The Beginning of the Cold War
advertisement

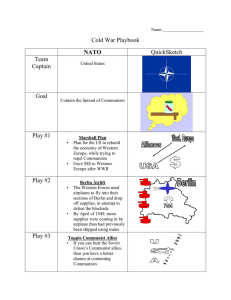
The Beginning of the Cold War Agenda Bell Ringer: Finish Holocaust Film. Examine photos (10) 1. Notes: Beginning of the Cold War (20) 2. Compare and Contrast Truman Doctrine and the Marshall Plan. (10) 3. Duck and Cover Analysis (15) 4. The H-Bomb Analysis, what changed from Hiroshima? (10) 6. NATO vs. Warsaw Pact Map (5) The Soviet Union vs. the United States • After the war, Germany is annexed into territories occupied by different forces. • Soviets take East Germany, US and the Allies occupy West Germany. • Berlin is divided in half. • Churchill claims an “iron curtain has divided East and West. Containment • Communism was spreading after World War II ended. Truman wants to stop it. • The Soviets wanted more territory, and China became communist under Mao Zedong. • Greece and Turkey were nearly taken by Communist forces. • Truman Doctrine added that it “must be the policy of the United States to support “free people” that are resisting Communism. Marshall Plan • Aid in the economic reconstruction of Europe. • Marshall’s idea was to provide economic assistance to ALL that would join in drafting a program for recovery. • Of course the Soviets refused, but it allowed Western Europe to rebuild major centers by 1950 and increase trade. Berlin Airlift • Occupation forces left West Germany by 1948, but Stalin wanted to keep Germany weak. • Blocks off Western Berlin, cuts off supply lines. • American and British forces launch the airlift, sending supplies to West Berlin for 11 months. • Soviets lift blockade in May 1949. The Cold War Begins • Diplomatic Hostility between Soviet Union and United States. • The United States wanted to stop the spread of Communism through containment. • 1949, Soviets have an atomic weapon, and nuclear age begins. NATO vs. Warsaw Pact • North Atlantic Treaty Organization. – Defensive military alliance that promised to attack anyone that messes with a NATO country. • Soviets, feeling threatened begin the Warsaw Pact. Nuclear Threats • The Soviets get the Hbomb in 1953. • Brinkmanship- the ability to go to the edge of war. • Mutually Assured Destruction- If a nuclear attack was launched, it was guaranteed the world would be destroyed.