2 is lost from the leaf, reducing the net uptake of CO2. CO2 O2 + + Carbon gain RuBP Carbon loss, photorespiration What determines the rate of carboxylation vs. oxygenation? What determines the reaction rates for any two competing substrates in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction? Rubisco CO2 O2 Determinants of carboxylation vs. oxygenation. 1. Concentration of CO2 & O2 2. Rubisco specificity for CO2 vs. O2 Concentration of O2 >> CO2, but Rubisco specificity favors CO2 binding. Chloroplast stroma Oxygenation of RuBP causes a loss of CO2 and reduces CO2 uptake. In low O2 air, 2%. In standard air, 21% O2. So why does Rubisco have this inefficient property? Consider Earth’s atmosphere 3 billion years ago. High CO2/low O2 20% CO2 no O2 Oxygenation was not a problem CO2/O2 ratio has decreased greatly over Earth’s history 0.04% CO2 (and rising) 21% O2 The O2 inhibition of CO2 uptake represents a huge selective pressure for plant characteristics to prevent carboxylation. How to avoid oxygenation? 1. Develop new Rubisco that’s insensitive to O2 2. Reduce O2 concentration in chloroplast 3. Increase CO2 concentration in chloroplast Plants like corn show no effect of O2 concentration; apparently no oxygenation by Rubisco. They also have different initial products; 14C label shows up first in 4 carbon organic acids - malic acid, aspartic acid. These are called “C4” plants. C4 plants have Rubisco, so how do they avoid oxygenation? a) Initial carboxylation is not by Rubisco in C4 plants b) C4 leaf anatomy differs How does C4 biochemistry differ from C3? • Primary carbon fixation step uses different substrates and enzymes. HCO3- + PEP --------> 4 carbon organic acids PEP carboxylase Phosphenol pyruvate = PEP Phosphenol pyruvate carboxylase = PEPcase Two important differences between PEPcase and Rubisco 1. PEPcase activity is not affected by O2. 2. PEPcase uses HCO3-, not CO2. [HCO3-] > [CO2] C4 leaf anatomy model (Fig 8.8d) Two distinct cell types: 1. Mesophyll (PEPcase) 2. Bundle sheath (Rubisco) C4 leaf anatomy (Fig. 8.9a) C4 leaf anatomy relates to its biochemistry Initial carboxylation is in mesophll cells and is spatially separated from the Calvin cycle in the bundle sheath cells The C4 biochemistry and anatomy concentrates CO2 in the b.s. cells at Rubisco. This is advantageous in warm environments because: 1) the solubility of CO2 decreases more with temperature than the solubility of O2, so photorespiration is a bigger problem in warmer environments. 2) C4 plants can operate with lower stomatal aperture (conductance), thereby losing less water. CO2 and O2 solubilities Web Topic 8.3 CO2/O2 Temp.. There’s no energetically free biochemical lunch!! The CO2 concentrating mechanism requires extra energy. 2 Extra ATP is needed to regenerate PEP, meaning that CO2 fixation by C4 plants requires more light energy than C3 photosynthesis. Symptoms of this added cost: 1. Quantum yield of C4 < C3 Extra ATP (light) cost is not a problem in high light environments, but is in low light environments. Few C4 “shade” plants. Corn vs. bean 1. Lower QY Corn, a C4 plant Bean, a C3 plant 2. Higher max. photosynthesis 3. Higher light saturation 4. O2 insensitive C4 has two features that are advantages in warm, dry environments. 1. Suppression of photorespiration (more C gain) 2. Lower stomatal conductance (less water loss) • C4 plants can achieve high photosynthetic rates at lower stomatal conductance than C3 plants. How? C4 Photosynthesis Stomatal conductance C3 C4 plants Because of the CO2 concentrating mechanism, the [CO2] at Rubisco is much higher than in the leaf internal air spaces. A saturating level of [CO2] at Rubisco can be achieved at low stomatal aperture and current atmospheric [CO2] C3 plants The [CO2] decreases from the leaf internal air spaces to the chloroplast, and photosynthesis is not saturated at current CO2 levels.