Autism - USD 333
advertisement

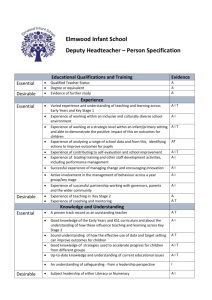
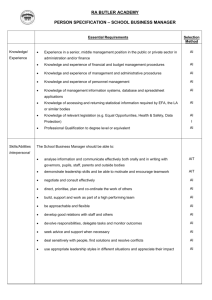
August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 1 Autism is a neurological disorder. The common characteristics are social interaction deficit, communication deficit, and behavior problems. Autism is a spectrum disorder that affects individuals differently and in varying degrees. The spectrum includes Autistic Disorder, Childhood Disintegrative Disorder, Asperger Disorder, Rett’s Disorder, and Pervasive Developmental Disorder—Not Otherwise Specified Every district has students identified with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Spectrum Disorders can be easily confused with ADD/ADHD, Obsessive Compulsive Disorder , Oppositional Defiant Disorder, Tourette’s Syndrome, Intellectual Disability August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 2 “Classic” Autism August 17 PDD-NOS Pervasive Developmental Disorder—Not Otherwise Specified Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants Asperger’s Disorder 3 Autism affects 1 in every 110 individuals (2010) It occurs before the age of 3 It is 4X more common in boys than girls Autism is found in all cultures, races, and social structures around the world. Parents notice a change in their child’s development as early as 12 months and characteristics become obvious by 2-6 years of age. ASD is the fastest growing developmental disability in the US Only 56% of students with ASD complete high school. No known single cause for ASD. It is generally accepted that it is caused by abnormalities in brain structure or function. Researchers are investigating a link between heredity, genetics, and medical problems. Some children are born with susceptibility to ASD, but researchers have not yet identified a single “trigger”. August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 4 •Does not babble or coo by 12 months •Does not gesture (point, wave, grasp) by 12 months •Does not say single words by 16 months •Does not say two-word phrases on his or her own by 24 months •Has any loss of any language or social skill at any age August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 5 Medical Diagnosis-physician diagnosis based on assessment of symptoms, diagnostic tests, and DSM-IV-TR (2000) Educational Identification-made by a multidisciplinary team comprised of various school professionals and parents to determine whether a student qualifies for special education services under Individual Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) (2009) August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 6 A new case of autism is diagnosed almost every 20 minutes August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 7 August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 8 Communication deficits Repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, and activities Social interaction deficits Social maturity of someone 1/3 to 2/3 of their age (Asperger’s) Behavior difficulties Sensory processing issues Emotional vulnerability Cognitive delays Motor skill deficits Difficulty generalizing skills August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 9 Lack of development of speech or use of gestures—receptive and expressive skill deficits Inability to initialize or sustain a conversation Repetitive use of language—echolalic speech Preoccupation and focus in areas of interest Preoccupation with parts of objects Monotone speech August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 10 August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 11 Lack of eye contact Prefer to play alone Lack of social reciprocity or empathy Lack of imitating social play Routines are important Lack of facial expressions August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 12 Sensitive reactions—more intense or lack of intensity than peers Lack caution when playing, impulsive to meet sensory input needs, excitability May seem uninterested, oblivious, unwilling to participate Hyperactive, easily upset, withdrawn Unable to complete tasks due to new stimuli capturing attention Difficulty learning from experiences May appear stubborn or self-absorbed August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 13 Must finish an interest activity before going to the next Poor organization skills Handwriting tends to be difficult Engage in activities beside and not with peers or no turn taking (reciprocity) Do not understand humor Literal thinkers—common expressions and idioms are understood literally Impulsivity Meltdowns—rages, aggressive or self-abusive behaviors, tantrums Transition is difficult—routines or environments August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 14 Home to bus Locker to class Class to first assignment Getting and organizing materials Between groupings (individual to peer groups) Class to lunch Waiting Ending the day Bus to home August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 15 Meltdowns Temper Tantrums Does not look to see reactions of others. Looks to see reaction of others. Does not consider his/her own safety. Takes precautions not to get hurt. Winds down slowly. Uses social situation. No one is in control. Ends when the situation is resolved. A want has not been permitted. Has purpose/goal. August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 16 Meltdowns and/or Rages August 17 Causes: Attention from peers or adults Frustration Confusion Power/control Sensory stimulation Fear or relief of fear To obtain something—activity, interaction, comfort, routine, object Expression of internal stimulation—sick, hungry, tired, too hot Unstructured time Change of routine/lack of schedule Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 17 Stress Excitement Fatigue Overstimulation To gain attention To escape/avoid August 17 To meet sensory needs Does not understand Self-esteem fears Need for control Need for “sameness” Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 18 August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 19 If the only tool you have in your toolbox is a hammer, then everything looks like a nail. (So if we do not see the autism, we are treating all students the same. Each child has individual needs. Let’s explore the other tools in our toolboxes.) August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 20 August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 21 Helps transition within and between activities Helps understand expectations Prepares student for a change Lessens anxiety Helps students comprehend verbal language Teaches independence August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 22 August 17 Schedules Color code Models of expected outcomes Graphic organizers Consistent Classroom rules Examples of how to head the paper Homework assignment area in the room Work stations Sticky notes for preparing or calming a student Example of correct finished products 5 point scale Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 23 August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 24 Class work Shorten assignments Odds/evens Circle the ones you want them to complete Top/bottom half Allow the student to circle and do X number of problems Highlight important or relevant points Graphic organizers Stopping and starting point on assignment August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 25 Extended time to complete Model expectations with visuals of the difference between an A paper and a C paper Fill in the blank notes for lectures Incorporate their interests in assignments Allow them choices that you are comfortable with Limit homework to daily in class work, an extra study time, no homework To ease handwriting, use a computer or scribe August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 26 I G Q August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 8 27 Priming—preparing the student before the activity by telling, showing with a visual schedule, or using a social narrative. Right before the activity The day before The period before The beginning of class August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 28 Social narratives and power cards use a student’s specific interest to engage the student. A story is written and illustrated with lots of visual pictures of what is acceptable behavior. Examples August 17 Preventing behaviors Teaching a new skills Showing a change in schedule (e.g., field trip) Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 29 Jeff and Matt Hardy are rule breakers on WWE. They are acting when they break the rules on TV. When Jeff and Matt go to school they follow the rules. They also follow the rules at home. When Jeff Hardy has to do something that the teacher tells him to do he does not complain. He knows that the teacher is in charge and sometimes he has to do things he doesn’t want to do. Matt Hardy does not tell people he is bored when he is doing something at school. Matt and Jeff Hardy follow the rules and then they get to have fun when they are done with their work. August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 30 Hidden curriculum is the unwritten social rules and expectations of social behavior that most students just seem to learn without direct instruction. Examples Raising your hand to go to the restroom When to use utensils and when not to when eating Don’t say everything you think (telling teacher she is fat or breath stinks) For kids with ASD, these skills often need to be taught directly through visual supports, examples, and role playing. August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 31 Allow a safe place or frequent sensory breaks They choose when they need a break Short breaks Walking, eating, fidgets, reinforcement of goals/behaviors Be alert for high anxiety levels or need for breaks August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 32 August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 33 Use language that is clear and concrete Ask questions of who, where, when, what, instead of why or how Use limited sarcasm, idioms, and inferences Tell the student what to do, instead of what not to do Give the student processing time (10-15 seconds) Give directions and new information in small segments, teaching each step separately Give praise often Pair verbal with visuals (pictures or gestures) Consistent routines August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 34 Understand that behavior is a form of communication and that a change is needed on our part. Encourage peer mentoring Build on strengths and interests Be aware of student’s sensory needs and concerns in all settings Do things “with” instead of “for” the student Have high expectations. We get what we expect! August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 35 Consider the physical environment (lighting, noise, temperature, color, smell) Treat the student with the same respect you treat your other students Empower the student to be an active participant in all classroom and social activities August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 36 August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 37 August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 38 Graph paper for math Pencil grips Mechanical pencils Highlighters Visual timers Air pillow/cushion Color code/paper Delineate work area Picture schedules/communication notebooks Comic strips August 17 Stress relievers Darkened rooms Chew toys Headphones Power cards Strategy cards Puppets Code words Social Narratives Weighted blanket Menu of reinforcers Graphic organizers Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 39 August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 40 http://www.usd333.com/vnews/display.v/SEC/Spec ial%20Education/LCNCK%7CAutism Go to usd333 website-special education-autism AIM Modules– http://www.ocali.org/aim/- The Ohio Center for Autism and Low Incidence (OCALI). The AIM project is developing online modules on ASD including characteristics, diagnosis, interventions and supports, transition, and employment. Autism Speaks- http://www.autismspeaks.org offers good information and links to helpful resources for parents and teachers. August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 41 iCAN – http://www.autismnetwork.org – The Interactive Collaborative Autism Network site is for anyone who lives with, teaches, or otherwise supports children and youth with autism spectrum disorders, including parents, teachers, and individuals with ASD. Kansas Autism Spectrum Disorders http://www.kansasasd.com/KSASD/Home.html -The Kansas Instructional Support Network (KISN) is one of the Kansas Statewide Technical Assistance Resource System (K-STARS) projects funded through a Title VI-B grant from the Kansas State Department of Education’s Student Support Services. Contains many informational links and technical assistance to districts. http://autismspectrum.illinoisstate.edu/courses/noncredit.shtml A 54 non credit contact hour course in autism. Basic level autism team training workshop August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 42 LCNCK Autism Intervention Team Deb Reha, Coordinator Anna Berger-Washington Elementary Anita Breen-Concordia High School Sharon Hartman—Clifton/Clyde Middle School Lorri Meyer—Concordia Elementary Lori Stahlman—SLP Deb Tipton—SLP Shawn Woolsey-Option/Opt2 LCNCK website August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 43 A.. Always U..Unique T.. Totally I.. Interesting S.. Sometimes M.. Mysterious August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 44 www.kansasasd.org National Institute of Child Health and Human Development www.autism-society.org August 17 Presented by Anita Breen and Lorri Meyer, AIT Consultants 45