CHAPTER 14

CHAPTER 14
COMPENSATING
SALESPEOPLE
THE SALES FORCE
REWARD SYSTEM
Financial compensation
Non-financial compensation
IMPORTANCE OF SALES
FORCE REWARDS
Sales force
Company
Customer relations and goodwill
Strategic planning
DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
Inherent conflicts
No plan fits all situations
Internal equity
External equity
COMPENSATION PLAN
OBJECTIVES
Correlate efforts, results, and rewards
Control activities
Ensure proper treatment of customers
Attract and keep good salespeople
BASIC REQUIREMENTS
Provision for two types of income
Flexibility and stability
Simplicity
Economy and competitiveness
Fairness
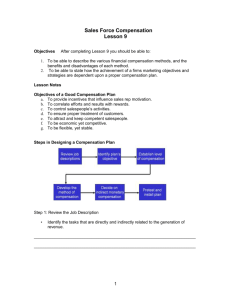
STEPS IN DESIGNING A
PLAN
1.
Review job analysis/description
2.
Determine objectives
3.
Determine job elements
4.
Establish level of compensation
5.
Pretest
6.
Administer/Evaluate
REVIEW JOB DESCRIPTION
Review nature, scope, and difficulty of job
SET OBJECTIVES
Increase volume
Obtain new accounts
Minimize expenses
ESTABLISH JOB
ELEMENTS
Controllable
Measurable
LEVEL OF COMPENSATION
Type of plan
Size of company
Age of salespeople
Industry
COMPENSATION ISSUE
Should sales managers always be paid more than the people they manage?
PRETEST
Start with one or two sales divisions
ADMINISTER/EVALUATE
Implement
Review and modify where necessary
METHODS OF
COMPENSATION
Straight salary
Straight commission
Combination
Team Selling
Optimum Pay Plans
STRAIGHT SALARY PLANS
Salary is a fixed element
Degree of security
Lower turnover
“Full” approach to selling
No direct incentive
WHEN TO USE
While in a training mode
Entering a new territory/new product market
Tremendous time to sell to one account
Missionary sales positions
Joint selling
STRAIGHT COMMISSION
PLANS
Based on a unit of accomplishment
Base, rate and starting point
Advances (drawing account)
Provides incentive
Weeds out poor performers
Supervision problems
Split commissions
WHEN TO USE
Company is weak financially
Great incentive required
Little non-selling work required
Supervision not possible
Long term relationships not important
Part-time sales people/manufacturer’s agents
RATE SCHEDULES
Progressive rate schedule
– 5% on first $20,000
– 7% on next $80,000
– 10% on amount over $100,000
Regressive rate schedule
COMBINATION PLAN
Most popular plan
Overcomes some of the weaknesses of straight salary and straight commission plans
TEAM SELLING
More common today
Difficult to provide rewards
Shared commissions/group bonuses
OPTIMUM PAY PLANS
Commission based on gross margin
Forces individuals to focus on items which maximize profits for the company
OTHER COMPENSATION
ISSUES
Bonuses
Drawing Accounts
Expense Accounts
BONUSES
Payment for above normal performance
No obligation to provide regularly
DRAWING ACCOUNT
Cash advance called a “draw”
DRAWING ACCOUNT
MTH DRAW SALES COMM EOM
PYMT
Jan $1,800 $40,000 $4,000 $2,220
Feb $1,800 $15,000 $1,500 0 (owes
$300)
Mar $1,800 $30,000 $3,000 $900
(10% commission rate)
EXPENSE ACCOUNTS
Reimbursement for travel and other sales related costs
A troublesome task for the sales manager!
EXPENSE BREAKDOWN
Meals
Air Travel
Automobile
Lodging
Entertainment
Other
16%
26%
24%
18%
13%
3%
CHARACTERISTICS OF A
GOOD EXPENSE PLAN
No net gain/loss
Equitable treatment
No curtailment of beneficial activities
Simple and economical
Avoidance of disputes
Company control/elimination of padding
CONTROLLING EXPENSES
Type of plan
– salary versus commission
– unlimited versus per diem
Automobiles
Training
Travel planning
FROM THE TEXT
Read everything in Chapter 14!!