blood ppt notes
advertisement

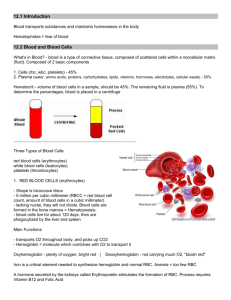
Blood Erythrocytes (RBC), Leukocytes (WBC), Platelets, & Plasma Blood Function Components Transport nutrients, wastes, body heat, etc thru bv 55% Plasma – fluid matrix 45% Erythrocytes (rbc) – O2 transport >1% Leukocytes (wbc) – protect body >1% Platelets – cell fragments used for clotting Fun Facts 4-6 liters of blood per person 7% of body weight Temp 38oC pH between 7.35 – 7.45 Salty-metallic taste 5x thicker than water Blood Plasma 90% water Distributes body heat through out body Contains dissolved nutrients, salts, resp. gases, hormones, plasma proteins, wastes, and products of cell metabolism Plasma Proteins Albumin – maintains osmotic pressure of blood Clotting Proteins – prevents blood loss from injured bv Antibodies – protect body from pathogens Erythrocytes (rbc) Biconcave disc shape (large s.a. to volume) Anucleate - lacks a nucleus Lack cellular organelles including mitochondria (so do not use O2 themselves) Hemoglobin (Hb) – Fe carries 4 molecules O2 1rbc carries 1 billion molecules O2 Avg male 13-18g Hb/100ml blood Avg female 12-16g Hb/100ml blood Anemia – low rbc or low Hb Polycythemia – high rbc (high alt or bone marrow cancer) Last 120 days – broken down by liver and spleen Leukocytes (wbc) Live days, months, or even years About 4,000-11,000 wbc/mm3 blood Can move in and out of bv Respond to chems sent out from damaged cells When in action – body doubles #wbc w/in hrs Leukocytosis >11,000 wbc indicates bacterial or viral infection Leukopenia Decrease in wbc Typically due to corticosteroids or anticancer drugs Leukemia Cancer of bone marrow Too many immature wbc to defend off pathogens Types of Leukocytes Granulocytes – granule containing wbc w/lobed nuclei Neutrophils – phagocytes at site of infection Eosinophils – increases w/allergies and infections by parasitic worms Basophils – histamine (chem incr. wbc to site) containing granules Agranulocytes – lack cytolasmic granules Lymphocytes – in lymphatic tissue (T cells and B cells) Monocytes – largest wbc Become macrophages when enter tissues Fight off chronic infections Platelets & Hemostasis 1. 1. 2. 2. 1. 3. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Platelets – irregularly shaped, needed for clotting process Hemostasis – local stoppage of blood flow Platelet Plug Forms Platelets become sticky and cling to damaged site Release clotting factors to increase platelets to site to create plug Vascular Spasms Occur Serotonin is released to cause bv to spasm and narrow to decrease blood loss Coagulation Injured tissue releases “Tissue Factor” (TF) TF combines with Ca+2, vitamin K, and PF3 prothrombin Prothrombin converted to thrombin Thrombin + fibrinogen Fibrin Fibrin traps rbc to start clot and pulls ruptured bv closer together Hematopoiesis – Blood Cell Formation Hemocytoblast stem cell in rbm takes 3-5 days to form rbc Rbc divides and synthesizes Hb Incr. Hb ejects nucleus and most organelles Enters bloodstream Rbc falls apart in 100-120 days Eliminated by phagocytes, spleen, and liver Erythropoietin hormone controls rate of rbc production Produced by kidneys and targets bone marrow Thrombopoietin – increases production of platelets Interleukins and colony stimulating factors increase production of wbc from bone marrow Released in response to inflam chems, bacteria, or toxins Blood Types & Transfusions Phlebotomist – hs degree + training + exam ABO Blood Groups Rh Blood Groups Based on 2 antigens A&B Antibodies formed in infancy Determined by anti-A, and antiB serums Once Rh- contacts Rh+ produces antibodies Pregnant Rh- mom carrying Rh+ baby RhoGAM prevents moms antibodies from attacking fetus Hemolysis – rupture of rbc Fetal Hb vs. Adult Hb By day 28 of fetal development – embryonic blood cells circulate in blood vessels Fetal Hb (HbF) differs from adult HbA HbF has a greater ability to pick up O2 b/c fetal blood less O2 rich than mothers If fetal rbc destroyed so quick that liver cannot rid of bile fast enough causes infant jaundice