Lecture 30 (4-18-11)
advertisement
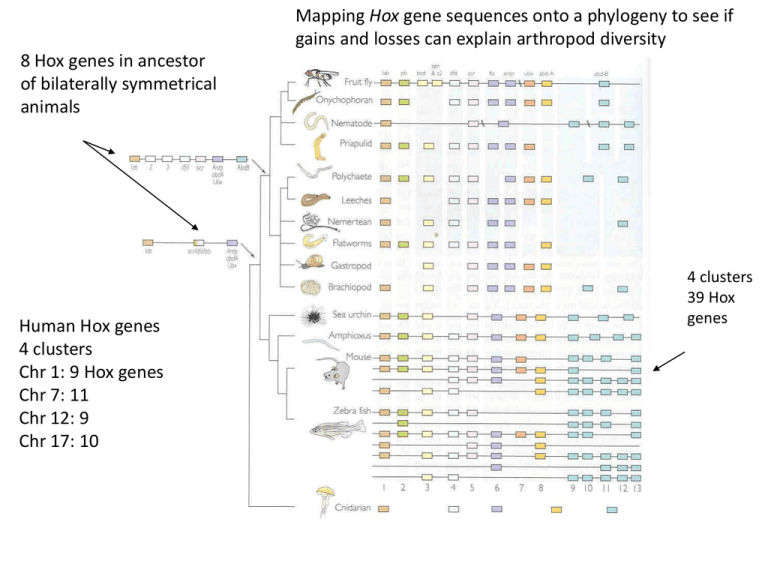
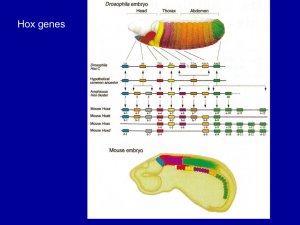
Mapping Hox gene sequences onto a phylogeny to see if gains and losses can explain arthropod diversity 8 Hox genes in ancestor of bilaterally symmetrical animals Human Hox genes 4 clusters Chr 1: 9 Hox genes Chr 7: 11 Chr 12: 9 Chr 17: 10 4 clusters 39 Hox genes Evolutionary diversification of arthropods partly based on sites of Hox gene expression Hox cluster of 9 loci for all arthropods abdA always expressed on ventral side of segment relative To Ubx Evolutionary change in where a Hox gene (e.g. pb) is expressed Insect Ubx (has an alanine-rich region) Supresses abdominal leg development. Crustacean Ubx (no alanine-rich area) No suppresion legs Ubx and abdA not expressed in posterior segments Tetrapod limb A Devonian lobe-finned fish With a prototypical tetrapod limb.(Tiktaalik) LF fishes: sister group to tetrapods Lungfishes: closest extant group to tetrapods Remember that bat wings to whale flippers are based on this same architecture. Homologous genes and developmental pathways homologous structures. Tetrapod limbs have a common ground plan Derived from a shared developmental program Length of limb: Length of time of expression Mesoderm induces formation of the AER (apical ectodermal ridge). Diffusion gradients of signal molecules provides positional information to cells. AER: Signal molecule: maintains mitotic activity of Progress Zone Progress zone grows distally defining the long axis of the limb. Fibroblast growth factors proteins 4 and 8: proximal-distal axis ZPA (zone of polarizing activity) Sonic hedghog gene product: anterior-posterior axis. Dorsal surface of limb bud. Wnt7a gene product: dorsal-ventral axis Hox genes respond to signals molecules as distal growth takes place. Homeotic genes and Flower Evolution C. 300,000 sps. of Angiosperms Four concentric whorls of modified leaves Normal order: sepals, petals, stamens, carpels Arabidopsis thaliana screened for homeotic mutants. Class A mutants: sepals and petals replaced by sex organs. Class B mutants: middle two whorls are altered. Class C mutants: inner two whorls are altered. Combinations of A-C mutant genes Replacement of sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels by leaflike structures Flower development model Interactions of protein products of A, B, and C-class genes produce the four flower organs. Flower homeotic genes sequenced. All produce transcription factors with a MADS box (DNA binding region) The homeotic genes are controlled by a master control gene: LEAFY