group_roles
advertisement

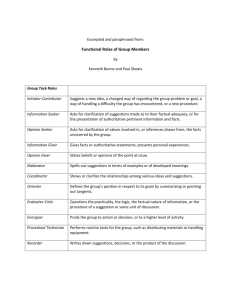
PARTICIPATION & DELEGATION The Continuum of Participation Organizational Structure Traditional organization Occasional use of teams and employee participation Team-based organization High management Total delegation Control – No employee High employee Participation Participation Management Control Criteria for Use of Participation When the task is complex and quality is important When follower commitment is needed When there is time When the leader and follower are ready When the leader and followers can easily interact Benefits of Participation , , , , Development of followers Better decision on complex tasks Increase in follower motivation and commitment Opportunity to empower followers Guidelines For Good Delegation Delegate pleasant and unpleasant tasks Clarify goals and expectations Delegate authority along with responsibility Provide support Monitor and provide feedback Delegate to different followers Excuses For Not Delegating “My followers are not ready.” “They do not not have the skills.” “I am uncomfortable delegating my tasks.” “I can do the job quicker myself.” “My followers are too busy.” “I am responsible for my followers mistakes.” “My own manager may think I am not working hard enough.” TEAMS Characteristics Of Teams Members are fully committed to common goals they develop Members are mutually accountable to one another Members trust one another Collaborative culture Shared leadership based on facilitation Synergy Self-Managed Teams Power to manage their own work Members with different expertise and experience No outside manager and power to implement team decisions Coordination with other teams Internal leadership based on facilitation Elements of Super Leadership b b b b Developing positive and motivating thought patterns Personal goal setting Observation and selfevaluation Self-reinforcement control and monitoring Building Trust Open communication Integrity Rewarding cooperation Competence And hard work Mutual respect And support Trust Fairness and equity Team Leadership Roles Continue to do real work Obtain needed training Clarify team boundaries Assess team skills SELFMANAGED TEAM Observe from a distance Counsel and encourage Help define tasks and goals Help develop implementation plan Manage conflict and relationships Characteristics of a WellFunctioning, Effective Group Relaxed, comfortable, informal atmosphere People express feelings Task well understood & ideas & accepted Consensus decision making Group aware of its operation & function Members listen well & participate Clear assignments made & accepted Conflict & disagreement center around ideas or methods External Conditions Imposed on the Group Organizational Strategy Authority Structures Formal Regulations Organizational Resources Personnel Selections Process Organizational Culture Physical Work Setting Group Leaders Department Manager Supervisors Foreman Project Leaders Task Force Head Chairperson Chief Executive Officer (CEO) Group Roles Definition: Set of expected behavior pattern, attributed to someone occupying a given position in a social unit Role Role Role Role Identity Perception Expectations Conflict Groupthink Irving Janis’ Model Antecedent Conditions + Cohesiveness Groupthink Symptoms Groupthink Symptoms Low Probability of Success Groupthink Characteristics Powerful Social Pressures Concurrence Seeking Dehumanizing Solutions Suppression of Deviant Thoughts Stress Diverse Teams Offer Both Advantages and Disadvantages in the Workplace Advantages Disadvantages •Increased number of perspectives •Increased ambiguity •Multiple interpretations likely •Increased complexity •Increased confusion •Greater openness to new ideas •Increased flexibility •Increased creativity •Improved problem solving •Improved understanding of foreign employees or customers Table 6-4 •Increased mistrust •Potential miscommunication •Difficulty in reaching agreements •Difficulty in reconciling diverse perspectives •Difficulty in reaching consensus •Decreased group cohesion Group Roles Four Categories of Roles Group Task Roles: roles which facilitate the selection and definition of a common problem and solution. Group Building and Maintenance: roles which increase the functioning of the group as a group. Individual Roles: roles which are oriented toward the satisfaction of individual’s needs. Creative Roles: roles which involve using creativity to identify possible solutions. Group Task Roles The Initiator- Contributor Suggests or proposes new ideas may include the suggestion: for a new group a new way to view a problem a new way to address a problem within the group a new procedure for the group a new way to organize the group The Information Seeker Seeks clarification of suggestions made in terms of their factual adequacy, for authoritative information and facets pertinent to the problem being discussed. The Opinion Seeker Asks not primarily for the facts of the case but for a clarification of the values pertinent to what the group is undertaking or of values involved in a suggestion made or in alternative suggestions. The Information Giver Offers facts or generalizations which are “authoritative” or relates his own experience pertinently to the group problem. The Opinion Giver States his/her belief or opinion pertinently to a suggestion made or to alternative suggestions. The emphasis is on his/her proposal of what should become the group’s view of pertinent values, not primarily upon relevant facts or information. The Coordinator Shows or clarifies the relationships among various ideas and suggestions Tries to pull ideas and suggestions together Tries to coordinate the activities of various members The Evaluator- Critic Subjects the accomplishments of the group to some standard or set of standards of group functioning in the context of the group task. May evaluate the “practicality”, “logic”, “Facts”, or “procedures” The Energizer Prods the group to action or decision. Attempts to stimulate or arouse the group to greater or higher quality work. The Recorder Writes down suggestions. Makes a record of group decisions (may be down via memory). The recorder role is the “group memory.” Group Building and Maintenance Roles The Encourager Praises, agrees with and accepts the contributions of others. Indicates warmth, solidarity in attitude toward others. Offers commendation and praise in various ways and indicates acceptance of others, The Harmonizer Mediates the differences between members Attempts to reconcile disagreements. Relieves tension in conflict situations. The Compromiser Operates from within a conflict in which his/her ideas or position is involved. May offer compromise by yielding status, admitting error, or by coming “halfway” in meeting another. The Gate-Keeper & Expediter Attempts to keep communication open by facilitating participation of others. Proposes regulation of the flow of communication. The Follower Goes along with the movement of the group. Passively accepts the ideas of others. Serves as an audience for others in the group as well as for group discussion and decision. Individual Roles Attempts by individuals to satisfy personal needs. Numerous types - from Sociology and Psychology. The Monopolist Def: One who chatters on incessantly due to anxiety when silent. Effect: Group gets concerned, then frustrated and angry. May be afraid to confront because then they must fill the void. Help-Rejecting Complainer Def.: requests help than rejects; takes problem in insolvability of problems; blames authority, conflicted about dependency feeling helpless and distrusting. Effects: seen as greedy and user of group energy; members become bored, confused, irritated and frustrated. Self-Righteous Moralist Def.: strong need to be right. Demonstrates superiority via poise and unconcerned about being liked. Deep underlying shame. Effect: mobilizes so much resentment that may be forced out of the group. Creative Group Roles Idea Generator Look for new ways to do things. Tend to focus only on ideas and concepts. Are result driven. Designers See the big picture. Provide guidance and tools. Define performance standards. Identify resources needed to complete projects. Promoters Visualize end result. Optimistic. Promote ideas and give momentum. Managers Can Use This Checklist to Diagnose the Roles Played by Each Team Member TASK ORIENTED MAINTENANCE INDIVIDUAL Agenda Setter Encourager Avoider Analyzer Follower Blocker Coordinator Gatekeeper Clown Evaluator Group Observer Dominator Information Giver Harmonizer Recognition Seeker Information Seeker Standard Setter Other Intuitor Other Other Mature Group Characteristics Purpose and Mission May be assigned or may emerge from the group Group often questions, reexamines, & modifies mission & purpose Mission converted into specific agenda, clear goals, & a set of critical success factors Mature Group Characteristics Behavioral Norms - well-understood standards of behavior within a group Formal & written Ground rules for meetings Informal but understood Intra-group socializing Dress codes