Management and Leadership
advertisement

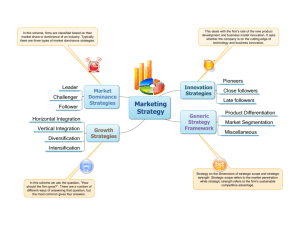
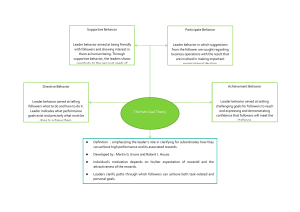
Needed: two sheets of paper and a writing utensil. Think about the best and worst teachers or bosses you’ve ever had. On the left side of the paper, list ten characteristics of the worst teachers/bosses you’ve had. What did they do that you disliked? On the right side of the paper, list ten characteristics of the best teachers/bosses you’ve had. What did they do that you liked? Put your name, the date, and period on one of the two sheets and begin writing. Save the other sheet. 8 note-takers. Note taking and sharing. List the leadership styles on each of the 8 boards (teacher-guided). Business Objective: simulate bad leadership environments and correct them using specific, transformational approaches. Warm-up Class discussions Brief Lecture Activity/Simulation Wrap-up Formative Quiz Leaders are hands-off and allow group members to make decisions. Little to no rules or expectations. Lowest productivity among group members. Can work if followers are motivated and highly skilled (Warren Buffet). But quite often, this is not the case. Example: IT managers asks a programming team to build new software and says, “you guys are the experts, do as you wish.” Poor leaders who use this style often lack a clear, attainable vision. Only hear back when things go wrong. Rarely tell you what you did right or how to improve. Does NOT encourage you to think. “Putting Out Fires!” Example: A teacher who has to punish constantly. Seeks to control behavior by a rigid set of standards. “Rules are rules!” Employees are liabilities, not assets. Example: A rock band front man tells his lead guitarist, “that’s not the note I wrote for you!” Monetarily reward employees based on meeting a certain standard Punish employees who do not meet the standard. However, no motivation to go beyond the standard. Example: The sunglasses hut Leaders attend to each follower’s needs. Address and build upon strengths, weaknesses, and aspirations. Every student/employee has a different story. Example: A leader has some “one-on-one” time to get to know the follower. Leaders motivate and stimulate followers by encouraging creativity and critical thinking. Opposite of Management by Exception (both) New ideas are usually implemented. Never publicly criticize followers for mistakes or bad ideas. Leaders have a vision and a purpose. They motivate followers to share their vision and purpose. Every employee is important for achieving organizational goals. Focus: the organization/cause Example: why eliminating AIDS is so important for the planet’s well-being. Followers respect, trust, and look up to the leader--he/she is worthy of followership. “Lead by example.” Strong pattern of positive consistency. Father/Mother figure. Example: Tom Landry Dallas Cowboys Coach 1960-1989 Laissez-Faire: Hands-off approach. Transactional: Control behavior through tangible rewards and/or punishments. (Liabilities) ◦ Management by Exception-Passive ◦ Management by Exception-Active ◦ Contingent Rewards Transformational: Boost morale through personal growth and development. (Assets) ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Individualized Consideration Intellectual Stimulation Inspirational Motivation Idealized Influence In your teams, you will create a business or organizational scenario where you demonstrate to the class your given leadership style. Only your team knows the leadership style you’ve been given. The class, based on your skit, must guess and justify the leadership style you employed.