DNA Notes Part 1
advertisement

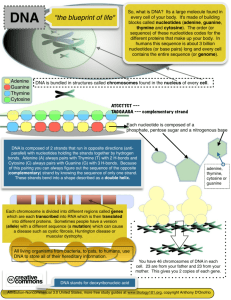
DNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Chapters 12 & 13, Pages 287-333 Chapter 12: I. Section 1 History A. Frederick Griffith- 1928 - Tried to figure out how bacteria made people sick? - Heat killed, disease-causing bacteria passed “something” along to harmless bacteria. - He called this process “Transformation.” B. Avery- 1944 - Determined DNA is the molecule of inheritance and not proteins. – Did this by destroying other cell parts piece by piece. C. Hershey & Chase- 1952 - Studied viruses, non-living particles that contain DNA. - Discovered that DNA is the genetic material responsible for transformation. Click for animation! D. Erwin Chargaff- Late 1940’s • Found there are 4 bases in a DNA molecule – Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine • Found that the amount of A = T and G = C Chargaff warned that “the technology of genetic engineering poses a greater threat to the world than the advent of nuclear technology. An irreversible attack on the biosphere is something so unheard of, so unthinkable to previous generations, that I only wish that mine had not been guilty of” II. DNA (DeoxyRibo Nucleic Acid) A. Discovery of Structure - The discovery of the structure of DNA was made in 1953 by two scientists named Watson & Crick. - Watson & Crick proposed that DNA is shaped like a “twisted ladder.” - This twisted ladder is also called a “Double Helix.” What about Rosalind Franklin? • Watson and Crick used the data from Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins Xray Crystallography to determine the structure. • Watson, Crick and Wilkins shared the Nobel prize, Franklin was robbed!! • Rosalind Franklin song B. What is DNA made of? - DNA is made of nucleotides. 1. Nucleotides consist of the following: a. Deoxyribose – a sugar b. A Phosphate Group c. A Nitrogen Base 1. Four possibilities a. Adenine (A) b. Guanine (G) c. Cytosine (C) d. Thymine (T) Nucleotide - These nucleotide bases join together to form a long single strand. - Each long single strand of nucleotides connects to “another” single strand of nucleotides. - The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds. C. Base Pairing Rules 1. Adenine always pairs with Thymine. 2. Cytosine always pairs with Guanine. - The different order of these bases is what makes organisms different. Example: Strand 1: A – G – T – T – C – T – A – G Strand 2: T – C – A – A – G – A – T – C Sample Exercise: Strand 1: C – G – A – T – G – T – A – C Strand 2: – – – – – – – Sample Exercise: Strand 1: C – G – A – T – G – T – A – C Strand 2: – – – – – – – - The more closely related two organisms are the more alike the order of their nucleotides in their DNA will be. Example: Humans Chimps Gorillas Orangutans Purines vs. Pyrimadines • Adenine and Guanine are PURINES • Thymine and Cytosine are PYRIMIDINES Purines and Pyrimidines • Purines can only pair with pyrimidines due to their size and shape. III. DNA Terminology A. Chromosomes - Tightly compacted strands of DNA found when a cell is dividing! - Hold all genetic information. - Chromosomes are passed on to an offspring by its parents. Examples: Humans = 46 Shrimp = 254 Chimps = 48 Chicken = 78 Gorilla = 48 Wolf = 78 B. Chromatin - When a cell is not dividing, DNA is in the form of chromatin. - Loosely packed DNA that is wrapped around proteins. C. Genes - A section of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific protein. IV. DNA Replication SECTION 2 A. DNA is copied before a cell divides so that each new cell has it’s own genetic copy. B. There are 4 main steps: STEP 1: - DNA is unzipped by the enzyme HELICASE and now two single strands begin to unwind. - Hydrogen bonds are broken. STEP 2: - Each unwound strand of DNA acts as a template to produce two new strands of DNA. STEP 3: - An enzyme named DNA Polymerase will read each unwound strand and join new complimentary nucleotides to each. STEP 4: - This occurs until the whole strand is replicated. - Now there are two identical DNA molecules. - Each strand contains one original and one complimentary strand. Click image for animation!