File
advertisement

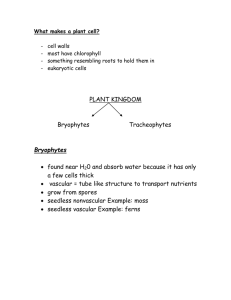
What is a Seed Plant? A seed plant is any plant that reproduces by producing ______________. 3 Characteristics of Seed Plants: 1. They all have ___________________ ___________________ 2. They use _________________ and ___________ to reproduce. 3. They all have roots, _______________, and _________________. More Facts: 4. Like seedless plants, seed plants have complex life cycles that include ___________________ and _________________ stages in their life cycles. 5. In seed plants, the plant you can actually see is the ______________________. They ____________________ are microscopic. Vascular Tissue Functions: 1. Provide support, strength, and stability 2. Transport ____________, _____________ and ___________ throughout the plant 2 Types of Vascular Tissue 1. __________________ is vascular tissue that moves food down from the leaves and throughout the plant 2. _________________ is vascular tissue that moves water and nutrients from the soil up through roots to the stem and leaves. Pollen and Seeds: 1. Unlike seedless plants, seed plants can live in a wide variety of ________________. 2. Seedless plants need water to complete their lifecycle. Seed plants do not. Instead, seed plants produce ___________ - tiny structures that contain the cells that become ___________ cells. 3. Pollen delivers the sperm cells directly near the __________. 4. Pollen is transported by _____________, ___________, and by self-pollination. 5. If the pollen fertilizes the egg, a ______________ develops. 6. A ______ is a structure that contains a young plant inside a protective covering. Seed Structure: Main Parts: 1. An _________________ 2. Stored ____________ Seed Coat Structure: 3 Main Parts: 1. Protects the ____________ 3. _____________ Coat 4. Seed leaves called And it’s _________ from drying _____________. These will out. be the first leaves to 2. In many plants, seeds are emerge and their job is to start photosynthesis surrounded by a ________. Compare and Contrast Seedless Plants with Seed Plants Seedless Plants Seed Plants