Essentials of Human Anatomy
advertisement

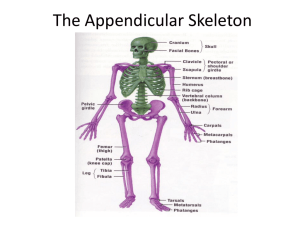
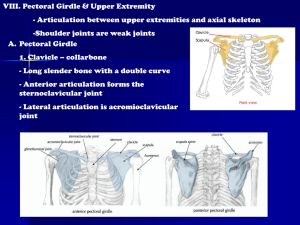
Essentials of Human Anatomy The Skeletal System 3 Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 5 Dr Fadel Naim Ass. Prof. Faculty of Medicine IUG 1 Appendicular Skeleton • Upper extremity – Consists of the bones of the shoulder girdle, upper arm, lower arm, wrist, and hand – Shoulder girdle • Made up of scapula and clavicle • Clavicle forms only bony joint with trunk, the sternoclavicular joint • At its distal end, clavicle articulates with the acromion process of the scapula Pectoral Girdle • shoulder girdle • clavicles • scapulae • supports upper limbs Clavicles • articulate with manubrium • articulate with scapulae (acromion process) Scapulae • spine • supraspinous fossa • infraspinous fossa • acromion process • coracoid process • glenoid cavity Upper Limb • Humerus • Radius • Ulna • Carpals • Metacarpals • Phalanges Humerus • The long bone of the upper arm • Articulates proximally with the glenoid fossa of the scapula and distally with the radius and ulna Humerus • head • greater tubercle • lesser tubercle • anatomical neck • surgical neck • deltoid tuberosity • capitulum • trochlea • coronoid fossa • olecranon fossa Radius – Long bone found on thumb side of forearm • Articulates proximally with capitulum of humerus and radial notch of ulna • articulates distally with scaphoid and lunate carpals and with head of ulna Radius • lateral forearm bone • head • radial tuberosity • styloid process Ulna • Long bone found on little finger side of forearm • Articulates proximally with humerus and radius and distally with a fibrocartilaginous disk Ulna • medial forearm bone • trochlear notch • olecranon process • coronoid process • styloid process Wrist and Hand • Carpals (16) • trapezium • trapezoid • capitate • scaphoid • pisiform • triquetrum • hamate • lunate • Metacarpals (10) • Phalanges (28) • proximal phalanx • middle phalanx • distal phalanx Appendicular Skeleton • Lower extremity Consists of the bones of –Hip –Thigh –lower leg –Ankle –Foot Pelvis • The adult pelvis is composed of four bones: – the sacrum, the coccyx, and the right and left ossa coxae. • Protects and supports the viscera in the inferior part of the ventral body cavity. • Pelvic girdle refers to the left and right ossa coxae only. Os Coxae • Commonly referred to as the “hip bone” or innominate bone. • Each is formed from three separate bones: – the ilium – the ischium – the pubis • Each articulates posteriorly with the sacrum at the sacroiliac joint. Pelvic Girdle • Coxae (2) • supports trunk of body • protects viscera Coxae • hip bones •acetabulum • ilium • iliac crest • iliac spines • greater sciatic notch • ischium • ischial spines • lesser sciatic notch • ischial tuberosity • pubis • obturator foramen • symphysis pubis • pubic arch Greater and Lesser Pelves Greater Pelvis • lumbar vertebrae posteriorly • iliac bones laterally • abdominal wall anteriorly Lesser Pelvis • sacrum and coccyx posteriorly • lower ilium, ischium, and pubis bones laterally and anteriorly Male and Female Pelvis Female • iliac bones more flared • broader hips • pubic arch angle greater • more distance between ischial spines and ischial tuberosities • sacral curvature shorter and flatter • lighter bones Lower Limb • Femur • Patella • Tibia • Fibula • Tarsals • Metatarsals • Phalanges Femur • longest bone of body • head • fovea capitis • neck • greater trochanter • lesser trochanter • linea aspera • condyles • epicondyles Patella • kneecap • anterior surface of knee • flat sesamoid bone located in a tendon Tibia • shin bone • medial to fibula • condyles • tibial tuberosity • anterior crest • medial malleolus Fibula • lateral to tibia • long, slender • head • lateral malleolus • does not bear any body weight Ankle and Foot • Tarsals (14) • calcaneus • talus • navicular • cuboid • lateral cuneiform • intermediate cuneiform • medial cuneiform • Metatarsals (10) • Phalanges (28) • proximal • middle • distal Ankle and Foot Arches of the Foot • The sole of the foot does not rest flat on the ground. • Helps it support the weight of the body. • Ensures that the blood vessels and nerves on the sole of the foot are not pinched when standing. Arches of the Foot • Medial longitudinal arch extends from the heel to the big toe. • Lateral longitudinal arch is not as high as the medial longitudinal arch. • Transverse arch runs perpendicular to the longitudinal arches. Hallux valgus • A lateral deviation of the great toe at the metatarsophalangeal joint • Its incidence is greater in women than in men • Associated with badly fitting shoes. • Often accompanied by the presence of a short first metatarsal bone. • Once the deformity is established, it is progressively worsened by the pull of the flexor hallucis longus and extensor hallucis longus muscles. Hallux rigidus • Osteoarthritic changes in the metatarsophalangeal joint, which then becomes stiff and painful Pes planus (flat foot) • A condition in which the medial longitudinal arch is depressed or collapsed. • As a result, the forefoot is displaced laterally • The head of the talus is no longer supported • The causes of flat foot are both congenital and acquired. THE END