Series and Parallel Resistors
advertisement

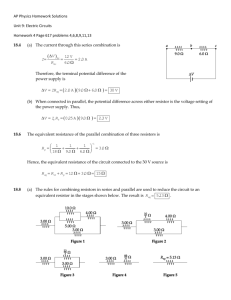
Series and parallel resistances pg. 51 Objectives • Calculate the equivalent resistance for resistors connected in both series and parallel combinations. • Construct series and parallel circuits of lamps (resistors). • Observe and explain relative lamp brightness in series and parallel circuits. Physics terms • series circuit • parallel circuit • equivalent resistance There are 2 Types of Circuits: Series Circuit A series circuit has only one path for the flow of electric current. I I Parallel Circuit In a parallel circuit the electric current can split apart and come back together again. I V V Impact of Resistors The battery and the resistors in these circuits are identical. What is different about these circuits? I1 I2 I3 The circuit with 3 resistors is 3 times harder for the current to flow through meaning each of the circuits has a DIFFERENT amount of current traveling through it. Equivalent resistance Equivalent resistance is the total combined resistance of a group of resistors. Think about it, what does equivalent mean? So if we replaced ALL of the resistors in a circuit with just 1 resistor, we would still have the same amount of current going through the circuit because the total resistance would still be the same. That 1 resistor had equivalent resistance to all the original resistors. Equivalent resistance These two circuits have the same total resistance . . . . . . so they will have the same total current, I. Equivalent resistance: series For resistors in series, you can find the equivalent resistance by simply adding up the individual resistances: Equivalent Resistance Practice Series 1. A 10 Ω resistor, a 15 Ω resistor, and a 5 Ω resistor are connected in series. What is the equivalent resistance of this arrangement? 10 Ω + 15 Ω + 5 Ω = 30 Ω 2. Two strings of tree lights, each with a resistance of 150 Ω, are connected together in series. What is the Req? 300 Ω 3. When you add resistors in series does Req increase or decrease? Req increases 4. Does total current increase or decrease when you add resistors? I decreases Practice What is the Req of each circuit? Req = 10 Ω Req = 15 Ω Adding resistors in series makes the total resistance increase. Practice How much current flows? I= 1A I = .67 A Equivalent resistance: parallel When you add resistors in parallel, total resistance goes DOWN. To find the Req you must add the inverse of the resistances: Equivalent resistance: parallel If you have two 4 Ω resistors in parallel, what is the equivalent resistance? A. ½ Ω B. 2 Ω C. 4 Ω D. 8 Ω Don’t forget to flip the fraction at the end! Parallel circuits In the circuit with parallel resistors: total current flow doubles because total resistance is halved. What is the Req for the parallel circuit? R 2R ½R Equivalent Resistance Practice Parallel 1. A 10 Ω resistor and a 15 Ω resistor are connected in parallel. What is the Req of this arrangement? 6 ohms 2. Two strings of lights, each with a resistance of 150 Ω, are connected together. What is the Req when the strings are connected in parallel? 75 Ω Practice What is the Req of each circuit? These are all 10 Ω resistors. Req = 10 Ω Req = 5 Ω Req = 3.3 Ω Adding resistors in parallel makes the total resistance decrease. Practice How much current flows? I=3A I= 6A I=9A Analogy for resistors in series What happens to the potential energy of the water as it passes through each water wheel? How is this analogous to the voltage drops across each resistor? Voltage drops: resistors in series 10 V drop 20 V drop 10 V drop What are the voltage drops across each resistor in both circuits? Voltage drops: resistors in parallel 4A 20 V drop 20 V drop 4A 20 V drop What are the voltage drops across each resistor in both circuits? Calculating total power What if a circuit contains more than one element? How do you calculate total power? Here are two ways: • Find the power of each element separately, and add them together to get the total power. OR •Calculate the total power by multiplying the total current by the total voltage. Power for resistors in series Two 40 Ω resistors are connected in series to a 60-V battery. a)How much total current flows through the circuit? b) What is the power output of this circuit? Power for resistors in parallel Two 40 Ω resistors are connected in parallel to a 60-V battery. a)How much total current flows through the circuit? b) What is the power output of this circuit? Homes are wired in parallel Your house is wired in parallel so each appliance will have 120 volts. Each device can be turned on and off without affecting the others. If you turn off that light bulb, you can still use the computer. Homes are wired in parallel What happens when you turn on more appliances? Because a house is wired in parallel, each additional appliance draws more current. Too much current? Each additional appliance draws more current from the same outlet. If the total current exceeds the safety limit, then a circuit breaker will trip or a fuse will blow. To fix the problem: • Unplug one or more appliances. • Replace a blown fuse or reset the circuit breaker by flipping the switch. Homework 1. Two resistors with resistances of 10 Ω and 30 Ω are connected in series with a 20 volt battery. a) What is the equivalent resistance of the circuit? b) What is the current flow through the circuit? Homework 2. Two resistors with resistances of 10 Ω and 30 Ω are connected in parallel with a 20 volt battery. a) What is the equivalent resistance of the circuit? 7.5 Ω b) What is the current flow through the circuit? Homework 3. If you connect these two identical resistors as shown, will they together draw more or less current than one of the resistors alone? They will draw more current, because they are connected in parallel. There are now two different, but identical paths for electricity to flow, so the current doubles! Homework 3. Two 30 Ω resistors are connected in series to a 120 volt outlet. a) How much current flows through the circuit? 2.0 amps b) What is the power output of this circuit? 240 watts Homework 4. Two 30 Ω resistors are connected in parallel to a 120 volt outlet. a) How much current flows through the circuit? 8.0 amps b) What is the power output of this circuit? 980 watts