Cells – the basic unit of life
advertisement

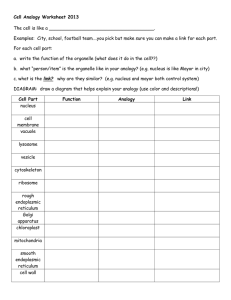
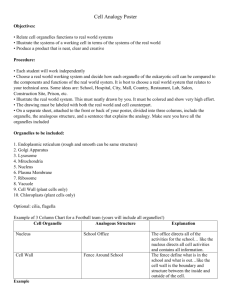
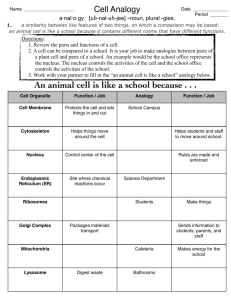
Cell Organelles Eukaryotic Cells O on the animal cell is a mitochondria Objectives: Label a plant and an animal cell Know the functions of cell organelles When finished turn into folder and work on active reading assignment Wednesday September 23, 2015 YOU WILL NEED: Cell notes from Monday, Cell Diagram worksheet • Standard: Cell Organelles • Which one is a prokaryote? Which one is a Eukaryote? How do you know? Cell Parts • Cells – the basic unit of life • Organelles - small structures inside a cell with specific functions. Analogy – City of Rocklin A) Cell Membrane/Plasma Membrane Cell membrane 1. Function: Regulates materials entering and exiting the cell. 2. Structure: Two layers of phospholipids, proteins Analogy – Rocklin city limits B) Cytoplasm Cytoplasm 1. Function: All cell contents that lie between the cell membrane and the nucleus. (organelles + cytosol) a. Cytosol = liquid portion/non-organelles. 2. Structure: made up of fluid and organelles except for nucleus Analogy – All air, water, life that are in Rocklin, except City Hall C) Nucleus Nucleus 1. Function: “Control Center.” Regulates DNA & RNA actions. 2. Structure: membrane bound, contains DNA Analogy – City Hall D) Nuclear Envelope Nuclear Envelope 1. Function: Regulates what enters or exits the nucleus. 2. Structure: Double Layer of Lipids Analogy – Walls & Doors of City Hall E) Nucleolus Nucleolus 1. Function: Produces RNA, which are used to make all proteins. 2. Structure: Inside Nucleus, separate from DNA Analogy – The Mayor F) DNA – Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA (chromatin) 1. Function: Genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all living organisms. information on how to make proteins. a. Chromatin – unorganized DNA (normal state) b. Chromosomes – organized DNA (present before cell division 2. Structure: Made up of nucleotides, locked in the nucleus Analogy – The Laws or City Code G) Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough ER Smooth ER 1. Function: Transportation route for proteins. a. Rough ER: has ribosomes b. Smooth ER: no ribosomes 2. Structure: tubes and channels Analogy – Roads & Sidewalks H) Ribosomes Ribosomes Free Ribosomes 1. Function: Makes proteins. 2. Structure: small circular organelles Analogy – Restaurants, Factories, Builders. I) Vacuoles & Vesicles Vesicles 1. Function: Storage for water, nutrients or waste. 2. Structure: small membrane-bound organelle. • Plant cells have a much larger, more central vacuole present Analogy – Grocery stores, water tanks. J) Lysosomes Lysosomes 1. Function: packets of enzymes that break down materials in a cell; “digestive system” of the cell 2. Structure: Small membrane-bound organelles Analogy – Recycling center K) Mitochondria Mitochondria 1. Function: Produce energy for the cell – site of cellular respiration. “The Powerhouse” 2. Structure: Double membrane-bound, kidney shaped. Analogy – Vectren L) Golgi Apparatus Golgi Apparatus 1. Function: Packages, labels and ships proteins out of the cell. 2. Structure: Pancake-shaped layered organelle Analogy – Post Office M) Cytoskeleton Microfilaments Microtubules 1. Function: Provide support and structure for the cell. a. Microfilaments b. Microtubules 2. Structure: Tubules Analogy – Wood, cement, steel beams N) Centrioles (Animal Cells Only) Centrioles 1. Function: microtubules that help divide the cell during cell division. • Structure: Tubules Analogy – Rocklin High School vs. Whitney High School O) Cilia & Flagella Flagella Flagella Cilia 1. Function: provides movement for the cell or objects moving by the cell. 2. Structure: a. Flagella – 1 long fiber b. Cilia – many short fibers Analogy – Cars or bicycles. P) Chloroplasts (Plants only) Chloroplasts 1. Function: site of photosynthesis (converting sun and CO2 into sugar). 2. Structure: Membrane bound organelles that contain chlorophyll Analogy – Solar Panels Q) Cell Wall (Plant cells only) Cell Wall 1. Function: Provides support for the cell and the plant. 2. Structure: Made of cellulose Analogy – ground, rock wall October 1, 2014: Wednesday • Standard: Cell Organelles • Identify the following organelles. What is each of their function in the cell? A) B) C) Cell Organelle Debate: • As a group, you have to pick the most important organelle in the cell. No groups can pick the same organelle. • In the debate, you will have two minutes to tell the name of the organelle, function, and why you think it’s the most important. • Once you have given your reasoning, you will have a minute debate against another organelle. Who you go up against will be decided by a bracket that I create. • Once each minute session is over, you will have 30 seconds to defend your position again to the class. • The winner of each round will be determined by the other groups in the class. • Once the final two groups have gone, the class will vote on which groups “wins” the debate. This will be a silent vote. The winner will be announced the next class period. Cell Parts Analogy • Create an analogy (besides the city analogy) for the cell and its parts • Possible ideas: – Stadium – School – Country – Restaurant – House – Mall – Waterpark Stadium Example: • • • • Cell membrane: wall of stadium, gates Cytoplasm: everything inside the stadium. Nucleus: the control room for the stadium. Etc…