Photosynthesis
advertisement

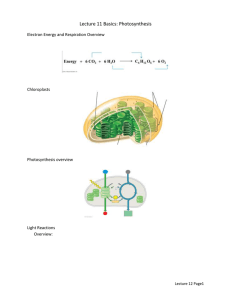
PHOTOSYNTHESIS AUTOTROPHS Auto = self Troph = eating Organisms that can produce their own food (energy) from inorganic materials (sunlight) HETEROTROPH Hetero = other Troph = eating Organisms that cannot make its own food. Requires organic compounds (other organisms) for its principle source of food. CHEMICAL ENERGY AND ATP All cells use chemical energy carried by ATPAdenosine triphosphate. Cells use ATP for functions such as building molecules and moving material through active transport. ATP The energy carried by ATP is released when a phosphate group is removed from the molecule. ATP become ADP (Adenosine diphosphate) ADP can become ATP again through a series of chemical reactions. ATP ATP is produced during the breakdown of carbon-based molecules. Different foods provide different amounts of ATP. Carbohydrates (glucose) can make ~ 36 molecules of ATP Lipids can make ~ 146 molecules SPECIAL CREATURES Some organisms do not need sunlight and photosynthesis as a source of energy. Some organisms live near cracks in the ocean and never see sunlight Chemosynthesis Process by which some organisms use chemical energy instead of light energy to make energystoring carbon-based molecules PHOTOSYNTHETIC ORGANISMS ARE PRODUCERS. • Producers – • Photosynthesis – • Produce the chemical energy for themselves and for other organisms. A process that captures energy from sunlight to make sugars that store chemical energy. Chlorophyll – A molecule in chloroplasts that absorb some of the energy in visible light PHOTOSYNTHESIS IN CHLOROPLASTS Chloroplasts are in leaf cells Grana are stacks of coin-shaped membrane-enclosed compartments called thylakoids. The membranes of thylakoids contain chlorophyll and protein Stroma is the fluid that surrounds the grana inside the chloroplast. PHOTOSYNTHESIS IN CHLOROPLASTS Light-dependent reactions 1. chlorophyll absorbs light. 2. energy is transferred to molecules that carry energy (ATP). Light-independent reactions 3. CO2 is added to build larger molecules. Energy from the light-dependent reactions is used. 4. A molecule of simple sugar is formed. C6H12O6 (glucose) FIRST STAGE: LIGHT-DEPENDENT REACTION Capture and transfer energy. There are two photosystems involved: photosystem II and photosystem I LIGHT-DEPENDENT REACTION Chlorophyll and other lightabsorbing molecules capture energy from sunlight. Water molecules are broken down into hydrogen ions, electrons, and oxygen gas (waste) Sugars are NOT MADE during this part of photosynthesis Day 1 LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTION: PHOTOSYSTEM II AND ELECTRON TRANSPORT • • Chlorophyll and other light absorbing molecules absorb energy from sunlight and that energy is transferred into chloropyll. The energy is then transferred to electrons. – 1. Energy is absorbed in sunlight • High energy electrons leave the chorophyll and enter the electron transport chain (a series of proteins in the thylakoid) 2. Water molecules split – 3. Hydrogen ions transported – LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTION: PHOTOSYSTEM I AND ENERGY-CARRYING MOLECULES Chlorophyll and other light-absorbing molecules absorb sunlight and add it to the electrons from photosystem II 4. Energy is absorbed from sunlight. Electrons are energized. 5. NADPH produced. In photosynthesis NADPH functions like ATP. The molecules of NADPH go to light-independent reactions. ATP PRODUCTION Final part of the light-reaction. 6. Hydrogen ion diffusion H+ ions flow through the thylakoid. 7. ATP produced ATP synthase take the ions as they flow and makes ATP by adding phosphate groups to ADP. LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTION: PHOTOSYSTEM II AND PHOTOSYSTEM I SUMMARY OF LIGHT-DEPENDENT REACTIONS PRODUCTS ARE: NADPH ATP Used later to make sugar. Used later to make sugar. Oxygen Given off as a waste. 2ND STAGE: LIGHT INDEPENDENT REACTION Uses energy from the first stage to make sugar. Light-independent reactions take place ANY time that energy is available (it doesn’t need sunlight). Light-independent reactions use the NADPH and ATP made during the light-dependent reactions to make sugar. THE CALVIN CYCLE Uses the NADPH and ATP from the lightdependent reaction, and CO2 from the atmosphere to make simple sugars. THE CALVIN CYCLE 1. Carbon dioxide added. CO2 molecules are added to five-carbon molecules already in the Calvin Cycle. Six-carbon molecules are formed. 2. Three-carbon molecules formed. ATP and NADPH is used to split the six-carbon molecules into two threecarbon molecules. THE CALVIN CYCLE 3. Three-carbon molecules exit. Most of the three-carbon molecules will stay IN the Calvin Cycle. ONE high energy threecarbon molecule will leave the cycle. When TWO three-carbon molecules leave the cycle, they will bond together to build a six-carbon sugar molecule. Glucose (C6H12O6) THE CALVIN CYCLE 4. Three-carbon molecules recycled. Energy from ATP is used to change the three-carbon molecules that stayed in the cycle to five-carbon molecules. These five-carbon molecules stay in the Calvin Cycle. They are added to new CO2 molecules that enter the cycle. THE CALVIN CYCLE SUMMARY OF LIGHT-INDEPENDENT REACTIONS PRODUCTS ARE: Glucose NADP+ Used to store energy. Return to the lightdependent reaction. Will be changed into NADPH there. ADP Return to the lightdependent reaction. Will be changed into ATP there. FUNCTIONS OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS Provides material for plant growth and development. Simple sugars are bonded together to form complex sugars like cellulose and starch. Starches store energy for the plant. Cellulose is a major component of the cell wall. Helps regulate the Earth’s environment. Removes CO2 from the atmosphere. PHOTOSYNTHETIC EQUATION 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 Light Dependent Reactions Includes Photosystem II Electron Transport Chain Photosystem I Light Independent Reactions Includes the Calvin Cycle PHOTOSYNTHETIC EQUATION