Unit 2.1 Review
advertisement

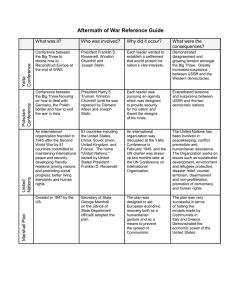
IGCSE Unit 2.1 Vocab Review Name: ______________________________ The Unit 2.1 Mini-Assessment will be on Wednesday 10/28. You may use any of your notes. Be prepared to work with documents, deal with any vocabulary (writing statements of significance), and address the guiding questions on the Major Themes sheet. 1. This trading organization between communist countries was set up to counter the Marshall Plan _____________________ 2. US president who replaced FDR. He took a much more hardline approach toward Stalin and the USSR. _____________________ 3. The political, economic, and ideological war between democratic countries led by US and communist countries led by USSR between 1945 and 1990. ________________________ 4. Government that responds to the will of the people. Free and fair elections are held. ____________________ 5. US program to spend over $13 Billion to help rebuild the economies of Europe after WW II. ________________ 6. Harry Truman’s policy of doing whatever was necessary to stop the spread of communism. This was first exercised in Greece & Turkey in 1947. _______________________ 7. The Big 3 at the Yalta Conference were __________________, ___________________, and _______________. 8. This document became the foundation for American thinking on the motives of the USSR in the Cold War, and it led the US to pursue the policy of containment at virtually any cost. _______________________ 9. Pro-communist leaders in Poland ________________________ 10. Soviet foreign minister during the early stages of the Cold War. He had a famously confrontational meeting with Harry Truman. _____________________ 11. The USSR created this organization to strengthen ties and communication between communist parties throughout Eastern Europe. ________________________ 12. Post-war Conference in July & August 1947 where real divisions emerged between the former allies. _____________________ 13. The first atomic bomb was dropped here in August 1947. This emboldened President Truman in his discussions with the USSR. _____________________ 14. Government/economic system that values equality over all. Government power enforces equality by limiting individual freedom. _____________________ 15. This was the 1944 event in Poland where the USSR allowed German soldiers to slaughter Polish resistance fighters. This shocked the US & Britain and showed them that the USSR didn’t really care about freedom. ________________________ 16. Winston Churchill coined this term in his famous speech in Missouri in March of 1946. ____________________ 17. Post-war conference where the Big 3 agreed to divide, occupy & rebuild Germany and to hold elections in Poland and throughout devastated countries in Europe. ______________________________ 18. This American diplomat wrote the Long Telegram _____________________ 19. Pro-democracy leaders from Poland who had fled to London during the War __________________ 20. The Big 3 at the Potsdam Conference were _________________, __________________, and _______________. IGCSE Unit 2.1 Vocab Review Name: ______________________________ The Unit 2.1 Mini-Assessment will be on Wednesday 10/28. You may use any of your notes. Be prepared to work with documents, deal with any vocabulary (writing statements of significance), and address the guiding questions on the Major Themes sheet. What would your argument be for each question? What specific historical evidence would you use (vocabulary)? 1. Why did the USA–USSR alliance begin to break down in 1945? 2. How had the USSR gained control of Eastern Europe by 1948? 3. How did the USA react to Soviet expansionism? 4. What were the consequences of the Berlin Blockade? (We’ll move this to 2.2) 5. Who was more to blame for starting the Cold War: the USA or the USSR? Table A Truman Doctrine & the Marshall Plan See pp. 108-111 in the Blue Book. Answer the following questions in your notes. If you have already answered them, be sure that you have sufficient responses. Work with your group to make sure that everyone has good information. Explain your responses to your neighbor. Talk through your answers with the group. Be sure you KNOW this material – not that you just have something written down. 1. What events prompted the beginning of the Truman Doctrine? What was the purpose of the Truman Doctrine? 2. How was the Truman Doctrine a change from the traditional foreign policy of the US? 3. What was the Marshall Plan, and what was its purpose? How successful was it? 4. How did the USSR react to the Truman Doctrine & the Marshall Plan? Table A Truman Doctrine & the Marshall Plan See pp. 108-111 in the Blue Book. Answer the following questions in your notes. If you have already answered them, be sure that you have sufficient responses. Work with your group to make sure that everyone has good information. Explain your responses to your neighbor. Talk through your answers with the group. Be sure you KNOW this material – not that you just have something written down. 1. What events prompted the beginning of the Truman Doctrine? What was the purpose of the Truman Doctrine? 2. How was the Truman Doctrine a change from the traditional foreign policy of the US? 3. What was the Marshall Plan, and what was its purpose? How successful was it? 4. How did the USSR react to the Truman Doctrine & the Marshall Plan? Table B American Motives in the Cold War See pp. 112-115 in the Blue Book. Read and discuss with your group. Answer the following in your notes. Work with your group to make sure that everyone has good information. Explain your responses to your neighbor. Talk through your answers with the group. Be sure you KNOW this material – not that you just have something written down. 1. Why was the US government so keen to confront the Soviet Union after 1945? a. How did wealth & confidence impact this? b. How did the atomic bomb influence this? c. How did memories of the 1930s affect this? d. How did George Kennan impact this? Table B American Motives in the Cold War See pp. 112-115 in the Blue Book. Read and discuss with your group. Answer the following in your notes. Work with your group to make sure that everyone has good information. Explain your responses to your neighbor. Talk through your answers with the group. Be sure you KNOW this material – not that you just have something written down. 1. Why was the US government so keen to confront the Soviet Union after 1945? a. How did wealth & confidence impact this? b. How did the atomic bomb influence this? c. How did memories of the 1930s affect this? d. How did George Kennan impact this?