METALS, NONMETALS, METALLOIDS, & NOBLE GASES
advertisement

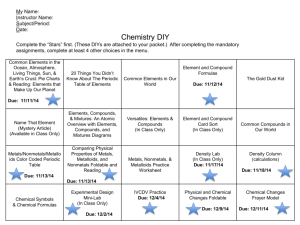
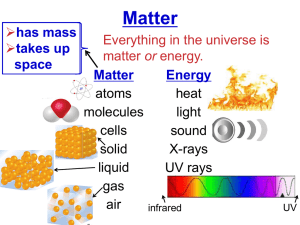
METALS, NONMETALS, METALLOIDS, & NOBLE GASES FOUR SECTION FOLDABLE ADVANCED ORGANIZER PROPERTIES OF METALS • Most elements are metals • Metals are located left of the Zig Zag line • Metals have few electrons in their outer energy level • Metals are solid at room temperature except Mercury which is a liquid PROPERTIES OF METALS • Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity • Metals are malleable which means they can be flattened into thin sheets • Metals are ductile which means they can be drawn into thin wires • Metals are shiny EXAMPLES OF METALS • • • • • • • Gold Silver Mercury Lead Iron Nickel Copper PROPERTIES OF NONMETALS • Nonmetals are located right of the Zig Zag line • Nonmetals have almost a complete set of electrons in their outer energy level • Nonmetals are mostly gases at room temperature PROPERTIES OF NONMETALS • Nonmetals are not good conductors of heat & electricity • Nonmetals are not malleable • Nonmetals are not ductile – they are brittle and will break or shatter when hit with a hammer • Nonmetals are not shiny EXAMPLES OF NONMETALS • • • • • • • Oxygen Nitrogen Sulfur Carbon Chlorine Fluorine Iodine PROPERTIES OF METALLOIDS • Metalloids are also called semiconductors • Metalloids border the Zig Zag line • Metalloids have a ½ complete set of electrons in their outer energy level • Metalloids have some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals. EXAMPLES OF METALLOIDS • Tellurium-shiny but brittle • Silicon-semiconductor • Boron-hard but brittle and a good conductor of electricity PROPERTIES OF NOBLE GASES • Noble Gases are Family 18 • Noble Gases have a complete set of electrons in their outer energy level – all but Helium have 8. Helium has 2. • Noble Gases are gases at room temperature • Noble Gases are nonmetals PROPERTIES OF NOBLE GASES • • • • Noble Gases are colorless Noble Gases are odorless Noble Gases are unreactive Noble Gases are found in very small amounts on Earth EXAMPLES OF NOBLE GASES • • • • • Helium Argon Krypton Xenon Radon (Radioactive gas) More Vocabulary • Period – a horizontal row of elements on the periodic table • Lanthanides – transition metals that follow lanthanum (first row at the bottom). They are shiny, reactive metals. Some are used to make steel. More Vocabulary • Actinides - transition metals that follow actinium (second row at the bottom). They are all radioactive and unstable. They can change into different elements. Elements after plutonium do not occur in nature. More Vocabulary • Family – also called a group, are the columns on the periodic table. Most of these elements in a family share similar properties • Metal – elements that are shiny and are good conductors of thermal energy and electric current; most metals are malleable and ductile More Vocabulary • Nonmetal – elements that are dull and are poor conductors of thermal energy and electric current • Metalloid – elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals; sometimes referred to as semiconductors. Additional Notes • The number at the top of the block on the Periodic Table is the ATOMIC NUMBER. • The ATOMIC NUMBER tells you how many PROTONS are in the nucleus of the atom. • The ATOMIC NUMBER is unique to each element.