Was the Industrial Revolution *Good* for the
advertisement

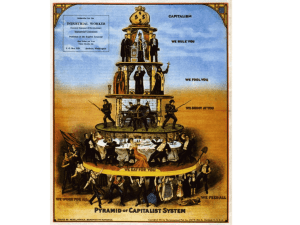
Was the Industrial Revolution “Good” for the United States? 1865-1910 The IR is a Civil War Aftermath • How and Why this occurred? – Natural Resources harnessed – New Industries emerged – New Markets Spark Rise of Consumerism – Railroads Transform Life – Big Business Emerges • It’s EFFECT • 1870-1920 – Nation’s Wealth Increased 5 ½ times • By 1920 U.S. is Leader in – Agricultural production – Industrial Production IR Evaluation • Was this beneficial for “United States”? – Business Owners – Workers – Investors – Consumers – Citizens – National Economy IR Good for “Big Business” Owners? Consolidation: organize to stabilize economy • Panic 1893 : A Four Year Depression • Vertical Integration – By 1901 U.S. Steel Corp. producing 80% all steel • Horizontal Consolidation – Standard Oil Company • Trusts – JP Morgan Company Social Darwinism • Carnegie “Rags to Riches” Story IR Good for U.S.? YES • • • • • • • • Patents Increase Number of Industrial Workers Increased Exports Increased Steel Production Increased Oil Production Increased Railroad Tracks Laid Increased National Wealth Increased Gospel of Wealth IR Good for U.S.? NO • Monopolies • Political Corruption – Social Darwinism – Influences Laissez-Faire Policy – Political Machines • Tammany Hall – Plutocracy • Gilded Age Income Inequality • Economic Tumult IR Consequences for Workers/Consumers • Positive – Increased number of jobs – Increased living standard – Decreased cost of goods – Cultural Enhancements – Technology Innovations (Conveniences) – Growth of Middle Class IR Consequences for Workers • Negative – Environmental harm (Oil Drilling) – Dangerous Working Conditions – Exploited Child Labor – Exploited Free Workers • “Wage Slaves” – Long Working Hours – Monotonous/Repetitive Work • “Part of the Machine” IR Mixed Benefit Triggered Response • Government Response • Worker Response • Business Owner Response Government Regulation b) Response to “Big Business” Behavior – Government Regulation • • Munn v. Illinois 1877 Wabash Case 1886 – • – Sherman Anti-Trust Act 1890 Court Rulings Dilute Anti-trust Legislation • • – Interstate Commerce Act 1887 U.S. Knight (1895) Maximum Freight Case (1897) Federal government consistently denied unions recognition as legally protected organizations under 14th Amendment Rise of National Labor Unions b) Response to “Big Business” Behavior – Rise of National Labor Unions • American Federation of Labor – National Labor Union Actions • Collective Bargaining • Strikes –1877 Great RR Strike –Haymarket Square Riot 1886 and Homestead Strike 1892 –Pullman Strike 1894 Response of Big Business Owners c) Response to Labor Union Actions – Employer Responses • Yellow-dog contracts • Closed Shops – Public Response to Worker Strikes: Disdain – Supreme Court Classified Strikes as Illegal Trust – Federal Government Support of Big Business • Combination of public disdain, federal government opposition limit union gains for 30 years!!! Interpretations of IR Effects • Big Business as – Robber Barons • Big Business as – Captains of Industry