RAH Day 4 agenda 09 - containment & Korea
advertisement

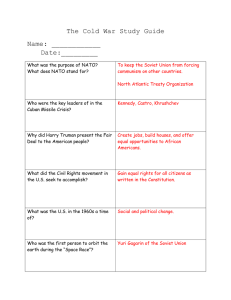
RAH Day 4 Agenda Goal – to understand and evaluate the effectiveness of the major containment policies including the Korean War. • Questions from homework • Complete (Packet 6 and 7) about containment policy • Marshall Plan (Packet 8 and 9) • Complete Korean War chart (Packet 10) • Video about Gordon Kahn – how were people affected by the red scare? • Complete (Packet 11-12) about Red Scare and Cold War at home • Draw a cartoon that shows how the international events of the early Cold War, like Greece and Turkey, Berlin, Korea, Spy rings and the USSR getting the A-bomb affected the US citizens here in the US socially and politically? Truman Doctrine Transcript Truman Doctrine – March 12, 1947 Policy – a statement of US foreign policy generally to oppose the spread of Soviet influence. Specifically it was an argument to Congress to scare them into approving spending $400million to help Greece and Turkey in 1947. Purpose – to stop the spread of Soviet influence in Greece and Turkey, and then the rest of the world. Soviet reaction – Soviets felt threatened and thus further supported “Communist” governments throughout the world including China and Korea. Evaluation of success – the doctrine was successful in Greece, Turkey, Western Europe, (Including Berlin) and Korea. But failed in China, North Korea, Vietnam and Cuba Economic cooperation Act – the Marshall Plan Post War Devastation Post War Devastation Marshall Plan rebuilds the town Marshall Plan – proposed 1947, passed into law April 3, 1948 Policy – a Congressional law called the Foreign Assistance Act that authorized the US government to spend up to $13billion over 4 years in Europe. Purpose – 1. to stop the spread of Soviet influence in Europe, 2. To help Europe rebuild after the devastation of WWII, 3. To link countries together through trade to help prevent war, 4. To help the US economy grow. Soviet reaction – Soviets felt threatened and thought the US was trying to undermine their system and turned down the aid for the USSR and Eastern Europe. Evaluation of success – the most successful foreign policy ever implemented by the US – all goals were achieved Berlin Airlift Berlin Airlift – June 1948-May 1949 Policy – 11 months of 277,000 flights into Templehof airport containing supplies of oil, coal, food and clothing. Purpose – to stop the spread of communist influence in Berlin, to prevent the fall of Berlin to the communists, to show the world our resolve in containing communism and to keep a bastion of democracy behind the Iron curtain. Soviet reaction – Soviets felt threatened but did not want war, so finally backed down and let West Berlin stay connected to West Germany Evaluation of success – very successful, all goals achieved. Led to strong economic, military and political ties with Germany to this very day. US still has major military bases in Germany NATO NATO Flag Map of Expansion of NATO – US and Canada were original founding members of the alliance not depicted on map Creation of NATO –1949 Policy – military alliance linking Canada and US to Western Europe Purpose – to stop the spread of communist influence in W. Europe, to help prevent war in Europe, and to act as a mutual defense arrangement, protecting its members from Soviet aggression. Soviet reaction – Soviets felt threatened and created the Warsaw Pact in 1955 Evaluation of success – very successful, all goals achieved. NATO still exists today, protecting the peace in Europe. No NATO countries fell to communism. But helped to lead to the arms race and the development and deployment of dangerous weapons in Europe and the world. Chinese Civil War CCP – Chinese Communist Party led by: Mao Zedong Guo Mindong – Chinese Nationalist Party led by: US tries to mediate war: but then helps Jiang Jiang Jieshi Support for Jiang Jieshi’s Guo Mindong (the Nationalists) government in China Policy – military and economic assistance to Chinese government of President Jiang Jieshi Purpose – to stop the spread of communist influence in China by giving military hardware and training to the Nationalist Army and to give economic aid so that Jiang’s government would be successful in helping his people Soviet reaction – Soviets and Chinese Communists felt threatened Soviets briefly aided Mao Zedong’s Communists, and helped to lead to Korean War Evaluation of success – failed – the Communists under Mao Zedong won the civil war in 1949 and kicked the Guo Mindong to Taiwan. Korean War - Active map of Korean War Policy – military invasion by US and UN forces Purpose – to stop the spread of communism into South Korea by defending South Korea after it was attacked by North Korea under the leadership Kim Il Sung Soviet reaction – Soviets were happy that the US interest was not solely focused on Europe. Chinese Communists felt threatened and entered to war on NK side in November 1950. Continued animosity between US and China for 20 more years. Evaluation of success – a success when looking at main goal of defending South Korea, which did not fall to communists and is an independent successful democracy today. But a failure if viewed as intending to rid all of Korea of communist control. 1946-1949 Events or issues in Asia that caused concern for the U.S Direct causes for the Korean Conflict China was taken over by Communists in 1949 - USSR installed a Communist puppet regime in North Korea. - The Korean Peninsula was divided after WWII at the 38th parallel between US- backed and USSR backed governments. - European colonies in Asia and other continents were weakened after WWII and decolonization. - Both North and South Korea wanted to reunify the peninsula - The US feared that _Communism would expand into Vietnam and other Southeast Asian nations. - The US indicated that it would not actively defend South Korea - The US feared that communist parties throughout the world were being aided and organized by the Comintern of the Soviet Union. - The USSR encouraged North Korea to invade South Korea - Major military events during the Korean War - North Korea invaded South Korea pushing all the way to Pusan. - The US encouraged the UN Security Council to authorize an international Military force to help defend South Korea. - The USSR had boycotted the UN, therefore the USSR could not veto the plan. - The UN forces were led by the US and entered the conflict on June 30, 1950. - UN and South Korean forces broke out of Pusan while General MacArthur led the US landing at Inchon on Sept 15, 1950. - The UN counteroffensive was successful in achieving the initial goal of pushing N. Korea back across the 38th Parallel. - Gen. MacArthur decided to push all the way to the Yalu River on the border with China. - 100,000s of Chinese troops entered the war on Nov. 4, 1950 and pushed the UN/US forces South of the 38th parallel. - The war turned into a Stalemate until July 27, 1953 when the armistice was signed. Results of Korean War on U.S. foreign policy - Korean War has/has not ended. - Beginning of war supports NSC - 68 report that concluded that the US needed to buildup conventional land and sea forces. - Development of the Domino theory that if one country falls to communism then others will as well. - USSR and China see US as an antagonistic adversary. - Truman’s use of pres. power to send troops without congress’s “yes” sets a long-term precedent - US saw UN as a solution for international problems. - US saw USSR as an enemy intent on world domination. - Ike changed military policy from use of conventional forces to reliance on Nuclearweapons and Massive Retaliation. Results of Korean War on U.S. domestic politics - Truman fired MacArthur resulting in Truman losing popular support. – he did not seek reelection in the 1952 election. - Americans greatly fear communism – led to theRed Scare and the rise of Sen. Joe McCarthy. - People lost jobs based on accusations only and then were blacklisted. - Fear of nuclear war - Americans built fallout-shelters and practiced air-raid drills. - Anti-communists were elected in US - Harsh anti-Communist laws were passed like the McCarran Act. - Huge build up of Nuclear arsenal - NASA was created in 1958 to build rockets -Republican Party won elections 1952 Expansion of Communism Soviets Get A- Bomb China Korea Espionage Rings Alger Hiss E. Europe Rosenbergs Fear and Suspicion of Communism in the US HUAC hearings (1946-1954 McCarthyism 1950-54 FELP 1947 Blacklisting “Witch” Hunts Cartoon of Cold War The Cold War Comes Home What were they accused of? How were they affected by the accusations? Were the accusations fair? The Hollywood Ten Being supporters and promoters of communism in films and not answering Congress’ questions They lost their jobs and went to jail for contempt of Congress No because being a communist cannot be illegal in the US due to the 1st Amendment Alger Hiss At first spying for the USSR, but later lying to congress about being a spy He went to jail for 5 years for the perjury charge At first no, the evidence was fishy. But we now know he was a minor spy Julius and Ethel Rosenberg Stealing nuclear secrets The were executed On the surface, not really, but the evidence now is fairly overwhelming McCarthyism What motivated McCarthyism? Why did it succeed at first? Motivated by Fear : of communists in US, fear personal desire of being accused of being a for political power communist, fear of the consequences of accusations like blacklisting, loss of elections, social stigma. Politically expedient : Congress saw that supporting McC could help w/ reelection and opposition would result in election loss. Ike did not oppose McCarthy (for the above reasons) Why did it fall out of favor? McCarthy was seen in the Army-McCarthy hearings for who he really was, a brutish lout with no real evidence. Once the public saw him for real, and Ike had come out against him, he was finished politically. Origins of Cold War Quiz 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. How did WWII lead to the Cold War? Describe 2 of the purposes for the Marshall Plan. What was the main goal of the Truman Doctrine? Why did the Berlin Airlift occur? What was the US concerned about in China in 1948? How did USSR respond to creation of NATO? Why were communist parties popular in Europe immediately following WWII? Explain two reasons for the incompatibility of communism and the American system. Origins of Cold War Quiz 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. How did WWII lead to the Cold War? USSR fear of invasion, dislike of Truman, death and devastation, division of Europe and Germany, no free elections Describe 2 of the purposes for the Marshall Plan. to help Europe rebuild to prevent spread of communism and help us economy What was the main goal of the Truman Doctrine? Containment directly re: Greece and Turkey Why did the Berlin Airlift occur? Soviet’s blockaded Berlin (entirely in E. Ger) and we did not want Berlin to fall to communism What was the US concerned about in China in 1948? Civil war b/t communists and nationalists Origins of Cold War Quiz 6. 7. 8. How did USSR respond to development of NATO? Created Warsaw Pact Why were communist parties popular in Europe immediately following WWII? Communism often sounds good to the poor and homeless because it promises that everyone equally will have food, a home and a job Explain two reasons for the incompatibility of communism and the American system. 1.Private property – only communal property, 2. belief in god – no religion, 3. political and personal choice – no choice, 4. limited government - totalitarian unlimited government, 5. spreading democracy & capitalism - world revolution to spread communism -