File
advertisement

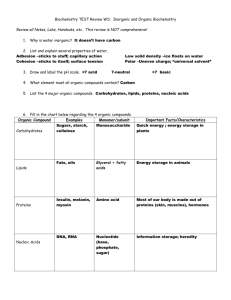
Biomolecules and Cells Elements of Life • A few major elements make up virtually all living things • Roughly 96% of an organism’s mass (including humans) is composed of just 4 elements – Oxygen – Carbon – Hydrogen – Nitrogen Elements of Life • Together, these 4 elements combine to make up almost all of the major organic and inorganic compounds in our bodies. • The need for more of these elements to grow, reproduce, and make and use energy underlies almost all of the competition and struggles of life Elements of Life • Organic compounds always contain 1 key element ? Elements of Life • Organic compounds always contain 1 key element ? – Carbon Though not all carbon containing compounds are organic Elements of Life • Important Inorganic Compounds in the body? Elements of Life • Important Inorganic Compounds in the body? – H2O (typically 60-80% of living things) – CO2 – Fe – Minerals (Bones, teeth) – Salts and Ion Electrolytes Elements of Life • Important Organic Compounds in the body? Elements of Life • Important Organic Compounds in the body? • Key Organic compounds typically fall under classes of Macromolecules: – Proteins – Nucleic Acids – Carbohydrates – Lipids Elements of Life- Proteins • Proteins are long, heavy organic compounds that have a function and whose function depends on the 3-D structure of the molecule(s) • Proteins are polymers (polypeptides) made up of amino acid monomers bonded together to form a chain Elements of Life- Proteins • Proteins consist primarily of C,H, O, & N – Also contain S (only macromolecule group that does…) • The protein structure is determined by the sequence of amino acids, which is determined by the genetic sequence of DNA. • This causes the protein to fold in certain ways to give the protein its 3-D conformation • Proteins are made using RNA in a process called Translation Elements of Life- Proteins • Protein functions include: – Structural support for cells and tissues – Energy production, storage, and consumption (Metabolism) – Signaling • Hormones, signal peptides, immune system – Enzymes • Chemical catalysts that increase reaction speed, or help the reaction to occur in the first place Elements of Life- Nucleic Acids • Nucleic Acids chains consist of nucleotides which consist of: – Nitrogenous Base (A,C,G,T) – Sugar molecule (deoxyribose or ribose- hence the name) – Phosphate backbone (negatively charged) • Genetic information encoded in DNA • Expressed from DNA to RNA in Transcription Elements of Life- Nucleic Acids • Nucleic Acids consist mainly of C,H,O,N and P due to the phosphate backbone • In humans and other Eukaryotes, the DNA is stored in the cell inside a membrane bound organelle called the Nucleus Elements of Life- Carbohydrates • Carbohydrates are hydrates of Carbon. This means they have the general formula (CH2O)n • Consist only of C,H, and O. Lack the other elements except in rare cases • Exist as monomers (single sugars) or polymers of sugars (disaccharides and polysaccharides) – Disaccharides have two monomers (Sucrose) – Polysaccharides have many monomers (Starch) Elements of Life- Carbohydrates • Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound on Earth. – Consists of glucose molecules bound together to form a polymer – Forms wood, bark, leaves, and other fibrous structures in plants • Why isn’t it easily digested like glucose or other starches? Elements of Life- Carbohydrates Image from FAMU Elements of Life- Lipids • Diverse group of compounds that share the main characteristic of being non-polar, hydrophobic • Main functions are in cell membranes, energy storage, and steroid hormones • Consist primarily of C and H, with some O and P Elements of Life- Lipids • Cell membranes consist mainly of phospholipids – These compounds contain a non-polar lipid “tail” end, and a polar “head” end consisting of a phosphate ion – In water, phospholipids align to create a bilayer that is polar on the surfaces and non-polar in the interior Cells and Levels of Organization • Cells are the smallest unit of life that can act independently and have all of the characteristics of living things – Eukaryotes: Membrane bound Nucleus and organelles- Plants, Animals, Fungi, protists – Prokaryotes: No membrane bound organelles or nucleus. Typically single celled- Bacteria and Archaea Cells and Levels of Organization • In Eurkaryotes, matter is organized into increasingly complex levels that allow for more complex roles and functions. • Atoms-> Molecules -> Macromolecules-> Organelles -> Cells -> Tissues -> Organs -> Organ Systems -> Organism Questions ?