Review Package - wondersofscience
advertisement

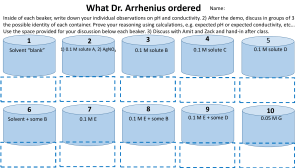
Review Package 1. The study of the behaviour of matter has made it possible to develop simple models such as the Bohr-Rutherford model of the atom. If the atomic number of oxygen is 8 and its mass number is 16, which diagram represents the oxygen atom according to the Bohr-Rutherford model? A) C) 8p 16 p 2e 6e 6e 2e B) D) 8p 8p 8e 16e 2e 2e 2. The illustration represents two elements X and Y: Atom X Atom Y a) What is the name of atom X and atom Y? X- Magnesium Y- Silicon b) Give a characteristic for each element. X- 2 valence electrons Y- 3 periods 3. The simplified atomic model of an element is shown below. What are, respectively, the Group and the Period of the Periodic Table to which the element belongs? A) IIA and 4 B) II A and 3 C) IV A and 2 D) IV A and 3 4. To which family in the periodic table do the elements of group II A (2) belong? A) The alkali metals C) The halogens B) The alkaline earth metals D) The inert gases 5. Label A B Characteristic Has 5 protons . Is an inert gas. C Has the following electron configuration : D E F G Is a halogen. Is a metalloid. Has the least number of protons. Must lose one electron to obtain the electron stability of element B. Is a soft metal, is very reactive and is stored in oil. Has 2 valence electrons and a complete outermost energy level. Can place its electrons in the first two energy levels. Is an alkaline-earth element. Belongs to the same family as element D and has a an atomic number greater that of element A. Element Boron He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn, UUO Neon 2 6 H I J K L F, Cl, Br, I, At B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, At Hydrogen Na Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr He Ne Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra F, Cl, Br, I, At 6. The following table gives the characteristics of four elements. Element Name of the Family Number of Valence Energy Levels Electrons Li Alkali metals 2 1 F 2 Halogen 7 2 Berylium Alkaline earth 1 metals 3 1 Sodium Alkali metals Using these characteristics and the periodic table of the elements, fill in the empty boxes of the table. 7. The table below provides certain information about the symbol, the electron configuration, the name of the chemical family and the period number of four elements in the periodic table. Name of the Symbol Electron configuration Period number chemical family )2e- )8e- )2eAlkaline Earth Mg Metals Alkali metals 2 Li )2e- )1e- 2 B )2e )3e Noble gas He )2e Using the above information and the periodic table, fill in the empty boxes in the table. 8. Complete the following sentence : A solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of... A) a solvent and a solution. C) a solvent and a solute. B) a solute and an electrolyte. D) a solute and a solution. 9. Listed below are several different concentrations of solutions of coffee : 1. 25.0 g/250.0 ml 3. 45.0 g/675.0 ml 2. 60.0 g/800.0 ml 4. 75.0 g/825.0 ml List the concentrations in increasing order. A) 1, 2, 3 and 4 B) 3, 2, 4 and 1 C) 3, 4, 2 and 1 D) 2, 3, 4 and 1 10. You are to prepare 750 mL of a 40 g/L solution of sodium chloride, NaCl. What mass of sodium chloride will you need to prepare this solution? 40/1000 = x/750 11. City regulations state that municipal swimming pools must be closed when the concentration of free available residual chlorine in the water is less than 0.3 ppm or greater than 5 ppm. The table below lists the concentrations of free available residual chlorine in water samples taken from four swimming pools. Table I - Concentration of Free Available Residual Chlorine in the Water From Four Swimming Pools Swimming pool Concentration of free available residual chlorine 1 0.00002% (m/V) 2 0.0004% (m/V) 3 0.0004 g/L 4 0.0058 g/L Which of these pools has water that complies with these regulations? A) Pools 1 and 3 B) Pools 1 and 4 C) Pools 2 and 3 D) Pools 2 and 4 12. Quantity of NaCl Volume of Solution in the given solution (g) the solution (mL) 1 5.0 500 2 4.0 200 3 0.5 100 Given the information in the table above, which sequence shows the solutions written from the lowest to the highest concentration? A) 1, 2 and 3 B) 2, 1 and 3 C) 3, 1 and 2 D) 3, 2 and 1 13. Explain the procedure for preparing a 40 g/L solution using 10 g of solute. 1. Mass 10g of solute 2. Measure 250 ml of water in volumetric flask 3. Add the solute to the solvent 4. Stir 14. In the laboratory, a student prepared four solutions of sodium chloride (NaCl). In the table below, she recorded the quantities related to each solution. Solution Quantity Volume of of solute (g) the solution (L) 1 10 2 2 2 0.5 3 15 1.75 4 1 0.1 Which of these solutions is the most concentrated? Solution 4 15. Which of the following procedures can be used to determine whether sugar is an electrolyte or a non-electrolyte? A) Check the electrical conductivity of a cube of sugar. B) Check the electrical conductivity of powdered sugar. C) Check the electrical conductivity of an aqueous sugar solution. D) Check the electrical conductivity of a heterogeneous mixture of sugar and alcohol. 16. The following four compounds are to be mixed (separately) with water: C6H12O6 MgSO4 C2H5OH KOH Which two of these compounds will produce an electrolytic solution when mixed with water? A) C6H12O6 and MgSO4 C) MgSO4 and KOH B) C6H12O6 and C2H5OH D) C2H5OH and KOH 17. Amanda, your lab partner, prepares 1 L of a solution A with a concentration of 25 g/L. You test its electrical conductivity and find that the bulb shines brightly. Then you dilute the solution to 5 g/L to prepare solution B. What do you expect to observe when you test the electrical conductivity of solution B? Justify your answer. The light will be less bright as the solution has a lower concentration 18. Which statement correctly defines an electrolyte? A) A substance that conducts an electric current B) A substance that does not conduct an electric current C) A substance that conducts an electric current when dissolved in an aqueous solution D) A substance that does not dissolve in water 19. The following table gives the colours of an acid-base indicator after it is added to solutions with different pH values. pH 2 Colour Orange 3 4 5 6 Yellow 7 8 Green 9 10 11 Blue What will be the colour of this indicator after it is added to a strongly basic solution? A) Blue B) Green C) Orange D) Yellow 20. To check the electrical conductivity of certain substances, a student used a conductivity apparatus equipped with a light bulb. Her observations are listed in the following table. Substances Observations HCl Bright light CH3OH No light MgCl2 Faint light NaOH Bright light CH3COOH Faint light CCl4 No light Which one of the following groups of substances contains only electrolytes? A) CH3OH and CCl4 C) CH3OH, NaOH and CH3COOH B) HCl, MgCl2 and CCl4 D) HCl, MgCl2, NaOH and CH3COOH 1. 2. 21. Which of the following are bases? NaOH 3. LiF 5. BeO HCl 4. NH4OH 6. HI A) 1, 4 and 7 B) 2, 3 and 8 C) 3, 5 and 6 7. KOH 8. CaCl2 D) 1, 3 and 7 1. 2. 22. Which of the following are acids? NaOH 3. LiF HCl 4. NH4OH A) 1, 5 and 8 B) 2 and 8 7. KOH 8. CaCl2 D) 3, 4 and 7 5. BeO 6. HI C) 5, 6 and 8 22. The electrodes of the circuits shown below were each immersed in a solution of NaOH(aq) and a solution of CH3COOH(aq). 12 Situation n 1 NaOH(aq) Situation n 2 CH3COOH(aq) You noticed that the light bulb in Situation n° 1 was much brighter than the light bulb in Situation n° 2. What is the reason for this? A) There are more molecules dissolved in Situation n° 1 B) Fewer solute molecules in Situation n° 1 were changed. C) All of the solute molecules in Situation n° 1 dissociated into ions. D) Many solute molecules in Situation n° 1 dissociated into ions.