File
advertisement

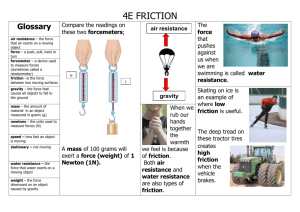
Name_________KEY____________________________________ Force, Motion and Dynamics Study Guide 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. Give an example of an exerting force. GRAVITY PULLING A KID DOWN A SLIDE What happens when two forces act in the same direction? ADD THE FORCES TOGETHER What happens when two forces act in opposite directions? SUBTRACT THE FORCES FROM EACH OTHER Define inertia. TENDENCY OF AN OBJECT TO RESIST CHANGE IN ITS MOTION What is the relationship between mass and inertia? THE GREATE THE MASS THE GREAT THE INERTIA Define weight. THE FORCE OF GRAVITY ON A PERSON/OBJECT ON THE SURFACE OF A PLANET Compare weight and mass. MASS OF AN OBEJCT IS THE AMOUNT OF MATTER. MASS REMAINS CONSTANT. WEIGHT IS BASED ON GRAVITATIONAL FORCE AND CAN CHANGE WHEN THE AMOUNT OF GRAVITY PRESENT CHANGES. According to Newton’s second law, how can you increase an object’s acceleration? DECREASE MASS (IF THE FORCE REAMINS THE SAME) Define rolling friction. FRICTION THAT IS PRESENT WHEN ONE OBJECT ROLLS OVER A FLAT SURFACE Define static friction. FRICTION THAT IS BETWEEN SURFACES THAT ARE STATIONARY Define kinetic friction. FRICTION BETWEEN MOVING SURFACES Define drag. Give an example. FRICTION LIKE FORCE. IT OPPOSES MOTION IN A FLUID. What type of force is air resistance? FRICTION Explain the law of universal gravitation. ANY TWO OBJECTS IN THE UNIVERSE ATTRACT EACH OTHER. LARGER THE MASS OR THE CLOSER THE OBJECTS, THE STRONGER THE ATTRACTION Forces can only be combined when… THEY ARE ACTING ON THE SAME OBJECT Describe Newton’s 1st law, give an example. AN OBJECT AT REST REMAINS AT REST AND AN OBJECT IN MOTION MAINTAINS ITS VELOCITY UNLESS IT EXPERIENCES A NET FORCE Describe Newton’s 2nd law, give an example. (Note: you will need to know how to use this formula to solve for any variable in the equation and know the correct units for each variable). F = MA Describe Newton’s 3rd law, give an example. FOR EVERY ACTIONA FORCE, THERE I AN EQUAL AND OPPOSITE REACTION FORCE Define force. Name and explain the forces investigated this year. PUSH OR PULL. GRAVITATIONAL FORCE, FRICTIONAL FORCE, NORMAL FORCE, TENSION, MAGNETIC FORCE, SEE NOTES FOR DESCRIPTIONS What is the relationship between friction and surface area? SURFACE AREA DOES NOT AFFECT FRICTIONAL FORCE Describe the motion of an object when the forces are balanced. NO MOTION/DON’T CHANGE THE MOTION IF MOVING AT A CONSTANT SPEED Describe the motion of an object when the forces are not balanced. MOTION IN THE DIRECTION OF THE NET FORCE What is the relationship between friction and weight? INCREASE THE WEIGHT, INCREASE THE FRICTION What is the formula for determining the weight of an object? (Note: you will need to know how to use this formula to solve for any variable in the equation and know the correct units for each variable). F =MG What is the gravitational constant for earth? 9.8 N/Kg How do you determine net force for objects acting in opposite directions (180 degree line)? SUBTRACT THE FORCES How do you determine the net force for objects acting in the same direction? ADD THE FORCES Describe the parallelogram method for finding net force. DRAW A LINE PARELLEL TO ONE VECTOR BEGINNING AT THE HEAD OF THE OTHER VECTOR. DRAW A SECOND LINE PARELLEL TO THE OTHER VECTORE BEGINNING AT THE HEAD OF THE FIRST VECTOR. WHERE THE TWO NEW PARELLEL LINES INTERSECT DRAW THE HEAD OF THE 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. RESULTANT. DRAW A DIAGONAL LINE CONNECTING THE HEAD OF THE RESULTANT WITH THE INTERSECTION OF THE TWO ORGINIAL VECTORS. Describe the head to tail method for finding net force. CHAIN THE VECTORS HEAD TO TAIL CREATING A BOX LIKE SHAPE. TO COMPLETE THE POLYGON DRAW A VECTOR CONNECTING THE VECTORS. THE HEAD OF THE RESULTANT SHOULD MEET THE HEAD OF THE LAST VECTOR AND THE TAIL SHOULD MEET THE FIRST VECTOR. Define net force. SUM OF ALL FORCES ACTING ON AN OBJECT Explain normal force. Give an example. IT IS THE REPULSIVE CONTACT FORCE THAT OCCURS BETWEEN TWO OBJECTS. IT IS PERPENDICULAR TO THE SURFACE OF CONTACT. Explain tension. Give an example. The tension force is the force that is transmitted through a string, rope, cable or wire when it is pulled tight by forces acting from opposite ends. The tension force is directed along the length of the wire and pulls equally on the objects on the opposite ends of the wire. What are field forces? What forces are field forces? FORCES THAT CAN ACT AT A DISTANCE WITHOUT CONTACT. GRAVITY, MAGNETIC AND ELECTRICAL. What are contact forces? What forces are contact forces? FORCES THAT CAN ONLY ACT WHEN TOUCHING. FRICTION, NORMAL AND TENSION. What is an interacting force pair, give an example. A BOOK EXERTS A FORCE ON THE TABLE AND THE TABLE EXERTS AN EQUAL FORCE ON THE BOOK On a speed vs. time graph, how can you tell the strength of a force? THE FASTER THE SPEED, THE GREATER THE FORCE (HINT: F=MA) What does a vector represent? DIRECTION AND MAGNITUDE How do you determine the length of a vector? LENGTH = SCALING FACTOR X FORCE How do you determine the force of a vector? FORCE = SCALING FACTOR X LENGTH Describe frame of reference/reference point? DETERMINING THE MOTION OF AN OBJECT BASED ON STATIONARY OBJECTS AROUND IT If an object is moving, what direction is kinetic friction? OPPOSITE DIRECTION OF THE MOTION. For the skier below, draw vectors to represent the forces affecting the skier. Note: the skier is not moving. NORMAL FRICTION GRAVITY