Intro to Business Unit 1 CH 2

Economic Resources and Systems
Introduction to Business
Unit 1, Chapter 2
Unit 1, Chapter 2
• Learning Targets
– Define scarcity.
– List four factors of production.
– Identify the differences between market and command economies
– Explain why most countries prefer a mixed economy.
Economics
Understanding economic resources and systems is essential to lessening economic problems.
What is Economics
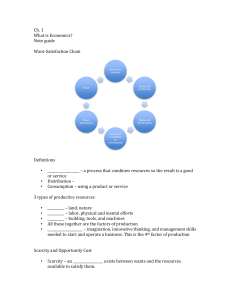
• Study of how society chooses to use resources to produce and distribute goods and services for people’s consumption
Unit 1 CH 2 Academic Vocabulary
To meet needs and wants, society must produce goods and services
• Factors of production –
The means to produce goods and services i.e. grow wheat, build tractors to harvest wheat • Scarcity – shortage of resources i.e. country may not have enough doctors
Unit 1 CH 2 Academic Vocabulary
• Natural Resources raw materials
– Renewable-can be reproduced i.e. wheat and cattle
– Non-renewable – limited or unable to be renewed i.e. coal, iron, oil
• Human Resources
Knowledge, efforts and skills people bring to work
• Capital Resources
Used to produce goods and services i.e. building materials, equipment
• Entrepreneurial
Resources
People who recognize need for new goods and services i.e. Apple IPAD
Making Decisions about Production
-What should be produced?
-How should it be produced?
-Who should share in what is produced?
Text to world connection
Find an article from The
New York Times about a product or service.
Copy and paste article into notes. Write a paragraph answering the following.
Identify what types of resources are required to produce product/service. Explain availability or scarcity of product/service.
Types of Economic Systems
• Market Economy
Economic decisions are made in the marketplace according to the laws of supply and demand i.e. USA
• Command Economy
Planned or managed economy in which a central authority (usually the government makes the key economic decisions i.e. communism
• Mixed Economy
State takes care of people’s needs while the marketplace takes care of people’s wants i.e. socialism
Academic Vocabulary
• Demand- amount of quantity of goods and services that consumers are willing to buy at various prices
• Supply- amount of goods or services the producers will provide at vaiours prices
• Equilibrium Price – price at which the amount supplied and the amount demanded meet
Unit 1 CH 2 Assessment
• Pg 31 Complete
– Review what you learned #14-22
– Understanding business concepts #23-30
– Critical thinking #31-32
– Examining the Image
• Pg 32-33
– Linking school to work
– Speculating on shortage