Click!
advertisement

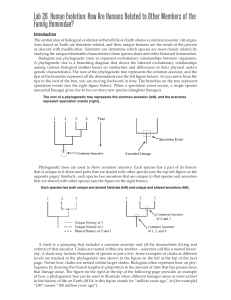
Understanding phylogenetic trees: http://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/reading-a-phylogenetictree-the-meaning-of-41956 What is a phylogenetic tree? Why are phylogenies useful for scientists? Gene flow is a mechanism behind evolution. How is it defined here? What are the two ways listed that can lead to genetic isolation? What is the founder effect? What is vicariance? How can genetically isolated populations become different from one another? Can natural selection act on these populations differently? After a long time, evolution can lead to… What do the “tips” of phylogenies represent? What are the three terms associated with the tips? What are nodes? (two words) What do nodes represent? What is a clade or monophyletic group? Why are phylogenetic trees important? Make sure you read the section on how to read phylogenetic trees for the next steps! Reading phylogenetic trees (copy and paste): http://www.tedaltenberg.com/teacher/wms/science/images/patterns_intro.gif According to this tree, primates are more closely related to… The clade that includes crocodiles and dinosaurs & birds is most closely related to the clade that includes… One trait that unites amphibians and rodents is… Ray-finned fishes have… Why are primates and crocodiles placed in the same clade? Reading phylogenetic trees (copy and paste): http://1.bp.blogspot.com/_YenikcxMppM/TO2v1VNqu2I/AAAAAAAAAJ4/KRRmG9vUD38/s1600/cladogram.gif Name two sets of sister taxa. Are birds more closely related to Acrocanthasaurus or Deinonychus? Name the most recent common ancestor of Tyranosaurus and Omithomimus.