3. Stages of Group Development
advertisement

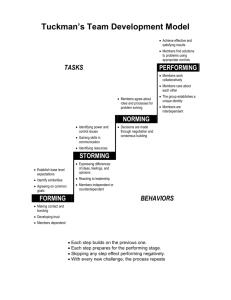
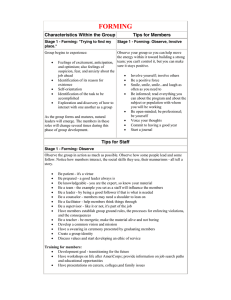
Group Dynamics Stages of Group Development Group Dynamics O This week we will be looking at the importance of working in groups O Positive and negative roles/attitudes that individuals can assume O Comparing formal and informal group structures O Advantages and Disadvantages of group structures in a business Stages of Group Development There are four stages to group development. They are: 1) Forming 2) Storming 3) Norming 4) Performing Forming Forming O The group comes together and gets to initially know one another and form as a group O At the end of the forming stage, team members should know the following: O The project’s overall mission O The main phases of the mission O The resources at their disposal O A rough project schedule O Each member’s project responsibilities O A basic set of team rules Forming O Activities usually found in this stage: O Making acquaintances O Sharing information O Discussing subjects unrelated to the task Storming Storming O Storming is when members of the team learn to bend and mold their feelings, ideas, attitudes, and beliefs to suit the team organization O Usually through competition and conflict O Questions about who is responsible for what, what the rules are, what the reward system is, and what the evaluation criteria are arise O These questions reflect conflicts over leadership, power, and authority O Team members must move from a testingand-proving mentality to a problem-solving mentality O Listening is the most helpful action Storming O Typical Activities found in this stage: O Expressing attitudes O Establishing norms O Establishing goals and discussing tasks openly Norming Norming O Team members actively acknowledge all members’ contributions O Team members build community O Team members maintain team focus and mission O Team members work to solve team issues O Members are willing to change their preconceived ideas or opinions O Leadership is shared O Cohesions occurs when individuals place trust in one another O Team members begin to experience a sense of group belonging Norming O Typical activities: O Working on tasks as a team O Being cooperative Performing Performing O Teams enjoy team members who work independently but also support those who can come back together to solve problems O Team is most productive at this stage O Team members are highly task-oriented and also highly people-oriented O Team is unified O Team identity is complete O Team morale is high O Team loyalty is intense O The task function becomes genuine problem solving, which leads to optimal solutions O Support for experimentation in solving problems, and an emphasis on achievement Performing O Typical activities include: O Working independently O Assigning tasks according to ability O Being spontaneous and flexible Roles within Group Structures O There are a variety of roles/attitudes that team members can embrace while working in a group O They can be positive roles/attitudes, but they can also play a negative role, or have a negative attitude Positive Positive Task Roles O Contributor O Information Seeker O Information Giver O Opinion Seeker O Opinion Giver O Elaborator O Evaluator O Energizer O Recorder Positive Social Roles O Encourager O Harmonizer O Compromiser O Gatekeeper O Observer O Follower Negative Negative Task Roles O Aggressor O Blocker O Recognition Seeker O Disruptor O Dominator